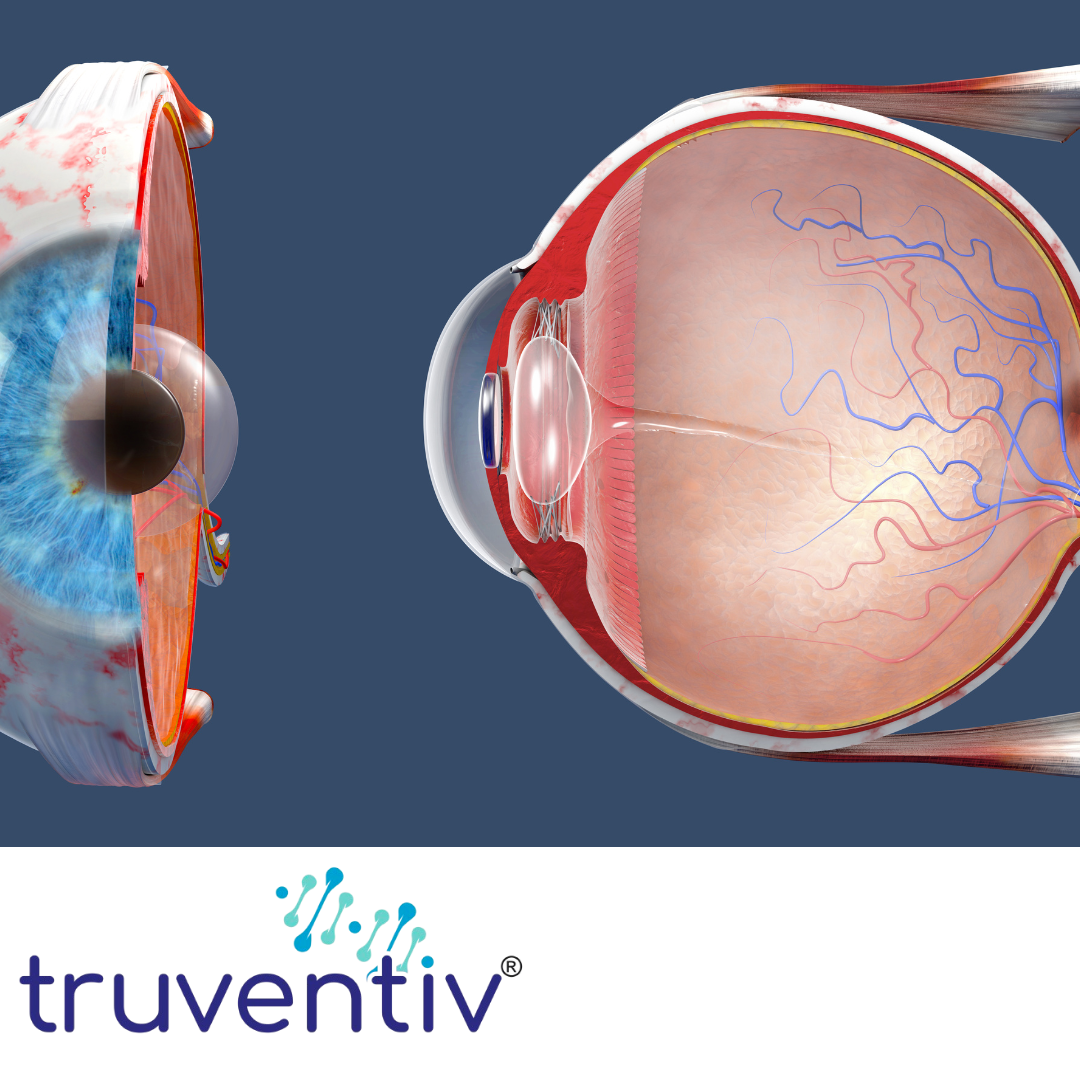
How does bilberry extract help in retinal & Optic Health ?

Bilberry extract is well-known for its benefits in supporting retinal and optic health due to its high content of anthocyanins, which are powerful antioxidants. Here's how bilberry extract contributes to eye health:
1] Enhances Retinal Health
- Antioxidant Protection: Anthocyanins in bilberry neutralize free radicals, preventing oxidative stress that can damage the retina.
- Improved Circulation: Bilberry extract enhances blood flow to the retina, ensuring a steady supply of oxygen and nutrients.
- Collagen Stabilization: Supports the structure of the retina by stabilizing collagen, a key component of the eye's connective tissues.
2] Supports Optic Nerve Health
- Reduced Inflammation: The anti-inflammatory properties of bilberry extract may protect the optic nerve from inflammatory damage.
- Neuroprotection: Bilberry helps prevent damage to the optic nerve by reducing oxidative stress and supporting neural health.
3] Improves Night Vision and Visual Acuity
- Rhodopsin Regeneration: Rhodopsin, a pigment in the retina crucial for night vision, is supported by the anthocyanins in bilberry extract.
- Contrast Sensitivity: It can enhance the eye's ability to distinguish between different levels of light and dark, improving overall visual clarity.
4] Prevents Age-Related Eye Disorders
- Macular Degeneration: The extract may delay the onset or progression of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) by protecting the macula from oxidative damage.
- Cataracts and Glaucoma: Its antioxidant properties help reduce the risk of cataracts and lower intraocular pressure, reducing the risk of glaucoma.
5] Maintains Capillary Integrity
- Strengthened Blood Vessels: Bilberry extract strengthens the capillaries in the eye, reducing the risk of microbleeds and ensuring a healthy blood supply.
How does bilberry extract help in Blue light Protection
Bilberry extract helps in blue light protection by leveraging its high concentration of anthocyanins, antioxidants that protect the eyes from the harmful effects of blue light exposure. Here’s how it contributes to blue light protection and overall eye health:
1] Neutralizes Free Radicals
- Antioxidant Shield: Blue light generates free radicals in the retina, leading to oxidative stress and cellular damage. The anthocyanins in bilberry extract neutralize these free radicals, reducing oxidative damage.
2] Prevents Retinal Damage
- Photoreceptor Protection: Blue light can damage photoreceptor cells in the retina over time. Bilberry extract protects these cells by enhancing their resistance to oxidative stress.
- Reduction of Lipid Peroxidation: Blue light-induced stress can lead to lipid peroxidation in retinal tissues. Bilberry’s antioxidants mitigate this process, preserving retinal health.
3] Supports Macular Health
- Preservation of Macular Pigment: The macula, responsible for central vision, contains pigments that filter blue light. Bilberry extract supports these pigments, enhancing the eye’s natural defense mechanism.
- Prevention of Macular Degeneration: Prolonged blue light exposure is a risk factor for age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Bilberry extract may delay or prevent the progression of AMD.
4] Improves Visual Fatigue and Recovery
- Reduction of Digital Eye Strain: Prolonged screen use exposes the eyes to blue light, leading to strain. Bilberry extract helps alleviate digital eye strain by improving blood flow and reducing inflammation.
- Enhanced Recovery: Studies suggest bilberry extract can aid faster recovery of visual acuity after intense light exposure, including blue light.
5] Strengthens Retinal Capillaries
- Improved Microcirculation: Blue light exposure can compromise the delicate blood vessels in the retina. Bilberry extract strengthens capillaries, ensuring better oxygenation and nutrient delivery to retinal cells.
6] Improves Night and Contrast Vision
- Rhodopsin Regeneration: Exposure to blue light can deplete rhodopsin, a pigment critical for low-light vision. Bilberry extract supports rhodopsin regeneration, improving contrast sensitivity and low-light vision.
How does bilberry extract help in Vitamin D absorption

Bilberry extract does not directly impact vitamin D absorption, as vitamin D is absorbed through the skin when exposed to sunlight or through dietary sources and supplements. However, bilberry extract may support processes indirectly related to vitamin D function and utilization in the body:
1] Anti-Inflammatory Properties
- Bilberry extract reduces inflammation, which can support overall nutrient absorption and metabolic health. Chronic inflammation may impair the body's ability to utilize vitamin D effectively.
2] Gut Health and Nutrient Absorption
- Bilberry contains compounds that promote gut health, such as antioxidants and fiber. A healthy gut lining is essential for the efficient absorption of vitamin D and other fat-soluble vitamins.
3] Synergistic Antioxidant Support
- Vitamin D plays a role in reducing oxidative stress, and bilberry extract complements this function by providing additional antioxidant protection. Together, they may promote better cellular health.
4] Bone Health Support
- Vitamin D is crucial for calcium absorption and bone health. Bilberry extract, rich in flavonoids, may indirectly support bone health by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in bone cells.
How does bilberry extract help in Antioxidant activity

Bilberry extract is renowned for its potent antioxidant activity, primarily due to its high content of anthocyanins, flavonoids, vitamin C, and other phenolic compounds. These antioxidants play a crucial role in protecting the body from oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals. Here’s how bilberry extract contributes to antioxidant activity:
1] Neutralizes Free Radicals
- Anthocyanins: These are the primary antioxidants in bilberry extract, which neutralize harmful free radicals by donating electrons, thereby preventing oxidative damage to cells, proteins, and DNA.
- Flavonoids and Phenolic Acids: These compounds enhance the overall antioxidant capacity by scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS).
2] Protects Cellular Health
- Prevention of Lipid Peroxidation: Bilberry extract inhibits the oxidation of lipids, a process that can damage cell membranes and lead to cell dysfunction.
- DNA Protection: The extract guards genetic material from oxidative stress, reducing the risk of mutations and associated diseases.
3] Reduces Inflammation
- Cytokine Modulation: By decreasing oxidative stress, bilberry extract lowers the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, indirectly mitigating inflammation caused by oxidative damage.
4] Supports Eye Health
- Retinal Protection: The retina is particularly vulnerable to oxidative stress. Bilberry extract protects retinal cells and photoreceptors, enhancing visual function and reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
5] Boosts Cardiovascular Health
- Improves Vascular Integrity: Bilberry extract strengthens blood vessel walls, reducing oxidative damage to vascular tissues.
- Prevention of Oxidized LDL: By preventing the oxidation of low-density lipoproteins (LDL), bilberry extract helps reduce plaque formation and cardiovascular risks.
6] Enhances Glutathione Levels
- Glutathione Support: Bilberry extract can enhance the body's endogenous antioxidant defenses, such as glutathione, which is crucial for detoxification and cellular repair.
7] Protects Against Aging
- Slows Cellular Aging: By reducing oxidative stress, bilberry extract slows down cellular aging processes, contributing to better skin, brain, and overall body health.
8] Synergistic Effects
- Vitamin C and Polyphenols: Bilberry's combination of antioxidants works synergistically to amplify its protective effects, making it more effective in neutralizing a wide range of free radicals.
How does bilberry extract help in Myopia

