How Lactobacillus Acidophilus helps in Digestion & Detoxification
Lactobacillus acidophilus is a type of beneficial bacteria (probiotic) that plays a key role in supporting digestion and detoxification.
- Supports Digestion:
- Breaks down food: L. acidophilus helps break down lactose (the sugar in dairy products), which can improve digestion for people who are lactose intolerant.
- Promotes a healthy balance of gut bacteria: It helps maintain a balanced gut microbiota, preventing harmful bacteria from taking over. A balanced microbiota aids in efficient digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Synthesis of digestive enzymes: L. acidophilus can produce certain enzymes that break down foods more effectively, aiding in smoother digestion.
- Detoxification :
- Gut health and detox: A healthy gut microbiome helps eliminate toxins and waste products from the digestive system more efficiently. L. acidophilus assists by improving gut motility (the movement of food and waste through the intestines), making detoxification more effective.
- Decreases inflammation: By maintaining gut health, L. acidophilus can help reduce gut inflammation, which is often linked to digestive issues and toxin buildup.
- Neutralizes harmful compounds: Some research suggests that probiotics like L. acidophilus may help neutralize or break down potentially harmful compounds in the digestive tract, preventing them from being absorbed into the bloodstream.
HOW LACTOBACILLUS ACIDOPHILUS HELPS IN MAINTAIN ENZYME BALANCE

- Production of digestive enzymes: L. acidophilus can produce certain enzymes, such as lactase, which is important for breaking down lactose (milk sugar) into simpler sugars. This is particularly beneficial for people who are lactose intolerant, as it allows them to digest dairy products more effectively.
- Support for other digestive enzymes: By promoting a healthy gut microbiome, L. acidophilus can indirectly support the action of other enzymes in the digestive process. A balanced microbiota helps create an optimal environment for the activity of various digestive enzymes produced by the stomach, pancreas, and small intestine.
- Enhancing nutrient absorption: The enzymes produced by L. acidophilus and other probiotics help break down nutrients more effectively, which can improve the absorption of vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients from the food you eat. This contributes to maintaining a good balance of digestive enzymes and promotes optimal digestive function.
- Stabilizing gut pH: L. acidophilus helps create a slightly acidic environment in the gut, which is conducive to the optimal functioning of digestive enzymes. The right pH balance ensures that enzymes, like proteases (which break down proteins) and amylases (which break down carbohydrates), work efficiently.
- Regulating enzyme production: A healthy population of beneficial bacteria like L. acidophilus can help regulate the body’s production of digestive enzymes. It can support the gut in producing the right amount of enzymes needed for optimal digestion, ensuring there is no overproduction or underproduction that could lead to digestive issues.
HOW LACTOBACILLUS ACIDOPHILUS HELPS IN PROBIOTIC SUPPORT & REDUCES BLOATING

- Restores Gut Microbiome Balance:
- L. acidophilus is a beneficial bacterium that helps restore the balance of the gut microbiota. When the balance is off (e.g., due to a diet high in processed foods or after antibiotics), harmful bacteria or yeast (like Candida) can overgrow, leading to bloating, gas, and digestive discomfort. By increasing the population of healthy bacteria, L. acidophilus helps crowd out these harmful organisms, reducing bloating.
- Improves Digestion:
- This probiotic helps break down food more efficiently, particularly lactose and other complex carbohydrates, reducing the chances of undigested food fermenting in the gut, which can produce gas and lead to bloating.
- Enhanced enzyme production by L. acidophilus also supports smoother digestion, further minimizing bloating related to incomplete digestion.
- Increases Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs):
- L. acidophilus helps ferment certain dietary fibers and sugars, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, acetate, and propionate. These SCFAs nourish the gut lining, improve overall gut health, and can help regulate gas production and bloating.
- Reduces Intestinal Inflammation:
- By promoting a healthier gut environment, L. acidophilus can reduce inflammation in the intestines. Inflammation can contribute to bloating, discomfort, and other digestive issues. A balanced gut microbiome reduces the likelihood of excessive gut inflammation, which can lead to a bloated feeling.
- Supports Gut Motility:
- Probiotics like L. acidophilus help improve gut motility, which is the process of moving food through the digestive tract. Slow motility can result in gas buildup, leading to bloating. By enhancing motility, L. acidophilus helps move food and waste through the system more efficiently, reducing the chances of bloating.
- Reduces Overgrowth of Gas-Producing Bacteria:
- L. acidophilus works by inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria that produce excessive gas in the gut, such as Clostridia and Enterobacteriaceae. This can help reduce the overall amount of gas produced during digestion, easing bloating symptoms.
- Enhances Immune Function:
- L. acidophilus can help support your immune system in the gut, further promoting digestive health. A well-functioning immune system reduces the chances of gut disturbances, such as infections or inflammation, which can also contribute to bloating.
HOW LACTOBACILLUS ACIDOPHILUS HELPS IN GERD,IBS & IBD MANAGEMENT

Lactobacillus acidophilus, a probiotic bacterium, can play an important role in the management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), and Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) by supporting gut health, reducing inflammation, and promoting a balanced gut microbiome.
1. GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
GERD is a chronic digestive condition where stomach acid or bile irritates the food pipe (esophagus), leading to symptoms like heartburn, regurgitation, and chest pain.
How L. acidophilus helps in GERD:
- Improves gut motility: Probiotics like L. acidophilus can help improve the motility of the digestive tract, ensuring that food and stomach acids move efficiently through the system. Slow motility can contribute to acid reflux, and better gut motility may reduce the likelihood of acid from the stomach moving up into the esophagus.
- Reduces inflammation: GERD is often associated with inflammation of the esophagus. L. acidophilus helps reduce gut inflammation by promoting a healthy balance of gut bacteria and reducing the growth of harmful bacteria that can contribute to irritation and inflammation in the digestive tract.