Bilberry extract is rich in anthocyanins, powerful antioxidants that help protect the eyes and improve vision. Here's how bilberry extract may help with myopia (nearsightedness):
1] Improves Retinal Circulation
- Bilberry anthocyanins enhance blood flow to the retina, ensuring better oxygen and nutrient delivery. This supports retinal health, which is crucial in preventing myopia progression.
2] Strengthens Blood Vessels in the Eyes
- It helps strengthen capillaries and reduce permeability, preventing microvascular damage in the retina, which is often associated with myopia.
3] Reduces Eye Fatigue
- Bilberry has been shown to reduce eye strain and enhance visual performance after prolonged near work (e.g., screen use, reading), which can contribute to myopia progression.
4] Increases Rhodopsin Production
- Rhodopsin is a light-sensitive pigment in the retina that enhances night vision and contrast sensitivity. Bilberry extract promotes its regeneration, which may help in reducing myopia-related vision strain.
5] Anti-Inflammatory & Antioxidant Effects
- Bilberry fights oxidative stress and inflammation in the eye tissues, which may slow down myopia progression by protecting against free radical damage.
6] Helps Reduce Myopia-Related Retinal Degeneration
- Some studies suggest that bilberry extract can slow down degenerative changes in the retina, which are common in high myopia cases.
How does Pine bark extract help in Retinal & Optic Health

Pine bark extract, especially standardized forms like Pycnogenol, is rich in proanthocyanidins, powerful antioxidants that offer significant benefits for retinal and optic health. Here’s how pine bark extract supports these critical components of eye health:
- Enhances Retinal Circulation
- Improved Microcirculation: Pine bark extract boosts blood flow to the retina by strengthening capillaries and promoting healthy blood vessel function. This ensures the retina receives adequate oxygen and nutrients.
- Reduced Capillary Leakage: It stabilizes capillary walls, reducing the risk of fluid leakage and swelling in the retina (important for conditions like diabetic retinopathy).
- Protects Against Oxidative Stress
- Antioxidant Activity: The proanthocyanidins in pine bark extract neutralize free radicals, preventing oxidative stress that can damage retinal cells and the optic nerve.
- Prevention of Retinal Degeneration: Oxidative damage is a major contributor to retinal diseases like macular degeneration and glaucoma. Pine bark extract helps reduce this risk.
- Reduces Inflammation
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Pine bark extract lowers inflammation in the retina and optic nerve, which is critical for preventing chronic eye conditions.
- Inhibition of Pro-Inflammatory Enzymes: It inhibits enzymes like COX and LOX, reducing inflammation-related damage in ocular tissues.
- Prevents and Manages Diabetic Retinopathy
- Regulates Blood Sugar and Vascular Health: Pine bark extract helps lower blood glucose levels and strengthens blood vessels, which can reduce the risk of diabetic retinopathy and related retinal complications.
- Reduction in Edema: It decreases swelling in the retina caused by fluid retention in diabetic patients.
- Supports Optic Nerve Health
- Neuroprotection: Pine bark extract protects the optic nerve from oxidative and inflammatory damage, reducing the risk of glaucoma and other optic neuropathies.
- Enhanced Nerve Function: Improved blood flow and reduced oxidative stress help maintain the health and function of the optic nerve.
- Improves Visual Acuity
- Night Vision Support: Proanthocyanidins enhance the regeneration of rhodopsin, a pigment crucial for vision in low-light conditions.
- Contrast Sensitivity: Pine bark extract helps improve contrast sensitivity, which is essential for better visual performance.
- Prevents Age-Related Eye Diseases
- Macular Degeneration Protection: Pine bark extract reduces the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) by protecting retinal cells from oxidative stress.
- Cataract Prevention: By neutralizing oxidative damage, it lowers the risk of cataract formation.
- Strengthens Collagen in Eye Tissues
- Stabilization of Connective Tissues: Pine bark extract supports collagen structures in the eye, which are vital for maintaining the integrity of blood vessels and other ocular tissues.
How does Pine bark extract help in Blue Light Protection

Pine bark extract, particularly forms like Pycnogenol, helps protect the eyes from blue light-induced damage by leveraging its potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and vascular-supportive properties. Here's how it contributes to blue light protection:
- Neutralizes Free Radicals
- Antioxidant Shield: Blue light exposure generates harmful free radicals that can damage retinal cells. Pine bark extract, rich in proanthocyanidins, neutralizes these free radicals, reducing oxidative stress.
- Lipid Peroxidation Prevention: Pine bark extract prevents the oxidation of lipids in retinal cells, which can otherwise lead to cell damage.
- Protects Retinal Cells
- Photoreceptor Protection: Blue light damages photoreceptor cells in the retina. The antioxidants in pine bark extract safeguard these cells, preserving vision.
- DNA Protection: Pine bark extract shields retinal cell DNA from oxidative damage caused by prolonged blue light exposure.
- Reduces Inflammation
- Anti-Inflammatory Effect: Blue light can induce inflammation in retinal tissues. Pine bark extract reduces the production of pro-inflammatory molecules, protecting delicate retinal structures.
- Microglial Modulation: It helps regulate microglial activity, preventing overactivation caused by blue light, which could lead to inflammation and tissue damage.
- Supports Macular Health
- Macular Pigment Preservation: The macula is responsible for filtering blue light and protecting the retina. Pine bark extract supports macular health by reducing oxidative damage and inflammation.
- Prevention of Macular Degeneration: Blue light exposure accelerates age-related macular degeneration (AMD), and pine bark extract helps reduce this risk by maintaining the structural integrity of retinal cells.
- Improves Retinal Circulation
- Enhanced Microcirculation: Pine bark extract boosts blood flow to the retina, ensuring that the cells have adequate oxygen and nutrients to combat blue light damage.
- Strengthened Capillaries: It stabilizes and strengthens the tiny blood vessels in the retina, reducing the risk of leakage and swelling caused by oxidative stress.
- Boosts Endogenous Antioxidants
- Glutathione Support: Pine bark extract stimulates the production of glutathione, a natural antioxidant that plays a critical role in detoxifying the retina and protecting it from blue light damage.
- Improves Visual Fatigue
- Relief from Digital Eye Strain: Prolonged screen time exposes the eyes to blue light, leading to digital eye strain. Pine bark extract alleviates this by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in the eyes.
- Faster Recovery: It supports quicker recovery of visual performance after exposure to bright light, including blue light.
- Prevents Long-Term Blue Light Damage
- Chronic Protection: Consistent use of pine bark extract can mitigate the cumulative effects of blue light exposure, reducing the risk of developing serious retinal disorders like AMD, cataracts, or glaucoma over time.
How does Pine bark extract help in Vitamin D Absorption

Pine bark extract does not directly enhance vitamin D absorption, as vitamin D absorption primarily occurs through sunlight exposure (via the skin) and dietary intake (from food or supplements). However, pine bark extract may support overall processes related to vitamin D metabolism and function in the following indirect ways:
- Improves Gut Health for Better Nutrient Absorption
- Pine bark extract supports a healthy gut environment by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, which can enhance the absorption of nutrients, including vitamin D, in the intestines.
- A well-functioning gut is essential for absorbing fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin D.
- Supports Bone Health
- Vitamin D is critical for calcium absorption and bone health, and pine bark extract complements this by protecting bone cells from oxidative stress and inflammation.
- By promoting better circulation and reducing inflammation, it helps maintain a healthy bone environment where vitamin D plays a crucial role.
- Reduces Chronic Inflammation
- Chronic inflammation can impair vitamin D metabolism and reduce the body’s ability to utilize it effectively. Pine bark extract’s anti-inflammatory properties may improve the body’s capacity to metabolize and utilize vitamin D efficiently.
- Enhances Circulation
- Improved blood flow, facilitated by pine bark extract, ensures efficient transport of vitamin D and other nutrients to various tissues, including bones and immune cells, where they are needed for optimal functioning.
- Synergistic Antioxidant Support
- Vitamin D is involved in reducing oxidative stress in the body, and pine bark extract’s potent antioxidant properties work synergistically with vitamin D to amplify its effects in maintaining cellular health.
- Potential Impact on Immune Function
- Both vitamin D and pine bark extract support the immune system. Pine bark extract may help reduce immune dysfunction associated with vitamin D deficiency, creating a supportive environment for vitamin D activity.
How does Pine bark extract help in Antioxidant activity

Pine bark extract, particularly standardized forms like Pycnogenol, is known for its powerful antioxidant activity, which helps neutralize free radicals and protect cells from oxidative damage. Here's how it contributes to antioxidant activity:
- Rich in Proanthocyanidins
- Proanthocyanidins, the key active compounds in pine bark extract, are potent antioxidants that neutralize harmful free radicals and reduce oxidative stress.
- These compounds are more powerful than vitamin C and vitamin E in scavenging free radicals.
- Prevents Oxidative Damage to Cells
- Pine bark extract protects lipids, proteins, and DNA in cells from damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are generated by pollution, UV radiation, and metabolic processes.
- This protection helps maintain cellular integrity and function.
- Regenerates and Synergizes with Other Antioxidants
- Pine bark extract enhances the activity of other antioxidants, such as vitamin C and vitamin E, by regenerating them after they have been oxidized. This creates a synergistic effect, amplifying the body’s overall antioxidant capacity.
- Protects Against Chronic Diseases
- By reducing oxidative stress, pine bark extract helps lower the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular conditions, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders that are linked to free radical damage.
- Supports Microcirculation
- It enhances blood flow to tissues, ensuring that antioxidants are efficiently delivered to where they are needed most, such as the skin, eyes, and vital organs.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects
- Oxidative stress often triggers inflammation, and the antioxidants in pine bark extract reduce this cascade by neutralizing ROS, helping to protect tissues from inflammation-related damage.
- Reduces Lipid Peroxidation
- Pine bark extract prevents the oxidation of lipids (fats), particularly in cell membranes and blood vessels, which is a key step in preventing conditions like atherosclerosis.
- Protects Against Aging
- The extract slows down cellular aging by reducing oxidative stress, which is a major contributor to age-related conditions like wrinkles, cognitive decline, and vision loss.
- Supports Skin Health
- Antioxidants in pine bark extract protect the skin from UV-induced oxidative damage, preventing premature aging, hyperpigmentation, and skin disorders.
- Boosts Endogenous Antioxidants
- Pine bark extract stimulates the production of natural antioxidants like glutathione, which is a key detoxifying and protective molecule in the body.
How does Pine bark extract help in Myopia