- Strengthens the gut barrier: A healthy gut lining is essential to prevent the reflux of stomach acids. L. acidophilus supports the gut’s protective barrier, making it less likely that stomach acid will leak into the esophagus, which can exacerbate GERD symptoms.
- Balances stomach acid production: By supporting gut health and improving the microbial balance, L. acidophilus may help regulate stomach acid production, reducing the chances of excessive acid secretion, a contributing factor to GERD.
2. IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
IBS is a common digestive disorder characterized by symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, constipation, or alternating between both.
How L. acidophilus helps in IBS:
- Restores gut microbiome balance: IBS is often linked to an imbalance in the gut microbiome, where harmful bacteria can outnumber beneficial bacteria. L. acidophilus helps restore the balance of gut flora, promoting a healthy microbiome and improving digestive function.
- Reduces bloating and gas: L. acidophilus helps in the breakdown of undigested food in the colon, reducing fermentation and gas production. This can alleviate common IBS symptoms such as bloating, discomfort, and excessive gas.
- Improves gut motility: L. acidophilus supports smoother and more regular bowel movements by improving gut motility. This is particularly helpful for those with IBS-related constipation. Additionally, it can help reduce diarrhea, a common symptom of IBS, by regulating the speed of digestion.
- Modulates gut inflammation: In IBS, there can be mild inflammation or hypersensitivity in the gut. L. acidophilus can help reduce this inflammation, leading to a reduction in pain and discomfort.
3. IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease) — Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
IBD refers to chronic inflammatory conditions of the gastrointestinal tract, with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis being the two main types. These conditions cause severe inflammation, ulceration, and other symptoms in the intestines.
How L. acidophilus helps in IBD:
- Reduces inflammation: Chronic inflammation is a key feature of IBD. L. acidophilus can help modulate the immune system and reduce excessive inflammation in the gut. It promotes the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines and helps balance the immune response, which can reduce IBD flare-ups and severity.
- Supports intestinal barrier function: In IBD, the intestinal lining becomes compromised, allowing harmful bacteria and toxins to leak into the bloodstream, contributing to inflammation. L. acidophilus helps strengthen the intestinal barrier, improving its integrity and preventing harmful substances from causing further damage.
- Regulates immune responses: L. acidophilus supports the immune system in the gut, helping it to differentiate between harmful and harmless substances. This can help reduce the likelihood of an immune system attack on the gut tissue, which is a hallmark of IBD.
- Promotes healing of the gut lining: L. acidophilus can support the healing of damaged tissue in the intestines by maintaining a healthy gut environment. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with ulcerative colitis, where the colon lining is severely damaged.
- Helps manage gut dysbiosis: IBD is often accompanied by dysbiosis (an imbalance of gut bacteria), which can worsen symptoms. L. acidophilus helps restore a healthy balance of beneficial bacteria, potentially alleviating symptoms and reducing the frequency of flare-ups.
acidophilus aids in the breakdown of food, improves nutrient absorption, and helps regulate digestion, which can ease symptoms like bloating, constipation, diarrhea, and cramping.
HOW LACTOBACILLUS ACIDOPHILUS HELPS IN ACIDITY

- Promotes a Healthy Gut Microbiome:
- A balanced gut microbiome plays a crucial role in maintaining overall digestive health. L. acidophilus, as a beneficial probiotic, helps restore balance by increasing the population of good bacteria in the gut. An imbalance in gut bacteria (dysbiosis) can lead to digestive issues, including acid reflux and increased stomach acid production. By supporting a healthy microbiome, L. acidophilus helps reduce the likelihood of these issues.
- Regulates Stomach Acid Production:
- L. acidophilus can help regulate the production of stomach acid. Overproduction of stomach acid is a primary factor in acidity and acid reflux. By balancing the gut flora and supporting optimal digestion, L. acidophilus may help ensure that the body produces the right amount of stomach acid, preventing excessive acid secretion that can lead to discomfort or acid reflux.
- Improves Gut Motility:
- Slow digestion or delayed gastric emptying can cause food to remain in the stomach for too long, which may lead to increased acid production and acid reflux. L. acidophilus promotes better gut motility (the movement of food through the digestive tract), which helps food move efficiently through the stomach and intestines. This reduces the chances of acid building up in the stomach and flowing into the esophagus, which can cause heartburn or acid reflux.
- Strengthens the Intestinal Barrier:
- A compromised gut barrier can allow stomach acid to move into areas where it shouldn’t, contributing to symptoms of acid reflux. L. acidophilus helps maintain the integrity of the gut lining, preventing the leakage of stomach acid and other harmful substances into the digestive tract, which helps reduce the risk of acidity and acid reflux.
- Reduces Inflammation:
- Inflammation in the stomach or esophagus, often caused by excess acid, can exacerbate acidity and heartburn. L. acidophilus has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce gut inflammation, soothing the digestive tract and preventing irritation that leads to acid reflux and discomfort.
- Supports the Digestive Process:
- L. acidophilus can help improve the breakdown and digestion of food, especially complex carbohydrates and proteins. When food is digested more efficiently, there is less likelihood of undigested food fermenting in the stomach and producing excess acid or gas, both of which contribute to acidity.
- Help with Lactose Intolerance:
- Some individuals with acidity may also have difficulty digesting dairy products, which can contribute to bloating and discomfort. L. acidophilus produces lactase, an enzyme that helps break down lactose. This can be especially helpful for people with lactose intolerance, reducing the symptoms of indigestion and preventing secondary acid reflux caused by undigested dairy.
- Supports the Digestive Enzymes:
- L. acidophilus helps promote the production of digestive enzymes that break down food more effectively. This can aid in the more efficient digestion of meals, reducing the likelihood of food fermenting in the stomach, producing excess gas, and contributing to acid reflux or bloating.
- Helps Prevent SIBO (Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth):
- One of the causes of bloating and acidity is Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO), where bacteria grow excessively in the small intestine. L. acidophilus helps maintain a healthy balance of bacteria throughout the gastrointestinal tract, which can prevent the development of SIBO and reduce symptoms such as bloating, acid reflux, and discomfort.
HOW CLOSTRIDIUM BUTYRICUM HELPS IN DIGESTION & DETOXIFICATION

- Promotes Gut Health and Digestion
- Production of Butyrate: One of the primary benefits of Clostridium butyricum is its ability to produce butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) that is essential for gut health. Butyrate serves as the main fuel for colonocytes (the cells lining the colon) and promotes a healthy and efficient digestive system.
- Improves gut barrier function: Butyrate helps strengthen the gut lining, preventing the leakage of harmful substances into the bloodstream (known as "leaky gut"), which can lead to inflammation and digestive discomfort.
- Supports healthy gut motility: Butyrate also enhances gut motility, aiding in the smooth movement of food through the digestive system, which is important for proper digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Helps with the Breakdown of Fiber: Clostridium butyricum is effective at fermenting certain dietary fibers, particularly those that are not easily digested by the human digestive system. This fermentation process produces butyrate and other SCFAs, which helps break down and digest food more efficiently.
- Reduces Inflammation in the Gut: Chronic inflammation in the gut can impair digestion and nutrient absorption. The production of butyrate by Clostridium butyricum has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce inflammation in the intestines, which can improve overall digestion and alleviate conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) or Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).
- Regulates Gut Microbiome: A healthy balance of gut bacteria is essential for optimal digestion. Clostridium butyricum helps maintain this balance by supporting the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria. This results in improved digestion, better nutrient absorption, and reduced gastrointestinal issues like bloating and indigestion.
- Supports Detoxification
- Gut-Liver Axis and Detoxification: The gut and liver are closely connected in the body's detoxification process. Clostridium butyricum supports detoxification by enhancing the gut-liver axis, which refers to the direct communication between the gut and the liver. By promoting a healthy gut microbiome and reducing gut inflammation, Clostridium butyricum can help the liver function more efficiently in detoxifying harmful substances from the body.
- Binding and Eliminating Toxins: Butyrate, the key SCFA produced by Clostridium butyricum, can bind to and neutralize certain toxins and waste products in the gut. This helps prevent the absorption of these harmful substances into the bloodstream and promotes their elimination through the stool. By doing so, Clostridium butyricum indirectly supports the body’s detoxification efforts.
- Supports Immune System Function: Detoxification is not just about eliminating toxins but also about supporting the body’s defense mechanisms. Clostridium butyricum has been shown to support immune function by improving the health of the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). Since a large portion of the immune system is located in the gut, this support can help the body more effectively eliminate toxins and pathogens.
- Helps Balance Inflammatory Markers: Inflammation can impair the body’s ability to detoxify, as it may hinder liver and kidney function, which are responsible for eliminating toxins. By reducing gut and systemic inflammation, Clostridium butyricum can support more effective detoxification processes throughout the body.
- Improves Nutrient Absorption
- Increased Absorption of Essential Nutrients: Clostridium butyricum helps maintain the integrity of the intestinal lining, which is essential for absorbing nutrients from food. By promoting healthy digestion, Clostridium butyricum ensures that essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and amino acids are properly absorbed and used by the body, improving overall health and supporting the detoxification process.
- Improves Gut pH: The fermentation of fibers by Clostridium butyricum produces butyrate, which lowers the pH of the gut. A lower pH is conducive to the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibits the growth of harmful microbes. This not only supports digestion but also helps maintain a healthy gut environment for effective detoxification.
- Potential Role in Reducing Toxic Load:
- Detoxification of Metabolic Waste: Clostridium butyricum aids in breaking down waste products and metabolic byproducts that can accumulate in the body and contribute to a toxic load. This detoxification process helps to reduce the strain on organs like the liver and kidneys, which are responsible for detoxifying the body.
HOW CLOSTRIDIUM BUTYRICUM HELPS IN MAINTAIN ENZYME BALANCE
Clostridium butyricum plays an important role in maintaining enzyme balance in the gut, which is essential for healthy digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall digestive system function.
- Supports the Production of Digestive Enzymes
- Butyrate Production: One of the primary benefits of Clostridium butyricum is its ability to produce butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) that has a key role in gut health. Butyrate helps maintain the health of the cells lining the gut (colonocytes), which are involved in the secretion and activity of digestive enzymes.
- Butyrate stimulates the production of specific enzymes involved in nutrient breakdown, which supports the efficient digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.
- The presence of butyrate can enhance the overall digestive process by ensuring that the gut cells are functioning optimally, leading to the production of necessary digestive enzymes.
- Regulates Enzyme Activity and Function
- Balance of Gut Enzymes: Clostridium butyricum helps balance the activity of digestive enzymes by ensuring that they are produced in the right amounts and at the right time. This prevents both underproduction and overproduction of enzymes, which can cause digestive issues.
- For example, it may help regulate enzymes such as amylases (which break down starches), lipases (which break down fats), and proteases (which break down proteins). An imbalance in these enzymes can lead to malabsorption, bloating, or discomfort.
- Clostridium butyricum also has a role in optimizing the function of enzymes in the small intestine and colon, promoting better digestion and absorption of nutrients.
- Enhances Carbohydrate Fermentation and Fiber Breakdown
- Fermentation of Fiber: Clostridium butyricum is involved in the fermentation of non-digestible fibers (found in plant-based foods), producing butyrate and other short-chain fatty acids. This process helps regulate the activity of digestive enzymes involved in the breakdown of carbohydrates and fibers in the gut.
- By enhancing the fermentation of fiber, Clostridium butyricum indirectly helps maintain enzyme balance, as it ensures that fiber is properly processed, reducing the strain on the digestive system and allowing for more efficient enzyme activity.
- The increase in butyrate production also helps optimize the activity of carbohydrate-digesting enzymes, ensuring that carbohydrates are efficiently broken down and absorbed.