Pine bark extract, especially standardized forms like Pycnogenol, supports myopia (nearsightedness) management through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and vascular-enhancing properties. Although it doesn't directly cure myopia, it helps in mitigating its progression and alleviating associated complications. Here's how pine bark extract contributes to improving myopia:
- Enhances Retinal Health
- Protects the Retina: Pine bark extract is rich in proanthocyanidins, which help reduce oxidative stress in retinal cells. This protection is essential as oxidative damage may worsen vision issues, including myopia.
- Improves Blood Flow: By enhancing microcirculation, pine bark extract ensures better oxygen and nutrient supply to the retina, which is crucial for optimal retinal function in myopic individuals.
- Reduces Eye Fatigue
- Alleviates Visual Stress: Prolonged focus on near objects, such as during reading or screen use, can strain the eyes and exacerbate myopia. Pine bark extract reduces oxidative stress and inflammation in the eyes, relieving fatigue.
- Supports Faster Visual Recovery: It helps the eyes recover faster from visual stress or bright light exposure, which can be especially beneficial for those with myopia.
- Protects Against Blue Light Damage
- Defense Against Digital Strain: Excessive screen time can worsen myopia by increasing blue light exposure, leading to retinal stress. Pine bark extract reduces blue light-induced oxidative damage to retinal cells, which can help slow myopia progression.
- Prevents Myopic Complications
- Reduces Risk of Retinal Damage: High levels of oxidative stress and inflammation can weaken the retina in severe cases of myopia. Pine bark extract protects the structural integrity of the retina, reducing the risk of complications like retinal detachment.
- Strengthens Blood Vessels: Pine bark extract stabilizes the small capillaries in the eye, reducing the risk of microvascular complications associated with progressive myopia.
- Supports Collagen and Scleral Strength
- Collagen Stabilization: Myopia progression involves the elongation of the eyeball and stretching of the sclera (the white part of the eye). Pine bark extract strengthens collagen, which is essential for maintaining scleral integrity and preventing further eye elongation.
- Reduces Scleral Oxidative Stress: By protecting the structural proteins in the sclera, it helps maintain the eye's shape and function.
- Combats Inflammation
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Pine bark extract reduces inflammation in ocular tissues, which can contribute to myopia progression, particularly in cases of pathological myopia.
- Improves Visual Function
- Better Contrast Sensitivity: Pine bark extract enhances visual performance by improving contrast sensitivity, which can be impaired in individuals with myopia.
- Enhances Night Vision: It supports the regeneration of rhodopsin, a pigment essential for vision in low-light conditions, which can benefit those with myopia experiencing difficulty seeing in dim lighting.
- Clinical Evidence for Myopia Management
- Studies Suggest Benefits: Some studies suggest that pine bark extract, combined with other nutrients like lutein and zeaxanthin, can slow the progression of myopia and improve visual performance, though more research is needed for conclusive evidence.
How Lutein & Zeaxanthin help Retinal & Optic Health

Lutein and zeaxanthin are carotenoids that play a crucial role in protecting and maintaining retinal and optic health. These antioxidants are highly concentrated in the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision. Here's how they contribute:
- Filters Harmful Blue Light
- Lutein and zeaxanthin act as natural blue light filters, absorbing high-energy blue light before it reaches and damages the retina.
- This protection reduces oxidative stress, which is linked to conditions like age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and digital eye strain.
- Protects Against Oxidative Stress
- The retina is highly susceptible to oxidative damage due to constant exposure to light and oxygen.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin neutralize free radicals, preventing damage to retinal cells and slowing vision deterioration.
- Reduces Risk of Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
- Studies show that higher levels of lutein and zeaxanthin lower the risk of AMD, a leading cause of vision loss in older adults.
- They slow the progression of AMD by reducing inflammation and improving retinal function.
- Supports Retinal Blood Flow & Circulation
- Lutein and zeaxanthin improve microcirculation in the retina, ensuring that oxygen and nutrients reach retinal cells for optimal function.
- This helps prevent retinal diseases related to poor blood flow, such as diabetic retinopathy.
- Strengthens the Optic Nerve
- The optic nerve transmits visual signals from the retina to the brain.
- By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, lutein and zeaxanthin help protect the optic nerve, lowering the risk of conditions like glaucoma.
- Enhances Contrast Sensitivity & Visual Performance
- Improves contrast sensitivity, helping the eyes differentiate objects more clearly in low-light conditions.
- Beneficial for night vision and reducing glare, especially for people sensitive to bright lights.
- Prevents Retinal Damage in Diabetics
- Lutein and zeaxanthin help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress that contribute to diabetic retinopathy, a common complication of diabetes that affects the retina.
- Supports Eye Health in High Screen Exposure
- Helps reduce digital eye strain, dryness, and fatigue caused by excessive screen use.
- Protects the eyes from blue light exposure emitted from devices like phones and laptops.
- Slows Cataract Formation
- Lutein and zeaxanthin prevent oxidative damage to the eye’s lens, delaying the onset of cataracts.
How Lutein & Zeaxanthin Help in Blue Light Protection

Lutein and zeaxanthin are powerful carotenoids that act as natural blue light filters, protecting the eyes from damage caused by prolonged exposure to digital screens, LED lights, and sunlight. Here’s how they help:
- Absorbs High-Energy Blue Light
- Lutein and zeaxanthin accumulate in the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision.
- They act as a shield, absorbing harmful blue light before it reaches and damages the retinal cells.
- This prevents oxidative stress, which can lead to eye fatigue, digital eye strain, and long-term retinal damage.
- Reduces Oxidative Stress & Inflammation
- Blue light exposure generates free radicals, which cause oxidative damage to the retina.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin neutralize free radicals, protecting photoreceptor cells and slowing eye aging.
- Prevents Digital Eye Strain
- Long screen time can cause symptoms like dry eyes, headaches, and blurred vision due to excessive blue light exposure.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin help reduce eye fatigue and discomfort, improving visual performance during prolonged screen use.
- Supports Contrast Sensitivity & Visual Clarity
- Improves the eye’s ability to distinguish objects against blue light backgrounds, reducing glare and enhancing contrast sensitivity.
- This is especially beneficial for night driving and working in bright environments.
- Protects Against Macular Degeneration & Retinal Damage
- Long-term blue light exposure increases the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of vision loss.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin slow down macular degeneration by protecting retinal cells from light-induced stress.
- Improves Sleep Quality
- Blue light exposure at night disrupts melatonin production, leading to poor sleep.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin help reduce the impact of blue light on sleep cycles, promoting better rest.
- Supports Long-Term Eye Health
- By acting as a natural blue light filter, they help maintain healthy vision, reducing the risk of cataracts and retinal damage over time.
How Lutein & Zeaxanthin Help in Vitamin d absorption

Lutein and zeaxanthin do not directly enhance vitamin D absorption, but they may support the process indirectly by improving overall eye health, reducing inflammation, and promoting optimal nutrient metabolism. Here’s how:
- Supports Gut Health for Better Nutrient Absorption
- Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin, meaning it requires a healthy digestive system for proper absorption.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that support gut lining health, ensuring better absorption of vitamin D and other fat-soluble nutrients.
- Reduces Oxidative Stress & Inflammation
- Chronic inflammation can impair vitamin D metabolism and its effectiveness in the body.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin reduce systemic inflammation, allowing the body to process and utilize vitamin D more efficiently.
- Enhances Calcium Metabolism & Bone Health
- Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption and bone strength.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin protect bone cells from oxidative stress, supporting vitamin D’s role in maintaining strong bones.
- Supports Skin Health for Vitamin D Synthesis
- The body produces vitamin D when exposed to sunlight, but oxidative damage can affect skin health and this process.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin protect skin cells from UV damage, indirectly supporting efficient vitamin D synthesis.
- Improves Blood Circulation for Nutrient Transport
- Better circulation helps transport vitamin D to various tissues where it is needed.
Lutein and zeaxanthin improve blood flow and microcirculation, ensuring vitamin D reaches the bones, muscles, and immune system effectively.
How Lutein & Zeaxanthin Help in Antioxidant activity

Lutein and zeaxanthin are powerful carotenoid antioxidants that protect the body from oxidative stress and free radical damage. They play a crucial role in maintaining eye health, brain function, and overall well-being by neutralizing harmful molecules that can cause cellular damage.
- Neutralizes Free Radicals
- Free radicals are unstable molecules that cause oxidative damage to cells, accelerating aging and increasing the risk of diseases.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin scavenge these free radicals, reducing cellular damage in the eyes, brain, skin, and cardiovascular system.
- Protects Retinal Cells from Oxidative Stress
- The retina is highly susceptible to oxidative stress due to constant exposure to light and oxygen.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin protect photoreceptor cells from light-induced oxidative damage, lowering the risk of macular degeneration, cataracts, and vision loss.
- Reduces Inflammation & Supports Immune Function
- Chronic inflammation contributes to aging and diseases like arthritis, heart disease, and neurodegenerative conditions.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin have anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce systemic inflammation and boost immune function.
- Shields Against Blue Light Damage
- High-energy blue light exposure from digital screens and artificial lighting generates oxidative stress in the eyes.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin filter blue light and prevent retinal cell damage, reducing eye strain and fatigue.
- Supports Brain Health & Cognitive Function
- The brain is vulnerable to oxidative stress, which can lead to memory decline and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin cross the blood-brain barrier, protecting neurons from oxidative damage and enhancing cognitive function, memory, and focus.
- Enhances Skin Protection Against UV Damage
- Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun cause oxidative damage, leading to premature aging, wrinkles, and skin diseases.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin protect skin cells from UV-induced free radical damage, reducing signs of aging and promoting healthy skin.
- Protects Cardiovascular Health
- Oxidative stress contributes to heart disease by damaging blood vessels and increasing cholesterol oxidation.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin help reduce arterial inflammation and oxidative damage, supporting heart health and reducing the risk of atherosclerosis.
- Supports Cellular Function & Longevity
- By reducing oxidative stress, these carotenoids promote healthy cell function, slowing the aging process and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
How Lutein & Zeaxanthin Help in Myopia