- Promotes Gut Lining Integrity and Enzyme Function
- Gut Barrier Function: A healthy gut lining is essential for proper enzyme function. Clostridium butyricum helps maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier by nourishing gut epithelial cells with butyrate. A strong gut lining allows for proper secretion and activity of digestive enzymes.
- Without a healthy gut lining, digestive enzymes may not be released properly, leading to digestive issues such as bloating, gas, or malabsorption.
- Influences the Gut Microbiome to Support Enzyme Balance
- Gut Microbial Balance: The gut microbiome has a significant impact on enzyme production and activity. Clostridium butyricum helps maintain a healthy balance of beneficial gut bacteria, which in turn promotes the production of enzymes required for digestion.
- By reducing the abundance of harmful bacteria and promoting beneficial strains, Clostridium butyricum ensures that enzymes are produced in optimal quantities, supporting efficient digestion and absorption.
- The presence of healthy gut flora also promotes the activity of lactase, an enzyme that breaks down lactose, which can be particularly helpful for individuals who experience lactose intolerance or other enzyme-related digestive issues.
6. Regulates Enzyme Expression through Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
- SCFA Production and Enzyme Regulation: Butyrate and other SCFAs produced by Clostridium butyricum play a critical role in regulating the expression of enzymes in the gut. SCFAs influence the gene expression of gut cells involved in enzyme production.
- SCFAs, especially butyrate, can act on the gut's epithelial cells to stimulate the expression of enzymes involved in nutrient breakdown. This regulation helps maintain a balanced enzyme profile, promoting better digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Influences Enzyme Secretion in the Pancreas
- Pancreatic Enzyme Secretion: Clostridium butyricum, by promoting gut health and reducing inflammation, can influence the secretion of enzymes from the pancreas. The pancreas produces essential digestive enzymes like amylase, lipase, and trypsin, which are necessary for the digestion of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
- A healthy gut and balanced microbiome contribute to proper signaling in the gut-pancreas axis, ensuring that enzymes are secreted at the right time and in the correct amounts to aid digestion.
HOW CLOSTRIDIUM BUTYRICUM HELPS IN PROBIOTIC SUPPORT & REDUCES BLOATING

Clostridium butyricum is a beneficial probiotic bacterium that plays an important role in supporting gut health and reducing bloating. Here’s how it works:
- Produces Butyrate for Gut Health
- Butyrate Production: One of the primary benefits of Clostridium butyricum is its ability to produce butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) that is essential for maintaining gut health. Butyrate serves as the primary fuel for colonocytes, the cells that line the colon. It helps maintain a healthy gut barrier, reduces inflammation, and supports overall digestive function.
- By promoting the health of the gut lining, butyrate helps prevent intestinal permeability (also known as "leaky gut"), which can lead to bloating, discomfort, and digestive issues. When the gut barrier is compromised, bacteria and toxins can leak into the bloodstream, triggering inflammation and bloating. Butyrate helps prevent this by strengthening the gut lining.
- Supports a Healthy Gut Microbiome
- Balance of Gut Bacteria: Clostridium butyricum helps maintain a healthy balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which is crucial for overall digestive health. A balanced microbiome is essential for proper digestion and the efficient breakdown of food.
- Gut Dysbiosis (an imbalance in the gut microbiome) is often linked to bloating and discomfort. By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and reducing harmful bacteria, Clostridium butyricum supports a healthy microbial environment, reducing the chances of fermentation and gas buildup, which are common causes of bloating.
- Reduces Inflammation in the Gut
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Bloating is often caused or worsened by gut inflammation. Clostridium butyricum produces butyrate, which has powerful anti-inflammatory effects. Butyrate helps reduce intestinal inflammation, which can improve the gut’s ability to function efficiently and reduce bloating.
- By reducing inflammation in the gut, Clostridium butyricum helps calm the digestive tract and reduces the risk of bloating and other discomforts related to conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD).
- Improves Digestive Motility
- Gut Motility: Proper digestive motility is crucial for the smooth movement of food through the intestines. Slow motility can lead to the buildup of gas and undigested food in the stomach, contributing to bloating and discomfort.
- Clostridium butyricum promotes gut motility, helping food and gas move through the digestive tract more efficiently. This reduces the likelihood of bloating, as it helps prevent the accumulation of gas in the stomach or intestines.
- Ferments Fiber and Reduces Gas Production
- Fermentation of Fiber: Clostridium butyricum is involved in the fermentation of certain fibers that are not easily digested by the human body. This fermentation process produces butyrate and other short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which can help with nutrient absorption and reduce bloating.
- The fermentation of fiber also reduces the likelihood of gas buildup, as it helps break down undigested carbohydrates in the gut. When carbohydrates ferment in the gut without proper microbial breakdown, they can produce gas, leading to bloating and discomfort. Clostridium butyricum helps manage this process, reducing gas production.
- Helps Prevent Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO)
- SIBO Prevention: Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) is a condition where bacteria in the small intestine grow excessively, leading to symptoms like bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Clostridium butyricum helps maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the gut, preventing the overgrowth of harmful bacteria in the small intestine.
- By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and maintaining a balanced microbiome, Clostridium butyricum reduces the risk of SIBO and helps reduce bloating associated with it.
- Regulates Gas Production and Absorption
- Regulation of Gas: The healthy bacteria supported by Clostridium butyricum help regulate gas production in the gut. Excessive gas production is one of the primary causes of bloating. By promoting efficient fermentation and digestion of food, Clostridium butyricum reduces the likelihood of excessive gas production in the intestines.
- In addition, Clostridium butyricum helps improve the absorption of gas in the intestines. This ensures that the gas produced during digestion is absorbed into the bloodstream and exhaled, rather than accumulating in the digestive tract and causing bloating.