Lutein and zeaxanthin play a vital role in protecting and maintaining eye health, which can indirectly help in preventing or slowing the progression of myopia (nearsightedness). Myopia occurs when the eye grows too long, causing distant objects to appear blurry. While these carotenoids do not cure myopia, they provide protective benefits that can help manage its progression.
- Protects the Retina from Oxidative Stress
- Myopia is linked to retinal oxidative damage due to prolonged exposure to light and screen time.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin act as antioxidants, reducing oxidative stress and protecting the retinal cells and photoreceptors.
- Filters Harmful Blue Light
- Excessive blue light exposure from digital screens can cause eye strain and accelerate myopia progression.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin act as natural blue light filters, preventing light-induced damage to the macula and retina.
- Strengthens Retinal Blood Flow
- Proper blood circulation is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the retina.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin improve microcirculation, ensuring better oxygen supply to retinal tissues, reducing the risk of retinal thinning and detachment, which are complications of severe myopia.
- Reduces Inflammation in the Eyes
- Chronic inflammation can contribute to myopia progression.
- These carotenoids have anti-inflammatory properties, reducing stress on retinal and scleral tissues, which are involved in myopia development.
- Supports Visual Contrast Sensitivity
- Myopic individuals often experience poor contrast sensitivity, making it harder to see details in low-light conditions.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin enhance visual contrast and reduce glare sensitivity, improving overall vision quality.
- Helps Prevent Myopic Maculopathy
- Severe myopia increases the risk of macular degeneration and retinal damage.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin protect the macula from degeneration, helping to prevent long-term vision loss in high myopia cases.
- Help Slow Myopia Progression in Children
- Studies suggest that oxidative stress and inflammation play a role in myopia progression.
- Antioxidants like lutein and zeaxanthin support eye health in children and young adults, potentially slowing down the rate of myopia progression.
How does Astaxanthin Help Retinal & Optic Health
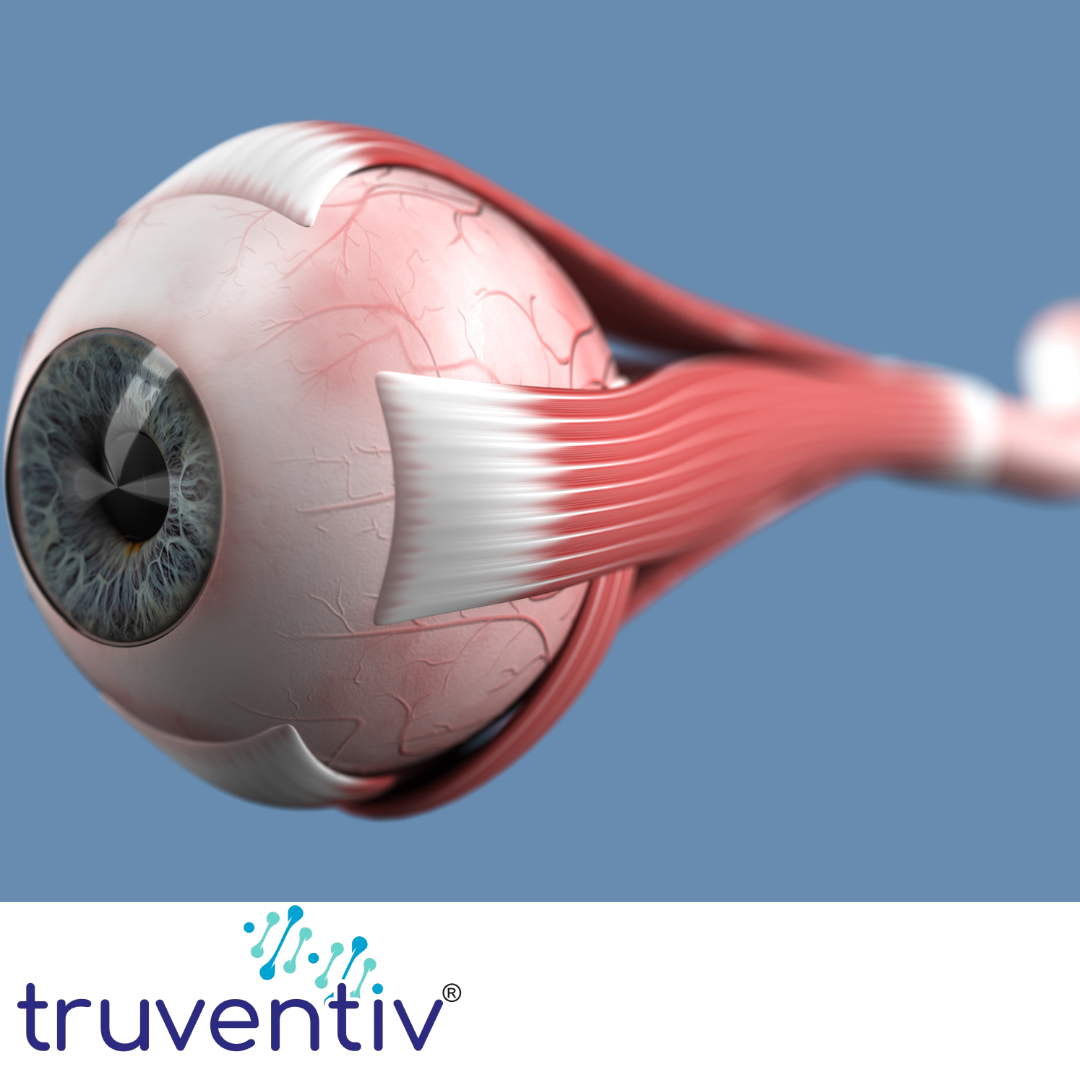
Astaxanthin is a powerful antioxidant carotenoid that provides neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory benefits for the eyes, particularly the retina and optic nerve. It helps in preventing eye diseases, reducing oxidative stress, and improving blood flow, ensuring optimal retinal and optic health.
- Protects the Retina from Oxidative Stress
- The retina is constantly exposed to light and oxygen, making it highly susceptible to oxidative damage.
- Astaxanthin is 5,000 times stronger than vitamin C in neutralizing free radicals, protecting retinal cells from degeneration and damage.
- Enhances Blood Flow to the Retina & Optic Nerve
- Poor circulation can lead to retinal disorders, glaucoma, and optic nerve damage.
- Astaxanthin improves ocular blood flow, ensuring better oxygen and nutrient delivery to the retina and optic nerve.
- Reduces Inflammation & Prevents Retinal Diseases
- Chronic inflammation can lead to conditions like diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration, and glaucoma.
- Astaxanthin has strong anti-inflammatory properties, reducing retinal inflammation and protecting against vision loss.
- Supports the Optic Nerve & Prevents Glaucoma
- Glaucoma occurs due to increased intraocular pressure (IOP), leading to optic nerve damage.
- Astaxanthin helps reduce IOP and oxidative stress, protecting the optic nerve from degeneration.
- Prevents Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
- AMD is a leading cause of blindness caused by oxidative stress and retinal damage.
- Astaxanthin protects the macula, preventing the development of AMD and preserving central vision.
- Shields Against Blue Light & UV Damage
- Continuous exposure to blue light (from screens) and UV rays accelerates retinal damage.
- Astaxanthin filters harmful blue light and protects the eyes from photo-oxidative damage, reducing eye strain and fatigue.
- Enhances Visual Acuity & Contrast Sensitivity
- Astaxanthin improves contrast sensitivity and visual sharpness, making it beneficial for:
- Night vision
- Reading clarity
- Reducing glare sensitivity
- May Help in Diabetic Retinopathy
- Diabetic retinopathy is caused by high blood sugar damaging the retina’s blood vessels.
- Astaxanthin improves microcirculation, reduces oxidative damage, and protects the retina from diabetic complications.
How does Astaxanthin Help blue light protection

Astaxanthin is a potent antioxidant that plays a crucial role in protecting the eyes from blue light damage caused by digital screens, LED lights, and sunlight. Blue light exposure leads to oxidative stress, eye strain, and retinal damage, increasing the risk of digital eye fatigue, macular degeneration, and vision loss.
- Neutralizes Blue Light-Induced Oxidative Stress
- Blue light penetrates deep into the retina, generating free radicals that damage eye cells.
- Astaxanthin is 5,000 times stronger than vitamin C in neutralizing free radicals, protecting retinal cells from oxidative stress.
- Protects Retinal Cells & Macula
- The macula (central part of the retina) absorbs blue light, making it prone to damage over time.
- Astaxanthin shields the macular pigment, reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and vision deterioration.
- Reduces Eye Strain & Digital Fatigue
- Prolonged screen exposure causes eye fatigue, dryness, and blurred vision.
- Astaxanthin enhances blood flow to eye muscles, reducing eye strain, tiredness, and discomfort from long hours of digital screen use.
- Improves Contrast Sensitivity & Visual Performance
- Blue light exposure reduces contrast sensitivity, making it harder to see clearly in low-light conditions.
- Astaxanthin enhances contrast perception and sharpness, improving night vision and reducing glare sensitivity.
- Protects Against Retinal Inflammation
- Continuous exposure to blue light triggers inflammatory responses in the retina.
- Astaxanthin has anti-inflammatory properties, reducing retinal swelling and preventing long-term damage.
- Enhances Macular Pigment Density
- The macular pigment (lutein, zeaxanthin, and meso-zeaxanthin) naturally protects the retina from blue light.
- Astaxanthin supports macular pigment density, enhancing the eye’s natural defense against high-energy blue light.
- Prevents Photo-Oxidative Damage from UV & Blue Light
- UV rays and blue light together accelerate retinal degeneration.
- Astaxanthin reduces photo-oxidative stress, lowering the risk of light-induced vision loss.
How does Astaxanthin Help vitamin D absorption

Astaxanthin does not directly increase vitamin D absorption, but it plays a supportive role in enhancing vitamin D metabolism, activation, and effectiveness in the body. Here’s how:
- Reduces Oxidative Stress for Better Vitamin D Activation
- Vitamin D needs to be converted into its active form (calcitriol) in the liver and kidneys.
- Oxidative stress impairs this conversion, reducing vitamin D availability.
- Astaxanthin, being a powerful antioxidant, protects these organs and enhances vitamin D activation and efficiency.
- Protects Skin from UV Damage Without Blocking Vitamin D Synthesis
- Sunlight (UVB rays) is essential for the skin to produce vitamin D.
- Most sunscreens block UVB, reducing vitamin D production.
- Astaxanthin provides natural skin protection from UV damage while still allowing the skin to synthesize vitamin D.
- Supports Gut Health for Better Vitamin D Absorption
- Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin, meaning it requires a healthy gut and proper fat metabolism for absorption.
- Astaxanthin reduces inflammation in the gut and supports lipid metabolism, which may improve the body's ability to absorb fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin D.
- Reduces Inflammation for Optimal Vitamin D Function
- Vitamin D plays a crucial role in reducing inflammation and supporting immunity.
- Chronic inflammation can interfere with vitamin D function.
- Astaxanthin’s anti-inflammatory properties help vitamin D work more effectively in bone health, immunity, and cellular function.
- Enhances Bone and Muscle Health Alongside Vitamin D
- Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption and bone strength.
- Astaxanthin supports bone and joint health by reducing oxidative stress in bone cells, complementing vitamin D’s role in maintaining strong bones and muscle function.
- Improves Immune System Function with Vitamin D
- Both astaxanthin and vitamin D support immune health.
- Astaxanthin helps regulate immune responses, reducing excessive inflammation and working alongside vitamin D to boost immune defense against infections.
How does Astaxanthin Help antioxidant activity