- Enhances Nutrient Absorption and Reduces Indigestion
- Better Digestion and Absorption: Clostridium butyricum helps improve the breakdown and absorption of nutrients in the intestines. Inefficient digestion can lead to undigested food particles in the gut, which may ferment and produce gas, leading to bloating.
- By improving digestion and nutrient absorption, Clostridium butyricum helps prevent indigestion and reduces the chances of gas buildup, both of which can contribute to bloating.
- Supports Healthy Immune Function
- Gut-Immune System Connection: A healthy gut microbiome plays a key role in immune function. Clostridium butyricum supports immune function by enhancing the health of the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), which is involved in immune responses.
- A properly functioning immune system helps prevent inflammation and other gut issues that can lead to bloating. By supporting the gut’s immune system, Clostridium butyricum indirectly helps reduce bloating and improve overall digestive health.
HOW CLOSTRIDIUM BUTYRICUM HELPS IN GERD,IBS & IBD MANAGEMENT

- Clostridium Butyricum and GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
GERD is a condition where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing symptoms like heartburn, chest pain, and regurgitation. Here’s how Clostridium butyricum can help manage GERD:
- Improves Gut Health and Barrier Function:
- Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by Clostridium butyricum, plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the intestinal lining. Butyrate strengthens the gut epithelial cells, which can help reduce gut permeability. By protecting the gut barrier, Clostridium butyricum may reduce the risk of acid reflux and inflammation in the esophagus, which are common in GERD.
- It also helps reduce the inflammation that often accompanies GERD by promoting a healthier microbiome and reducing gut irritation caused by acid.
- Supports Gut Motility:
- Proper motility (the movement of food through the digestive system) is crucial for preventing acid reflux. Clostridium butyricum can enhance motility in the gastrointestinal tract, which can help food and acid pass through the stomach more efficiently, reducing the chances of acid regurgitating into the esophagus.
- Balances Gut Microbiome:
- An imbalance in gut bacteria is often associated with GERD and other digestive disorders. Clostridium butyricum helps restore the balance between beneficial and harmful bacteria in the gut, which may indirectly reduce the occurrence of acid reflux by promoting overall digestive health.
- Clostridium Butyricum and IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
IBS is a chronic digestive condition that causes symptoms like bloating, abdominal pain, constipation, and diarrhea. Clostridium butyricum has several benefits for people with IBS:
- Reduces Inflammation in the Gut:
- Butyrate produced by Clostridium butyricum has strong anti-inflammatory effects, particularly in the gut. Inflammation is a significant contributor to IBS symptoms, and butyrate can help reduce it, alleviating discomfort associated with bloating and pain.
- Supports Gut Motility:
- IBS often involves irregular bowel movements (either constipation or diarrhea), which can be influenced by impaired gut motility. Clostridium butyricum helps regulate motility by enhancing the function of the intestinal muscles and ensuring proper food transit through the gut, which can help normalize bowel movements in IBS patients.
- Restores Microbiome Balance:
- Dysbiosis, or an imbalance of gut bacteria, is often seen in people with IBS. Clostridium butyricum helps restore a healthy gut microbiome, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and reducing the levels of harmful bacteria that can contribute to IBS symptoms.
- Relieves Gas and Bloating:
- One of the most common complaints in IBS is bloating and excessive gas. Clostridium butyricum promotes healthy digestion and fermentation of fiber, helping to reduce gas buildup and the uncomfortable bloating that often accompanies IBS.
- Improves Digestion and Absorption:
- By improving overall digestion and nutrient absorption, Clostridium butyricum can reduce the gastrointestinal discomfort often experienced by IBS patients. Better digestion leads to less undigested food fermenting in the gut, which helps reduce symptoms like gas, bloating, and abdominal discomfort.
- Clostridium Butyricum and IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease)
IBD, which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, is characterized by chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. Clostridium butyricum has shown promise in managing IBD through the following mechanisms:
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects:
- Butyrate, produced by Clostridium butyricum, has potent anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce the inflammation associated with IBD. Butyrate not only nourishes the colon cells but also inhibits the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, helping to reduce the inflammation in the intestines that causes the symptoms of IBD.
- Improves Gut Barrier Integrity:
- A compromised gut barrier is a hallmark of IBD. Clostridium butyricum enhances the integrity of the intestinal epithelial cells and strengthens the gut lining, helping to prevent the leakage of harmful substances into the bloodstream (a process called leaky gut). This is particularly important for IBD patients, as gut barrier dysfunction is associated with disease flares.
- Promotes Healing of the Intestinal Lining:
- In IBD, the gut lining is often damaged due to chronic inflammation. Butyrate plays a crucial role in promoting the healing of the intestinal lining. By supporting the growth and repair of the epithelial cells in the gut, Clostridium butyricum helps to reduce the damage caused by inflammation and promotes recovery from flare-ups.
- Reduces Symptoms of Diarrhea:
- Many IBD patients experience diarrhea due to inflammation in the intestines. By improving gut health and reducing inflammation, Clostridium butyricum can help control diarrhea episodes, providing relief from one of the most distressing symptoms of IBD.
- Supports Immune Function:
- Clostridium butyricum also plays a role in modulating the immune system. IBD is often linked to immune system dysfunction, where the body attacks its own tissues. By supporting a balanced immune response, Clostridium butyricum helps reduce the inflammatory response that contributes to the progression of IBD.
- Reduces Abdominal Pain and Discomfort:
- The anti-inflammatory properties of Clostridium butyricum help reduce the abdominal pain often experienced during IBD flare-ups. By soothing the intestinal inflammation and improving gut motility, it can alleviate discomfort associated with both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
HOW CLOSTRIDIUM BUTYRICUM HELPS IN ACIDITY

- Reduces Inflammation in the Gut
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Butyrate: Clostridium butyricum produces butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid that is highly beneficial for gut health. Butyrate helps to reduce inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, including the stomach and intestines. In conditions like acidity or acid reflux, inflammation of the esophagus or stomach lining can worsen symptoms. By reducing inflammation, Clostridium butyricum can alleviate the discomfort caused by acid-related conditions.
- Supports Gut Motility
- Improved Digestion and Transit: One of the causes of acidity can be impaired motility of the digestive tract, which leads to delayed gastric emptying and acid reflux. Clostridium butyricum helps to promote healthy gut motility, ensuring that food moves efficiently through the stomach and intestines. This can help prevent the backup of stomach contents into the esophagus (which leads to acid reflux) and improve digestion, reducing symptoms of acidity.
- Enhances Gut Barrier Function
- Strengthening the Intestinal Lining: Clostridium butyricum strengthens the gut lining by supporting the intestinal epithelial cells that form the protective barrier of the gut. This helps to prevent leaky gut, which can allow harmful substances to enter the bloodstream, causing inflammation and contributing to conditions like acid reflux or gastritis.
- By promoting a strong gut barrier, Clostridium butyricum reduces the risk of stomach acid irritating the esophagus or intestines, which can lead to acidity symptoms.
- Promotes Healthy pH Levels in the Gut
- Regulation of pH: The production of butyrate by Clostridium butyricum lowers the pH of the colon, which helps maintain an acidic environment in the lower parts of the digestive tract. This supports the balance of digestive enzymes and promotes overall digestive health.
- A balanced pH in the stomach is important because it ensures proper gastric acid secretion for digestion. However, if the stomach's acid production is either too low or too high, it can lead to discomfort, acid reflux, or indigestion. By supporting a healthy gut pH, Clostridium butyricum helps maintain digestive balance.
- Supports a Healthy Microbiome
- Balancing Gut Flora: Acidity and acid reflux are often linked to an imbalance in the gut microbiome. Clostridium butyricum helps to restore balance by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibiting harmful ones. A healthy microbiome supports the proper digestion of food, reducing the likelihood of fermentation and gas production, which can contribute to bloating, reflux, and acidity.
- Prevents Overgrowth of Harmful Bacteria: An overgrowth of harmful bacteria, such as Helicobacter pylori (linked to stomach ulcers and gastritis), can worsen symptoms of acidity. Clostridium butyricum helps regulate the growth of these harmful bacteria, reducing the chances of infection or imbalance that can lead to increased acid production and discomfort.
- Improves Digestion and Absorption
- Efficient Breakdown of Food: One of the causes of acidity can be poor digestion, where undigested food remains in the stomach too long, leading to acid production. Clostridium butyricum supports the breakdown of food, especially fiber, and enhances nutrient absorption. This helps reduce gastric acid buildup due to inefficient digestion, thus helping to relieve acid reflux and heartburn.
- Reduces Gastrointestinal Discomfort
- Relief from Bloating and Gas: Clostridium butyricum helps reduce bloating and excessive gas production by promoting proper digestion and fermentation of fiber. Excess gas can increase pressure in the stomach and lead to acid reflux or heartburn. By managing gas production, Clostridium butyricum helps reduce discomfort associated with acidity and reflux.
HOW LACTOBACILLUS RHAMNOSUS HELPS IN DIGESTION & DETOXIFICATION
- Supports Healthy Gut Flora
- Restores Balance in the Gut Microbiome: Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps maintain or restore a balanced gut microbiome, which is essential for proper digestion. It promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria and suppresses harmful bacteria that can lead to digestive issues like bloating, indigestion, or diarrhea. By supporting a healthy microbiome, Lactobacillus rhamnosus ensures that the gut operates efficiently, aiding in digestion.
- Enhances Nutrient Absorption
- Improves Nutrient Digestion and Absorption: By supporting the gut’s digestive enzymes, Lactobacillus rhamnosus enhances the breakdown and absorption of key nutrients from food, such as vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids. This ensures that the body receives adequate nourishment from the foods you eat, which is essential for overall health and well-being.
- Supports Digestive Enzyme Activity
- Stimulates Enzyme Production: Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps promote the activity of digestive enzymes, which are responsible for breaking down food particles in the stomach and intestines. This helps food move more smoothly through the digestive tract, reducing bloating, gas, and indigestion.
- It also enhances the activity of enzymes like lactase, which is important for people who may have difficulty digesting lactose. By improving enzyme production, Lactobacillus rhamnosus supports better digestion of dairy products and other foods.
- Aids in the Fermentation of Fiber
- Fermentation of Dietary Fiber: Lactobacillus rhamnosus contributes to the fermentation of dietary fiber in the gut, which produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate. Butyrate has several benefits for gut health, including supporting the gut lining, reducing inflammation, and maintaining a healthy pH in the colon. Proper fiber fermentation also helps improve stool consistency and bowel regularity.
- Enhances Detoxification Processes
- Toxin Removal: Lactobacillus rhamnosus can assist in the detoxification process by helping the body eliminate harmful substances. It may bind to toxins in the digestive tract, such as heavy metals or pathogens, and facilitate their removal. This detoxifying effect helps reduce the burden on the liver and other organs involved in detoxification.
- Supports Liver Function: A healthy gut microbiome, supported by probiotics like Lactobacillus rhamnosus, is linked to better liver health. The gut and liver are closely connected through the gut-liver axis, and a balanced gut microbiome can reduce the strain on the liver and help it detoxify more effectively.
- Reduces Gut Inflammation
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Lactobacillus rhamnosus produces lactic acid, which lowers the pH in the intestines, creating an environment where beneficial bacteria can thrive while harmful bacteria are suppressed. This helps reduce inflammation in the gut, which is often linked to digestive issues like bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
- Reducing gut inflammation is particularly helpful for those dealing with inflammatory conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), where inflammation can disrupt digestion and contribute to discomfort.
- Prevents Pathogenic Overgrowth
- Fights Harmful Bacteria: Lactobacillus rhamnosus competes with harmful bacteria and yeasts, like Candida, for space and nutrients in the gut. This helps prevent overgrowth of these harmful organisms, which can cause digestive disturbances and affect detoxification processes. By preventing the growth of pathogens, Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps maintain a healthy balance in the gut.