Astaxanthin is one of the most potent natural antioxidants, providing superior protection against oxidative stress compared to other antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta-carotene. It helps neutralize free radicals, reduce inflammation, and prevent cellular damage, benefiting overall health, including eye, skin, brain, and heart health.
- 6,000 Times Stronger Than Vitamin C
- Astaxanthin is a lipid-soluble carotenoid, meaning it can penetrate cell membranes and provide deep cellular protection.
- It is:
- 6,000x stronger than VITAMIN C
- 800x stronger than COQ 10
- 110x more potent than VITAMIN E & 75x stronger than ALA
- 10x stronger than beta-carotene in fighting free radicals.
- Neutralizes Multiple Free Radicals at Once
- Unlike other antioxidants that handle one free radical at a time, astaxanthin can neutralize multiple free radicals simultaneously, providing stronger and longer-lasting protection.
- Protects Both Water-Soluble & Fat-Soluble Cells
- Many antioxidants work only in water (e.g., vitamin C) or only in fat (e.g., vitamin E).
- Astaxanthin spans both water and fat environments, protecting every part of the cell, including cell membranes and mitochondria.
- Prevents Oxidative Stress & Cellular Damage
- Oxidative stress leads to premature aging, chronic diseases, and inflammation.
- Astaxanthin reduces oxidative damage in:
- Brain cells (protecting against neurodegeneration).
- Heart and blood vessels (reducing heart disease risk).
- Skin cells (preventing premature aging and UV damage).
- Eye cells (protecting against macular degeneration).
- Supports Mitochondrial Health & Energy Production
- The mitochondria (cell’s powerhouse) produce energy but also generate free radicals.
- Astaxanthin protects mitochondria from oxidative damage, improving energy levels and reducing fatigue.
- Reduces Chronic Inflammation
- Oxidative stress leads to chronic inflammation, which is linked to arthritis, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
- Astaxanthin lowers inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP), helping to prevent inflammation-related disorders.
- Prevents Lipid Peroxidation & Protects DNA
- Astaxanthin prevents LDL cholesterol oxidation, reducing the risk of heart disease.
- It also protects DNA from free radical damage, lowering the risk of mutations and chronic diseases.
- Crosses the Blood-Brain Barrier for Neuroprotection
- Many antioxidants cannot reach the brain, but astaxanthin crosses the blood-brain barrier, protecting neurons from oxidative stress.
- It helps prevent Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and cognitive decline.
How does Astaxanthin Help Myopia

Myopia (nearsightedness) is a condition where distant objects appear blurry due to elongation of the eyeball or issues with the retina and optic nerve. Astaxanthin, a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory carotenoid, supports eye health and may help reduce eye strain, slow myopia progression, and improve visual function.
- Reduces Eye Strain & Fatigue from Prolonged Near Work
- Excessive screen time, reading, and near work can cause eye fatigue and strain, worsening myopia symptoms.
- Astaxanthin improves blood flow to eye muscles, reducing eye strain, fatigue, and discomfort.
Benefit: Helps prevent worsening of myopia due to excessive near work.
- Improves Blood Circulation to the Retina & Ciliary Muscles
- Poor blood circulation can weaken the ciliary muscles, which control the eye's focus.
- Astaxanthin enhances ocular blood flow, ensuring better oxygen and nutrient supply to the eyes.
- Benefit: Supports healthy vision and reduces myopia progression.
- Protects the Retina from Oxidative Stress & Blue Light Damage
- Blue light from screens and sunlight can cause oxidative damage to the retina, leading to worsening of myopia.
- Astaxanthin is 5,000 times stronger than vitamin C in neutralizing free radicals, protecting the retina and macula.
Benefit: Shields the eye from myopia-related retinal damage.
- Prevents Inflammation in the Eye
- Chronic inflammation in the eye can contribute to retinal degeneration and myopia progression.
- Astaxanthin has strong anti-inflammatory properties, reducing swelling and preventing eye tissue damage.
Benefit: Helps maintain a healthy retina and optic nerve.
- Strengthens the Sclera & Reduces Abnormal Eye Elongation
- Myopia is linked to excessive elongation of the eyeball, weakening the sclera (white part of the eye).
- Astaxanthin protects collagen and connective tissues, helping to maintain scleral strength and prevent excessive stretching.
Benefit: May slow myopia progression and reduce high myopia risk.
- Enhances Contrast Sensitivity & Visual Acuity
- Myopia can reduce contrast sensitivity, making it harder to see in low light or high-glare environments.
- Astaxanthin improves visual sharpness, contrast perception, and night vision.
Benefit: Helps reduce glare, improve clarity, and enhance vision quality.
- Supports Recovery from Digital Eye Strain
- Staring at screens for long hours can cause temporary worsening of myopia due to digital eye strain.
- Astaxanthin speeds up recovery from eye fatigue, improving focus flexibility.
Benefit: Reduces temporary vision blur and improves focusing ability.
HOW L-GLUTATHIONE HELPS IN RETINAL AND OPTIC HEALTH

L-Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant that plays a crucial role in maintaining retinal and optic nerve health. Here’s how it benefits eye health:
1. Protects Against Oxidative Stress
- The retina and optic nerve are highly susceptible to oxidative damage due to constant exposure to light and high oxygen consumption.
- L-Glutathione neutralizes free radicals, preventing cellular damage in the retina and optic nerve.
2. Prevents Retinal Degeneration & Macular Damage
- Low glutathione levels are linked to age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and retinal diseases.
- It helps protect the macula (central part of the retina) from oxidative stress, reducing the risk of vision loss.
3. Supports Optic Nerve Function
- The optic nerve transmits visual signals from the retina to the brain.
- L-Glutathione prevents neuroinflammation and oxidative damage, reducing the risk of conditions like glaucoma and optic neuropathy.
4. Detoxifies the Eye Tissues
- The eyes are exposed to toxins from pollution, UV rays, and metabolic byproducts.
- L-Glutathione acts as a detoxifier, clearing out harmful substances that could impair vision.
5. Prevents Cataract Formation
- The lens of the eye requires high levels of glutathione to maintain transparency.
- L-Glutathione prevents protein aggregation and oxidative damage, reducing the risk of cataracts.
6. Enhances Blood Flow to the Retina
- It helps improve microcirculation, ensuring that the retina and optic nerve receive sufficient oxygen and nutrients for optimal function.
HOW L-GLUTATHIONE HELPS IN BLUE LIGHT PROTECTION

L-Glutathione plays a key role in protecting the eyes from blue light damage by acting as a powerful antioxidant and detoxifier. Here’s how it helps:
1. Neutralizes Blue Light-Induced Oxidative Stress
- Blue light (high-energy visible light, HEV, 400–500 nm) penetrates deep into the retina and generates free radicals, leading to oxidative stress.
- L-Glutathione neutralizes these free radicals, preventing damage to retinal cells and photoreceptors.
2. Protects the Retina from Photoreceptor Damage
- Continuous exposure to blue light can cause retinal phototoxicity, damaging cone and rod cells.
- L-Glutathione helps repair and maintain photoreceptor integrity, reducing the risk of blue light-induced retinal degeneration.
3. Enhances Mitochondrial Function in Retinal Cells
- The retina has a high energy demand, making it susceptible to mitochondrial dysfunction due to blue light exposure.
- L-Glutathione supports mitochondrial health, ensuring that retinal cells function optimally.
4. Reduces Inflammation & Eye Fatigue
- Blue light exposure can cause ocular inflammation and strain, leading to symptoms like dry eyes, blurry vision, and headaches.
- L-Glutathione lowers inflammation, reducing blue light-induced eye discomfort.
5. Supports the Natural Antioxidant System of the Eye
- The retina and lens rely on glutathione for antioxidant defense.
- Supplementing with L-Glutathione helps replenish depleted antioxidant levels, protecting against cumulative blue light damage.
6. Prevents Macular Degeneration (AMD) Linked to Blue Light
- Prolonged exposure to blue light is linked to age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
- L-Glutathione helps protect the macula from oxidative stress, slowing the progression of vision loss.
7. Works Synergistically with Other Eye-Protecting Nutrients
- Lutein & Zeaxanthin: These carotenoids filter blue light before it reaches the retina.
- Vitamin C & E: Work with glutathione to neutralize oxidative stress.
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA): Helps regenerate glutathione levels for sustained protection.
HOW L-GLUTATHIONE HELPS IN VITAMIN D ABSORPTION

L-Glutathione plays an important role in enhancing Vitamin D absorption and activation in the body. Here’s how it helps:
1. Supports Liver & Kidney Function for Vitamin D Activation
- Vitamin D must be converted into its active form (calcitriol) by the liver and kidneys.
- L-Glutathione supports liver detoxification and protects kidney cells from oxidative damage, ensuring efficient conversion of Vitamin D into its usable form.
2. Enhances Gut Absorption of Vitamin D
- Vitamin D absorption occurs in the intestines, but oxidative stress and inflammation can impair this process.
- L-Glutathione protects the gut lining and enhances nutrient absorption, ensuring better uptake of Vitamin D.
3. Reduces Oxidative Stress That Lowers Vitamin D Levels
- High oxidative stress lowers circulating Vitamin D levels by damaging Vitamin D receptors (VDRs).
- L-Glutathione acts as a master antioxidant, protecting Vitamin D receptors and enhancing their function.
4. Supports Immune System Regulation
- Both glutathione and Vitamin D modulate immune function and work together to reduce inflammation.
- Higher glutathione levels can optimize immune responses, helping the body utilize Vitamin D more effectively.
5. Helps Maintain Bone Health
- Vitamin D enhances calcium absorption, which is crucial for strong bones.
- L-Glutathione helps reduce inflammation and oxidative damage in bone cells, supporting overall bone mineralization and preventing bone loss.
6. Prevents Vitamin D Deficiency in Chronic Conditions
- People with chronic diseases (diabetes, autoimmune disorders, liver/kidney dysfunction) often have low Vitamin D levels.
- L-Glutathione protects against cellular damage and inflammation, ensuring better Vitamin D metabolism in such conditions.
HOW L-GLUTATHIONE HELPS IN ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY

L-Glutathione is known as the "master antioxidant" because it plays a central role in neutralizing free radicals, regenerating other antioxidants, and detoxifying harmful substances. Here’s how it supports antioxidant activity:
1. Neutralizes Free Radicals & Oxidative Stress
- Free radicals cause cellular damage, aging, and chronic diseases.
- L-Glutathione directly neutralizes reactive oxygen species (ROS), preventing oxidative damage to DNA, proteins, and cell membranes.
2. Regenerates Other Antioxidants (Vitamin C & E)
- L-Glutathione helps recycle and restore Vitamin C and Vitamin E, making them active again after they neutralize free radicals.
- This creates a synergistic antioxidant effect, enhancing overall cellular protection.
3. Detoxifies Harmful Compounds
- L-Glutathione binds to heavy metals, toxins, and pollutants, making them water-soluble for easier elimination from the body.
- This prevents oxidative stress and inflammation caused by toxin buildup.
4. Strengthens the Immune System
- Glutathione enhances the function of white blood cells (T-cells, NK cells, and macrophages) to combat infections and inflammation.
- It also reduces chronic inflammation, which is linked to oxidative stress and immune dysfunction.
5. Protects Mitochondrial Health & Energy Production
- Mitochondria are the energy powerhouses of cells but are highly susceptible to oxidative damage.
- L-Glutathione protects mitochondria, ensuring optimal ATP (energy) production and reducing fatigue.
6. Supports Brain & Nervous System Function
- The brain is highly sensitive to oxidative stress, which contributes to neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, etc.).
- L-Glutathione protects neurons, reduces brain inflammation, and enhances cognitive function.
7. Delays Aging & Promotes Skin Health
- Oxidative stress accelerates skin aging, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation.
- L-Glutathione helps reduce melanin production, brighten skin, and protect against UV damage.
8. Improves Cardiovascular Health
- L-Glutathione helps reduce oxidative stress in blood vessels, preventing inflammation and plaque buildup.
- It supports healthy circulation, reducing the risk of hypertension and heart disease.
HOW L-GLUTATHIONE HELPS IN MYOPIA

L-Glutathione plays a crucial role in protecting eye health and potentially slowing down the progression of myopia (nearsightedness) through its powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Here’s how it helps:
1. Reduces Oxidative Stress in the Retina
- Myopia progression is linked to oxidative stress in the retina and sclera (the white part of the eye).
- L-Glutathione neutralizes free radicals that cause oxidative damage, protecting the retina and preventing myopia-related degeneration.
2. Protects the Sclera & Maintains Eye Shape
- Myopia occurs when the eyeball elongates excessively, causing light to focus in front of the retina instead of directly on it.
- Oxidative damage weakens scleral tissue, making it more prone to elongation.
- L-Glutathione helps maintain collagen integrity and scleral strength, reducing the risk of excessive elongation.
3. Supports Retinal Blood Flow & Nutrient Supply
- Myopia is associated with poor blood circulation in the retina, leading to a lack of oxygen and nutrients.
- L-Glutathione enhances blood flow and microcirculation, ensuring better oxygenation and nutrient delivery to the eye tissues.
4. Prevents Retinal Degeneration & Myopia-Related Eye Diseases
- High myopia increases the risk of retinal detachment, macular degeneration, and glaucoma due to oxidative stress.
- L-Glutathione protects the retina from degeneration, reducing the chances of these complications.
5. Reduces Blue Light-Induced Damage
- Excessive screen time and blue light exposure contribute to oxidative stress, worsening myopia.
- L-Glutathione protects retinal cells from blue light-induced damage, reducing strain and preventing further deterioration of vision.
6. Enhances Lens Transparency & Prevents Cataracts
- Myopia is linked to early-onset cataracts, where oxidative stress damages the lens proteins, causing clouding.
- L-Glutathione maintains lens clarity by preventing protein oxidation.
7. Works Synergistically with Other Eye Nutrients
- L-Glutathione works well with Lutein, Zeaxanthin, Vitamin C, and Zinc, which are essential for eye health.
- These nutrients together enhance antioxidant protection and slow myopia progression.
HOW DHA HELPS IN RETINAL AND OPTIC HEALTH

DHA is a long-chain omega-3 fatty acid that is highly concentrated in the retina and optic nerve, playing a critical role in visual function, neuroprotection, and reducing inflammation. Here’s how it benefits eye health:
1. Essential for Retinal Cell Structure & Function
- DHA makes up 30–50% of the total fatty acids in the retina, particularly in the photoreceptor membranes.
- It maintains cell membrane fluidity, ensuring efficient light signal transmission for clear vision.
2. Supports Photoreceptor Function & Visual Acuity
- Photoreceptor cells in the retina require DHA for optimal function.
- DHA enhances visual acuity and contrast sensitivity, helping in low-light conditions and reducing blurry vision.
3. Protects Against Retinal Degeneration
- DHA reduces the risk of retinal degenerative diseases, such as:
- Age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Retinitis pigmentosa
- It prevents oxidative damage and inflammation, which contribute to these conditions.
4. Enhances Optic Nerve Health & Neuroprotection
- The optic nerve transmits visual signals from the retina to the brain.
- DHA promotes nerve cell survival, improves blood flow to the optic nerve, and protects against glaucoma and optic neuropathy.
5. Reduces Inflammation & Oxidative Stress
- DHA is a precursor to neuroprotectin D1 (NPD1), a compound that reduces inflammation and prevents retinal cell apoptosis (cell death).
- This helps prevent damage from oxidative stress, UV light, and blue light exposure.
6. Prevents Dry Eye Syndrome & Improves Tear Production
- DHA, along with EPA (another omega-3), supports tear film stability and reduces dry eye symptoms.
- It enhances meibomian gland function, which produces the oily layer of tears, preventing evaporation and eye irritation.
7. Supports Fetal & Infant Eye Development
- DHA is crucial during pregnancy and early childhood for retinal and brain development.
- Infants with higher DHA intake have better visual acuity and cognitive function.
8. Works Synergistically with Other Eye Nutrients
- DHA is often combined with Lutein, Zeaxanthin, Vitamin A, and Zinc for enhanced retinal protection.
- Together, these nutrients slow age-related vision decline and improve overall eye health.
HOW DHA HELPS IN BLUE LIGHT PROTECTION

DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid) is a critical omega-3 fatty acid that plays a key role in protecting the eyes from blue light-induced damage. Blue light (400–500 nm) penetrates deep into the retina and generates oxidative stress, leading to retinal cell damage, digital eye strain, and age-related vision decline. Here’s how DHA helps:
1. Protects Retinal Cells from Blue Light Damage
- The retina is rich in DHA, particularly in photoreceptor membranes that detect light.
- DHA stabilizes these membranes, preventing blue light-induced phototoxicity and apoptosis (cell death).
2. Reduces Oxidative Stress & Free Radical Damage
- Blue light exposure increases reactive oxygen species (ROS), which damage retinal cells.
- DHA is a powerful antioxidant, neutralizing ROS and protecting the macula and photoreceptors.
3. Supports the Macular Pigment for Blue Light Filtration
- The macula (central retina) absorbs blue light to prevent damage.
- DHA supports macular integrity, enhancing the effectiveness of lutein and zeaxanthin, which act as natural blue light filters.
4. Enhances Tear Film Stability & Reduces Digital Eye Strain
- Excessive screen exposure leads to dry eyes, irritation, and fatigue.
- DHA improves tear production and supports the meibomian glands, reducing dry eye symptoms linked to blue light exposure.
5. Prevents Neuroinflammation in the Optic Nerve
- DHA is a precursor to Neuroprotectin D1 (NPD1), which reduces inflammation in the retina and optic nerve.
- This protects against blue light-induced neurodegeneration, reducing the risk of glaucoma and optic neuropathy.
6. Maintains Mitochondrial Function in Retinal Cells
- The retina has a high energy demand, making it vulnerable to mitochondrial dysfunction due to blue light.
- DHA supports mitochondrial health, ensuring optimal ATP production and cellular repair.
7. Works Synergistically with Other Blue Light Protectors
- Lutein & Zeaxanthin: Filter out blue light before it reaches retinal cells.
- Vitamin A & Zinc: Support night vision and reduce oxidative stress.
- L-Glutathione & Astaxanthin: Provide additional antioxidant defense for retinal cells.
HOW DHA HELPS IN VITAMIN D ABSORPTION

DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid) plays a supportive role in Vitamin D absorption, activation, and function through its effects on cell membrane health, fat metabolism, and anti-inflammatory pathways. Here’s how DHA enhances Vitamin D utilization in the body:
1. Enhances Vitamin D Absorption in the Gut
- Vitamin D is fat-soluble, meaning it needs dietary fats for proper absorption.
- DHA, being an omega-3 fatty acid, improves the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, including Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol), in the intestines.
2. Supports Liver & Kidney Activation of Vitamin D
- Vitamin D must be converted into its active form (calcitriol) in the liver and kidneys.
- DHA reduces inflammation and oxidative stress in these organs, ensuring optimal Vitamin D metabolism.
3. Improves Cell Membrane Function & Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) Activity
- DHA is a key component of cell membranes, making them more fluid and functional.
- This enhances Vitamin D receptor (VDR) activity, improving how Vitamin D is transported and used by cells.
4. Reduces Inflammation for Better Vitamin D Utilization
- Chronic inflammation can impair Vitamin D function and metabolism.
- DHA produces anti-inflammatory compounds (resolvins and protectins) that enhance Vitamin D’s ability to regulate the immune system and bone health.
5. Works Synergistically with Vitamin D for Bone & Immune Health
- Vitamin D and DHA together enhance calcium absorption, supporting bone density and strength.
- Both DHA and Vitamin D play crucial roles in immune modulation, helping prevent inflammatory and autoimmune conditions.
6. Prevents Vitamin D Deficiency in Omega-3 Deficient Individuals
- Studies suggest that low omega-3 levels are associated with poor Vitamin D status.
- Supplementing with DHA may help maintain optimal Vitamin D levels, especially in people with deficiencies.
HOW DHA HELPS IN ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY

DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid) is not only a structural component of cell membranes but also plays a significant role in antioxidant defense mechanisms. While DHA itself is not a direct antioxidant, it supports antioxidant activity in several ways:
1. Reduces Oxidative Stress in Cell Membranes
- DHA is highly unsaturated, making cell membranes more fluid and resilient, which helps protect against oxidative damage.
- It prevents lipid peroxidation, a process where free radicals damage cell membranes, leading to aging and disease.
2. Produces Anti-Inflammatory & Antioxidant Derivatives
- DHA is a precursor to Neuroprotectin D1 (NPD1), Resolvins, and Protectins, which:
- Reduce oxidative stress in neurons and other tissues.
- Prevent apoptosis (cell death) caused by free radicals.
- Enhance cellular repair mechanisms after oxidative damage.
3. Supports Glutathione Production & Recycling
- DHA helps maintain levels of glutathione (GSH), the body's master antioxidant.
- It enhances glutathione peroxidase activity, which neutralizes harmful free radicals.
4. Works Synergistically with Other Antioxidants
- DHA enhances the effects of Vitamin E, Vitamin C, and CoQ10, improving their ability to fight oxidative stress.
- It protects Lutein and Zeaxanthin, key antioxidants in the eyes, from degradation.
5. Protects the Brain & Nervous System from Oxidative Damage
- The brain is highly susceptible to oxidative stress, contributing to neurodegenerative diseases.
- DHA reduces free radical damage in neurons, lowering the risk of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and cognitive decline.
6. Prevents Mitochondrial Damage & Boosts Energy Production
- Mitochondria are highly sensitive to oxidative stress, leading to fatigue and cell dysfunction.
- DHA supports mitochondrial function, ensuring efficient ATP production while minimizing oxidative damage.
7. Protects the Cardiovascular System
- DHA reduces oxidation of LDL cholesterol, preventing plaque buildup in arteries.
- It improves blood vessel function, reducing oxidative stress that leads to heart disease.
HOW DHA HELPS IN MYOPIA

DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid) is an essential omega-3 fatty acid that plays a key role in retinal health, eye development, and reducing oxidative stress—all factors that influence the progression of myopia (nearsightedness). Here’s how DHA helps:
1. Supports Retinal Development & Function
- DHA is a major structural component of the retina and photoreceptor cells, ensuring proper visual signal transmission.
- Deficiency in DHA can lead to retinal dysfunction and impaired visual acuity, which may contribute to myopia progression.
2. Reduces Retinal Oxidative Stress & Inflammation
- Myopia progression is linked to oxidative damage in the retina and sclera (eye’s outer layer).
- DHA has strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, protecting retinal cells from oxidative stress and slowing the elongation of the eyeball.
3. Prevents Scleral Weakening & Eye Elongation
- Myopia develops when the eyeball becomes elongated, causing light to focus in front of the retina instead of directly on it.
- DHA supports collagen integrity and scleral remodeling, preventing excessive eye elongation.
4. Enhances Blood Flow to the Retina
- Poor circulation in the retina can contribute to myopia progression.
- DHA improves blood flow and oxygen supply to the retinal tissues, supporting overall eye health and function.
5. Protects Against Blue Light Damage & Digital Eye Strain
- Excessive screen time and blue light exposure contribute to eye strain and may worsen myopia.
- DHA protects retinal cells from blue light-induced oxidative stress, reducing digital eye strain and fatigue.
6. Supports Tear Film Stability & Reduces Dry Eyes
- Dry eyes are common in people with high myopia and excessive screen exposure.
- DHA improves tear quality and lubrication, reducing dryness, irritation, and discomfort.
7. Works Synergistically with Other Eye Nutrients
- DHA works best when combined with:
- Lutein & Zeaxanthin (blue light protection)
- Vitamin A (supports retinal health)
- Zinc (aids in visual signal transmission)
- L-Glutathione (reduces oxidative stress)
HOW METHYLCOBALAMIN HELPS IN RETINAL AND OPTIC HEALTH