- Promotes Healthy Bowel Movements
- Regulates Bowel Function: Lactobacillus rhamnosus can help regulate bowel movements by improving gut motility, which ensures that food and waste products are moved through the digestive system efficiently. It can be particularly helpful for individuals with constipation, as it helps soften stool and promotes regularity. Healthy digestion and regular bowel movements support the body’s natural detoxification process by facilitating the elimination of waste products and toxins.
- Reduces Gas and Bloating
- Prevents Excess Gas Production: Bloating and excessive gas can result from inefficient digestion or fermentation of food in the gut. Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps improve the overall digestion process, reducing the likelihood of undigested food fermenting in the gut and producing gas. This helps reduce bloating and discomfort after meals, supporting a smoother digestion process.
- Supports Immune Function
- Boosts Immune System: A significant portion of the body’s immune system is located in the gut. Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps support immune function by stimulating the production of beneficial immune cells, such as IgA (Immunoglobulin A). A healthy immune system is essential for protecting the body from harmful invaders and supporting overall digestive health, including effective detoxification.
HOW LACTOBACILLUS RHAMNOSUS HELPS IN MAINTAIN ENZYME BALANCE

- Stimulates Digestive Enzyme Production
Lactobacillus rhamnosus can stimulate the production of digestive enzymes in the gut. These enzymes are essential for breaking down food and nutrients, allowing your body to absorb them more efficiently. For example, it has been shown to enhance the secretion of amylase (which breaks down starches) and lipase (which breaks down fats) in the digestive system.
By boosting enzyme production, Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps support the overall digestive process, improving the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and other nutrients.
- Enhances Lactase Activity
One of the specific enzymes Lactobacillus rhamnosus is known to affect is lactase, an enzyme responsible for breaking down lactose (milk sugar). Many people are lactose intolerant, meaning they don’t produce enough lactase to properly digest dairy products, leading to discomfort like bloating and gas.
By promoting lactase production, Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps those with lactose intolerance digest dairy more effectively, reducing the symptoms of discomfort that often accompany lactose consumption.
- Regulates the Balance of Gut Enzymes
Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps to regulate the balance between digestive enzymes, ensuring they are produced in the right amounts at the right time. When enzyme production is imbalanced, it can lead to digestive issues, such as malabsorption or fermentation of undigested food. By promoting proper enzyme regulation, Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps prevent these problems and supports smooth digestion.
- Increased efficiency in the breakdown of food: This leads to better absorption of nutrients and less undigested food left behind in the gut, which can cause gas, bloating, or discomfort.
- Promotes Enzyme Activity in the Small Intestine
Lactobacillus rhamnosus has a role in enhancing enzyme activity in the small intestine, which is where most digestion and nutrient absorption occur. By improving enzyme activity in this part of the digestive system, Lactobacillus rhamnosus ensures that carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are properly digested and absorbed before moving into the large intestine.
- Supports the Fermentation of Fiber and Carbohydrates
Lactobacillus rhamnosus also aids in the fermentation of fiber in the colon. Though this process is not directly related to digestive enzymes, it is connected to the overall digestive balance. Through fermentation, Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, which nourish the gut lining and help maintain a healthy pH in the intestines. This can indirectly support the proper functioning of digestive enzymes by keeping the environment in the gut healthy.
- Assists in the Breakdown of Proteins
Lactobacillus rhamnosus also helps with protein digestion. It produces proteases, enzymes that break down proteins into their constituent amino acids. These amino acids are crucial for various body functions, including muscle repair, immune support, and enzyme production. By aiding in protein digestion, Lactobacillus rhamnosus ensures that proteins are broken down efficiently and absorbed for use in the body.
- Reduces Enzyme Deficiencies
Certain digestive disorders, such as pancreatic insufficiency or IBS, can lead to enzyme deficiencies, which impair digestion and nutrient absorption. Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps in such cases by boosting the overall efficiency of digestion, compensating for enzyme deficiencies, and helping the body better process food, even when enzyme production is suboptimal.
- Balances Gut pH to Support Enzyme Function
By producing lactic acid, Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps maintain an acidic environment in the gut. This lower pH is essential for the optimal activity of digestive enzymes, as many digestive enzymes (like pepsin in the stomach) function best in acidic conditions. The acidic environment also helps prevent the overgrowth of harmful bacteria, ensuring that beneficial enzymes are able to work effectively
HOW LACTOBACILLUS RHAMNOSUS HELPS IN PROBIOTIC SUPPORT,REDUCES BLOATING

1. Probiotic Support and Gut Health
- Restores Gut Microbiome Balance:
One of the primary roles of Lactobacillus rhamnosus is to restore and maintain a healthy balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut. Our digestive system relies on a complex community of bacteria, and an imbalance, known as dysbiosis, can contribute to digestive issues, including bloating, gas, and discomfort. Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps to replenish the population of beneficial bacteria, ensuring that harmful bacteria, yeast (like Candida), or pathogens don’t overgrow and disrupt digestion. - Supports Gut Barrier Function:
Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier (the gut lining), preventing harmful substances and toxins from leaking into the bloodstream (a condition called leaky gut). A strong gut lining helps prevent inflammation and discomfort, which can often manifest as bloating, indigestion, and gas. - Enhances Immune Function in the Gut:
As part of the microbiome, Lactobacillus rhamnosus contributes to the function of the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), which plays a role in immune defense. A balanced immune system in the gut helps reduce the risk of infections and inflammation that can lead to bloating and other digestive discomforts.