Methylcobalamin is the active, neurologically beneficial form of Vitamin B12, essential for nerve function, red blood cell production, and retinal health. It plays a key role in protecting the optic nerve, reducing oxidative stress, and preventing vision-related disorders. Here’s how it helps:
1. Protects the Optic Nerve & Prevents Optic Neuropathy
- The optic nerve transmits visual signals from the retina to the brain.
- Methylcobalamin prevents degeneration of the optic nerve by reducing nerve inflammation and demyelination (nerve coating loss).
- It is especially effective in preventing nutritional optic neuropathy and glaucoma-related nerve damage.
2. Enhances Retinal Blood Circulation
- Methylcobalamin supports red blood cell production, ensuring adequate oxygen delivery to the retina.
- This helps prevent conditions like diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration (AMD), where poor blood flow damages the retina.
3. Reduces Oxidative Stress & Retinal Degeneration
- The retina is highly susceptible to oxidative stress, which accelerates vision loss.
- Methylcobalamin acts as an antioxidant, reducing damage caused by free radicals and inflammation in retinal cells.
4. Supports Myelin Sheath & Nerve Regeneration
- The optic nerve is covered by a protective myelin sheath, which helps in fast and accurate signal transmission.
- Methylcobalamin supports myelin regeneration, preventing conditions like optic neuritis and multiple sclerosis-related vision loss.
5. Prevents Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
- Vitamin B12 deficiency has been linked to increased homocysteine levels, which can damage blood vessels in the retina.
- Methylcobalamin helps reduce homocysteine, lowering the risk of macular degeneration and retinal damage.
6. Supports Eye Health in Diabetics
- Diabetic patients are at risk of diabetic retinopathy, leading to blindness.
- Methylcobalamin reduces nerve damage, improves circulation, and prevents retinal complications in diabetes.
7. Helps in Glaucoma & Cataract Prevention
- Glaucoma causes optic nerve damage due to high intraocular pressure (IOP).
- Methylcobalamin protects retinal ganglion cells, reducing the risk of glaucoma progression.
- It also prevents lens protein oxidation, slowing cataract formation.
8. Works Synergistically with Other Eye Nutrients
- DHA & Lutein: Support photoreceptor and optic nerve function.
- L-Glutathione & Vitamin C: Reduce oxidative damage in the retina.
- Zinc & Vitamin A: Enhance night vision and retinal health.
HOW METHYLCOBALAMIN HELPS IN BLUE LIGHT PROTECTION

Methylcobalamin, the active form of Vitamin B12, plays a significant role in protecting the eyes from blue light-induced damage by supporting nerve health, reducing oxidative stress, and enhancing cellular repair. Here's how it helps:
1. Protects Retinal Nerve Cells from Oxidative Stress
- Blue light exposure generates reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to oxidative stress and retinal cell damage.
- Methylcobalamin acts as an antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals and protecting the retina from oxidative damage.
2. Supports Optic Nerve Health
- Prolonged blue light exposure can damage the optic nerve and retinal ganglion cells, increasing the risk of optic neuropathy.
- Methylcobalamin helps regenerate the myelin sheath, which protects the optic nerve and maintains visual signal transmission.
3. Reduces Neuroinflammation in the Retina
- Blue light can trigger inflammatory pathways in retinal tissues.
- Methylcobalamin has anti-inflammatory properties, reducing retinal inflammation and protecting photoreceptor cells.
4. Prevents Digital Eye Strain & Fatigue
- Excessive blue light exposure from digital screens causes eye fatigue, dryness, and blurry vision.
- Methylcobalamin helps in nerve repair and muscle relaxation, alleviating symptoms of digital eye strain.
5. Enhances Blood Circulation in the Retina
- Methylcobalamin improves blood flow to the optic nerve and retina, providing essential nutrients and oxygen to combat blue light-induced damage.
6. Reduces Risk of Macular Degeneration
- Long-term blue light exposure is linked to age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
- Methylcobalamin reduces homocysteine levels, which helps prevent damage to the macular blood vessels.
7. Supports DNA Repair in Retinal Cells
- Blue light can cause DNA damage in retinal cells, accelerating vision loss.
- Methylcobalamin plays a key role in DNA synthesis and repair, promoting faster recovery of damaged retinal cells.
8. Works Synergistically with Other Antioxidants
- Combines effectively with:
- Lutein & Zeaxanthin: Blue light filters
- DHA: Photoreceptor protection
- Glutathione & Vitamin C: Antioxidant support
HOW METHYLCOBALAMIN HELPS IN VITAMIN D ABSORPTION

Methylcobalamin, the active form of Vitamin B12, plays an indirect but essential role in Vitamin D metabolism, absorption, and function. While Vitamin D is fat-soluble and primarily absorbed through dietary fats, Methylcobalamin supports its activation, transport, and cellular function in the following ways:
1. Supports Gut Health for Better Vitamin D Absorption
- Vitamin D absorption occurs in the small intestine, where it requires a healthy gut lining and sufficient digestive enzymes.
- B12 deficiency can lead to gut inflammation, poor digestion, and malabsorption issues, indirectly reducing Vitamin D uptake.
- Methylcobalamin supports healthy gut microbiota and digestive function, optimizing Vitamin D absorption.
2. Enhances Liver & Kidney Activation of Vitamin D
- Vitamin D must be converted into its active form (calcitriol) in the liver and kidneys.
- Methylcobalamin supports liver detoxification and kidney function, ensuring efficient conversion of Vitamin D3 into its bioactive form.
3. Reduces Homocysteine Levels for Better Vitamin D Function
- High homocysteine levels impair Vitamin D metabolism and reduce its effectiveness in calcium regulation and bone health.
- Methylcobalamin helps lower homocysteine levels, improving Vitamin D’s ability to support bone density, immune health, and hormone balance.
4. Supports Calcium Metabolism & Bone Health
- Vitamin D helps in calcium absorption, but B12 deficiency can weaken bone structure and contribute to osteoporosis.
- Methylcobalamin works with Vitamin D to support bone mineralization, prevent fractures, and enhance skeletal strength.
5. Boosts Energy Metabolism & Mitochondrial Function
- Vitamin D and B12 both play essential roles in energy production and mitochondrial health.
- Methylcobalamin enhances cellular energy metabolism, ensuring that Vitamin D can effectively regulate immune function, bone strength, and muscle health.
6. Strengthens the Immune System
- Vitamin D is a powerful immune regulator, but its efficiency can be reduced by B12 deficiency.
- Methylcobalamin enhances immune cell function, allowing Vitamin D to work more effectively in preventing infections and inflammation.
7. Works Synergistically with Other Nutrients
Methylcobalamin helps optimize Vitamin D function by working alongside:
- Magnesium – essential for Vitamin D activation
- Omega-3 (DHA) – enhances Vitamin D receptor activity
- Folate & Vitamin B6 – work with B12 to regulate homocysteine and support bone health
HOW METHYLCOBALAMIN HELPS IN ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY

Methylcobalamin, the active form of Vitamin B12, plays a crucial role in neutralizing oxidative stress, reducing inflammation, and supporting cellular repair. While it is not a direct antioxidant like Vitamin C or glutathione, it enhances the body's natural antioxidant defense system in several ways:
1. Reduces Oxidative Stress & Free Radical Damage
- Methylcobalamin helps neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can damage cells and accelerate aging.
- It prevents lipid peroxidation, a process where free radicals harm cell membranes, especially in the brain, retina, and nervous system.
2. Supports Glutathione Production & Recycling
- Glutathione (GSH) is the body’s master antioxidant, crucial for detoxification and cellular protection.
- Methylcobalamin enhances glutathione synthesis and regeneration, ensuring continuous antioxidant activity.
3. Reduces Homocysteine Levels & Prevents Inflammation
- High homocysteine levels trigger oxidative stress and inflammation, increasing the risk of neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases.
- Methylcobalamin lowers homocysteine, reducing oxidative damage to brain cells, blood vessels, and organs.
4. Protects Brain & Nerve Cells from Oxidative Damage
- The brain and nervous system are highly vulnerable to oxidative stress, which contributes to conditions like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and neuropathy.
- Methylcobalamin supports nerve regeneration, prevents neuroinflammation, and enhances myelin sheath integrity (the protective layer around nerves).
5. Enhances Mitochondrial Function & Energy Production
- Mitochondria generate ATP (cellular energy) but also produce oxidative byproducts.
- Methylcobalamin enhances mitochondrial efficiency, reducing oxidative stress-related fatigue and cellular dysfunction.
6. Supports DNA Repair & Cellular Longevity
- Oxidative stress damages DNA, leading to premature aging and disease.
- Methylcobalamin aids in DNA synthesis and repair, ensuring healthy cell replication and longevity.
7. Works Synergistically with Other Antioxidants
Methylcobalamin enhances the effects of:
- Glutathione – Master detoxifier & antioxidant
- DHA (Omega-3) – Reduces lipid oxidation in brain and retina
- Vitamin C & E – Combat oxidative stress in tissues
- CoQ10 – Protects mitochondria from oxidative damage
HOW METHYLCOBALAMIN HELPS IN MYOPIA

Methylcobalamin, the active form of Vitamin B12, plays a key role in nerve protection, retinal health, and reducing oxidative stress, which are important factors in managing myopia (nearsightedness). While myopia is primarily caused by excessive eyeball elongation, Methylcobalamin helps by supporting the optic nerve, reducing inflammation, and preventing retinal damage.
1. Protects the Optic Nerve & Prevents Myopic Degeneration
- Myopia progression can lead to optic nerve strain and damage, especially in high myopia.
- Methylcobalamin regenerates the myelin sheath (nerve coating), improving visual signal transmission and reducing nerve stress.
- It may help prevent myopic neuropathy, a condition where the optic nerve is damaged due to excessive elongation of the eye.
2. Reduces Oxidative Stress & Retinal Damage
- High myopia increases the risk of oxidative damage to retinal cells, leading to complications like retinal thinning, detachment, and macular degeneration.
- Methylcobalamin acts as an antioxidant, reducing free radical damage and protecting the retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) from premature aging.
3. Supports Blood Flow & Nutrient Supply to the Retina
- Myopia is linked to poor circulation in the retina and choroid (the layer that supplies oxygen and nutrients to the eye).
- Methylcobalamin improves blood circulation, ensuring better oxygen and nutrient delivery to the retina, which may slow myopia progression.
4. Helps Prevent Myopia-Related Retinal Diseases
- Severe myopia increases the risk of retinal detachment, myopic maculopathy, and choroidal neovascularization (abnormal blood vessel growth).
- Methylcobalamin helps maintain retinal integrity, preventing these complications.
5. Reduces Digital Eye Strain & Supports Visual Comfort
- Excessive screen time contributes to accommodation stress, which worsens myopia progression.
- Methylcobalamin reduces nerve fatigue, improves eye muscle coordination, and lowers digital eye strain symptoms like dryness, blurriness, and headaches.
6. Works Synergistically with Other Myopia-Preventing Nutrients
- DHA (Omega-3s): Supports photoreceptor health and retinal elasticity.
- Lutein & Zeaxanthin: Protect against blue light damage.
- Vitamin D3: Linked to myopia prevention by improving eye growth regulation.
- Zinc & Magnesium: Support nerve function and prevent oxidative stress.
HOW CHOLECALCIFEROL HELPS IN RETINAL AND OPTIC HEALTH

Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) plays a crucial role in retinal and optic health due to its neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. Here’s how it supports eye health:
1. Neuroprotection for Retinal Cells
- The retina contains vitamin D receptors (VDRs), indicating its role in maintaining retinal health.
- Cholecalciferol supports retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), which are essential for transmitting visual signals to the brain.
- It protects against glaucoma-related neurodegeneration by reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis (cell death) in the optic nerve.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
- Reduces inflammation in the retina by inhibiting inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, which are linked to conditions like diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
- Helps prevent retinal vascular damage caused by chronic inflammation.
3. Protects Against Oxidative Stress
- Cholecalciferol enhances antioxidant enzyme activity, reducing oxidative damage to photoreceptor cells.
- Protects against light-induced retinal damage, which is a major contributor to macular degeneration.
4. Supports Retinal Blood Flow & Vascular Health
- Regulates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), preventing abnormal blood vessel growth in diseases like diabetic retinopathy.
- Maintains proper blood flow to the optic nerve, reducing the risk of ischemic optic neuropathy.
5. Reduces Risk of Autoimmune Eye Disorders
- Vitamin D3 helps regulate the immune system, lowering the risk of autoimmune conditions like uveitis and multiple sclerosis-associated optic neuritis.
6. Potential Role in Myopia Control
- Some studies suggest that Vitamin D3 deficiency may be linked to higher myopia (nearsightedness) progression, as it influences scleral remodeling and axial eye growth.
7. Supports Tear Film & Dry Eye Syndrome
- Helps maintain corneal integrity and tear production, reducing symptoms of dry eye disease (DED).
- Enhances meibomian gland function, improving the stability of the tear film.
HOW CHOLECALCIFEROL HELPS IN BLUE LIGHT PROTECTION

Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) plays a protective role against blue light-induced damage through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects. Blue light (especially from screens, LED lights, and sunlight) can cause oxidative stress, retinal cell damage, and digital eye strain. Here’s how Vitamin D3 helps:
1. Reduces Oxidative Stress & Retinal Damage
- Blue light exposure generates reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to oxidative stress in the retina.
- Cholecalciferol enhances antioxidant enzyme activity (e.g., glutathione, superoxide dismutase), neutralizing free radicals and protecting photoreceptor cells from damage.
2. Protects Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) & Photoreceptors
- The RPE cells help maintain photoreceptor function and remove toxic byproducts.
- Vitamin D3 reduces blue light-induced RPE apoptosis (cell death), preserving retinal integrity.
- Protects cones and rods from excessive light exposure, preventing phototoxicity.
3. Enhances Melatonin Regulation & Circadian Rhythm
- Excessive blue light exposure, especially at night, disrupts melatonin production, leading to sleep disturbances.
- Cholecalciferol supports melatonin synthesis, helping regulate circadian rhythms and minimizing sleep-related issues caused by blue light.
4. Reduces Inflammation & Prevents Retinal Degeneration
- Blue light exposure triggers inflammatory responses, accelerating retinal degeneration.
- Cholecalciferol suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β), reducing retinal inflammation and slowing age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
5. Strengthens the Tear Film & Reduces Digital Eye Strain
- Blue light exposure contributes to dry eye syndrome by affecting tear stability.
- Vitamin D3 improves tear film production and supports meibomian gland function, reducing dryness and irritation from prolonged screen use.
6. Supports Optic Nerve & Neuroprotection
- Chronic blue light exposure may damage the optic nerve, increasing the risk of glaucoma and neurodegeneration.
- Cholecalciferol protects retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and enhances neuronal survival, lowering the risk of optic nerve damage.
HOW CHOLECALCIFEROL HELPS IN VITAMIN D ABSORPTION

Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) itself does not "help" in Vitamin D absorption—rather, it is the primary form of Vitamin D that gets absorbed, metabolized, and activated in the body. However, let’s break down how Vitamin D3 is absorbed and utilized:
1. Cholecalciferol is the Most Bioavailable Form of Vitamin D
- Vitamin D exists in two main forms:
- Vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol) – found in plant sources.
- Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol) – found in animal sources and synthesized in the skin from sunlight.
- Vitamin D3 is better absorbed and utilized than Vitamin D2, making it the preferred form for supplementation.
2. Absorption Process of Cholecalciferol
- Fat-Soluble Vitamin:
- Cholecalciferol is absorbed in the small intestine, mainly in the duodenum and jejunum, with the help of dietary fats and bile salts.
- Transport via Chylomicrons:
- After absorption, Vitamin D3 is incorporated into chylomicrons and transported through the lymphatic system into the bloodstream.
3. Conversion to Active Vitamin D (Calcitriol)
- Liver Conversion (25-Hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D]):
- In the liver, cholecalciferol is converted into 25-hydroxyvitamin D (calcifediol), the storage form of Vitamin D.
- Kidney Activation (1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D [1,25(OH)2D]):
- In the kidneys, 25(OH)D is converted into 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (calcitriol), the biologically active form.
- Calcitriol regulates calcium and phosphorus metabolism, supporting bone health, immune function, and muscle strength.
4. Factors That Enhance Cholecalciferol Absorption
- Dietary Fat Intake: Since Vitamin D3 is fat-soluble, consuming it with healthy fats (e.g., avocado, nuts, olive oil) improves absorption.
- Bile Salt Production: Bile acids help emulsify and absorb Vitamin D3. Poor liver or gallbladder function can reduce absorption.
- Magnesium Levels: Magnesium is essential for converting Vitamin D3 into its active forms.
- Gut Health: A healthy gut microbiome and proper digestive enzymes enhance Vitamin D3 absorption.
5. Factors That Impair Cholecalciferol Absorption
- Fat Malabsorption Disorders: Conditions like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and pancreatitis can reduce Vitamin D3 absorption.
- Low Bile Production: Poor bile flow affects fat digestion and Vitamin D3 uptake.
- Aging & Obesity: Older adults and individuals with excess body fat may have reduced bioavailability of Vitamin D3.
HOW CHOLECALCIFEROL HELPS IN ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY

Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) indirectly enhances antioxidant activity by reducing oxidative stress, regulating antioxidant enzymes, and suppressing free radical production. This helps protect cells, tissues, and organs from oxidative damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammation.
1. Enhances Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
Cholecalciferol boosts the production and activity of key antioxidant enzymes that neutralize free radicals, including:
- Superoxide Dismutase (SOD): Converts harmful superoxide radicals into less toxic molecules.
- Catalase (CAT): Breaks down hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) into water and oxygen, preventing oxidative damage.
- Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx): Reduces lipid peroxides and protects cell membranes.
By increasing these enzymes, Vitamin D3 strengthens the body's defense against oxidative stress.
2. Reduces Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production
- ROS are unstable molecules that damage DNA, proteins, and lipids.
- Cholecalciferol lowers ROS levels by reducing NADPH oxidase (NOX) enzyme activity, which is responsible for generating oxidative stress.
- This is especially beneficial for the brain, heart, skin, and eyes, which are vulnerable to oxidative damage.
3. Lowers Inflammation & Oxidative Stress
Chronic inflammation increases oxidative stress. Vitamin D3 reduces inflammation by:
- Suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β).
- Enhancing anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10).
- Reducing NF-κB activation, a key pathway in inflammation and oxidative stress.
By controlling inflammation, Vitamin D3 helps reduce oxidative damage in chronic diseases like diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions.
4. Protects Mitochondrial Function
- Mitochondria are the energy powerhouses of cells, but they are also a major source of ROS.
- Cholecalciferol improves mitochondrial efficiency by reducing oxidative damage, maintaining ATP production, and preventing mitochondrial dysfunction.
- This is critical for brain health (neuroprotection), muscle function, and energy metabolism.
5. Prevents Lipid Peroxidation & DNA Damage
- Lipid peroxidation occurs when free radicals attack cell membranes, leading to cell damage and aging.
- Vitamin D3 reduces lipid peroxidation by stabilizing cell membranes and increasing glutathione levels, the body's master antioxidant.
- It also protects DNA from oxidative damage, lowering the risk of mutations and cancer development.
6. Supports Antioxidant Balance in the Brain & Nervous System
- The brain is highly sensitive to oxidative stress, which contributes to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Vitamin D3 protects neurons by:
- Increasing glutathione levels in the brain.
- Reducing oxidative damage in dopaminergic neurons (linked to Parkinson’s disease).
- Enhancing neurotrophic factors that support brain cell survival
HOW CHOLECALCIFEROL HELPS IN MYOPIA

Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) may help in myopia (nearsightedness) through several mechanisms:
1. Regulation of Eye Growth
- Myopia is caused by excessive elongation of the eyeball.
- Vitamin D3 plays a role in controlling scleral growth and remodeling, preventing excessive axial elongation.
- It may influence pathways like TGF-β, which regulates extracellular matrix synthesis in the sclera.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
- Myopia is associated with low-grade inflammation and oxidative stress in the eye.
- Vitamin D3 reduces inflammation by modulating cytokines like TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β.
- It also reduces oxidative stress, which can damage retinal and scleral tissues.
3. Dopamine Regulation in the Retina
- Dopamine is crucial for inhibiting excessive eye growth.
- Vitamin D3 enhances dopamine synthesis in the retina, preventing myopic progression.
- Low dopamine levels are linked to increased axial elongation and myopia.
4. Role in Calcium Metabolism & Eye Structure
- Vitamin D3 helps maintain calcium homeostasis, which is essential for scleral rigidity.
- A weaker sclera is more susceptible to elongation, leading to myopia.
5. Photoprotection & Sunlight Exposure
- Low outdoor exposure is a risk factor for myopia.
- Sunlight stimulates vitamin D3 synthesis, which indirectly benefits eye health.
- It also helps regulate melatonin and circadian rhythms, which can impact myopia development