- Reduction of Bloating
- Improves Digestion and Reduces Gas:
Bloating is often caused by undigested food fermenting in the gut, producing gas. Lactobacillus rhamnosus aids digestion by enhancing the breakdown of food, especially complex carbohydrates and proteins. It can help ensure that food is properly digested and absorbed in the small intestine, reducing the amount of undigested food that reaches the colon, where gas is produced by fermentation. - Reduces Excessive Gas Production:
By supporting the digestion of fiber and other carbohydrates, Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps prevent the overproduction of gas. When undigested carbohydrates ferment in the colon, they can produce excess gas, leading to bloating. The probiotic helps reduce the fermentation process by improving the efficiency of digestion, decreasing the amount of gas produced. - Balances Intestinal Motility:
Slow motility or irregular bowel movements can lead to bloating as food sits in the digestive tract for too long, giving bacteria more time to ferment it. Lactobacillus rhamnosus can help regulate intestinal motility, ensuring that food moves through the digestive tract at the right pace. This reduces the chances of bloating and discomfort caused by delayed digestion. - Promotes Healthy Fiber Fermentation:
Lactobacillus rhamnosus is involved in the fermentation of dietary fiber, which produces beneficial short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate. Butyrate has been shown to support a healthy gut lining, reduce inflammation, and contribute to the regulation of bowel movements. This process can help prevent the bloating that often occurs when there is an imbalance in the fermentation of fiber. - Reduces Inflammation:
Inflammation in the gut can contribute to bloating and discomfort. Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps reduce inflammation by modulating the immune response and producing metabolites like lactic acid that support a healthy gut environment. This can result in less bloating and discomfort associated with inflammatory conditions in the gut.
- Helps with Lactose Digestion
- Improves Lactose Digestion:
Bloating and gas can often be caused by lactose intolerance, where the body is unable to fully digest lactose (the sugar found in milk). Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps improve lactase activity, the enzyme that breaks down lactose. By enhancing the digestion of lactose, it can help reduce bloating, gas, and other symptoms in people who have mild to moderate lactose intolerance.
- Supports the Production of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds
- Butyrate and Other Metabolites:
As Lactobacillus rhamnosus ferments dietary fiber in the colon, it produces short-chain fatty acids like butyrate, which not only nourish the gut lining but also have anti-inflammatory effects. Reducing inflammation in the gut can significantly help with conditions that cause bloating and digestive discomfort, like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS).
- Relieves Symptoms of Digestive Disorders Linked to Bloating
- Helpful for IBS and Other Gut Disorders:
People suffering from IBS often experience bloating, gas, and cramping. Lactobacillus rhamnosus can be particularly beneficial for managing IBS symptoms by improving gut motility, reducing inflammation, and balancing the microbiome. Studies have shown that probiotics like Lactobacillus rhamnosus can reduce symptoms of bloating and discomfort associated with IBS.
- Prevents Overgrowth of Harmful Bacteria
Competitive Exclusion:
Lactobacillus rhamnosus competes with harmful bacteria, such as Clostridium and E. coli, for nutrients and space in the gut. This helps maintain a balance between good and bad bacteria. If harmful bacteria overgrow, they can produce gas and toxins that contribute to bloating. By maintaining a healthy balance, Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps reduce the overgrowth of these pathogenic bacteria, which in turn reduces bloating.
HOW LACTOBACILLUS RHAMNOSUS HELPS IN GERD,IBS & IBD MANAGEMENT

GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
- Restores Gut Microbiome Balance:
GERD is often linked to an imbalance in the gut microbiome, which can lead to issues like increased stomach acid production or poor digestion. Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps restore a healthy gut microbiome, reducing the overgrowth of harmful bacteria and promoting the growth of beneficial microorganisms. This balance can help reduce GERD symptoms like heartburn and acid reflux. - Reduces Inflammation:
GERD can lead to inflammation in the esophagus due to acid reflux, which causes pain and discomfort. Lactobacillus rhamnosus has anti-inflammatory properties and helps reduce inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. By modulating the immune system and promoting gut health, it can reduce the risk of esophageal inflammation, easing GERD symptoms. - Strengthens Gut Lining:
GERD is associated with damage to the esophageal lining due to repeated exposure to stomach acid. Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps to strengthen the gut lining by producing lactic acid, which supports the integrity of the intestinal walls. A strong gut lining prevents acid from damaging sensitive tissues in the esophagus and other parts of the digestive tract. - Improves Digestion and Reduces Gas:
Poor digestion can contribute to bloating and excess gas, which can exacerbate GERD symptoms. Lactobacillus rhamnosus supports proper digestion, ensuring that food is broken down efficiently and reducing the chances of fermentation and gas production in the stomach. This can help minimize bloating and discomfort associated with GERD.
2. IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
- Regulates Gut Motility:
One of the main symptoms of IBS is irregular bowel movements—either diarrhea, constipation, or alternating between the two. Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps regulate gut motility, ensuring that food moves through the intestines at a proper pace. By improving intestinal function, it helps prevent both diarrhea and constipation associated with IBS. - Reduces Inflammation and Pain:
IBS is often accompanied by gut inflammation, which contributes to pain and discomfort. Lactobacillus rhamnosus has anti-inflammatory effects that help reduce the inflammation in the intestines that causes abdominal cramping, bloating, and pain. By calming this inflammation, Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps alleviate these common symptoms of IBS. - Promotes Healthy Bowel Movements:
Lactobacillus rhamnosus supports regular bowel movements by improving the overall health of the digestive system. It can help increase the frequency of bowel movements in people who experience constipation and soften stools, which can relieve bloating and discomfort. - Balances Gut Microflora:
Dysbiosis (an imbalance of good and bad bacteria) is often present in people with IBS. Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps balance the microbiome by promoting beneficial bacteria and inhibiting harmful bacteria, which can trigger IBS symptoms. A balanced microbiome improves overall digestion and reduces bloating, gas, and discomfort. - Reduces Gas and Bloating:
Excess gas and bloating are common in IBS. Lactobacillus rhamnosus can help reduce these symptoms by supporting proper digestion, improving gut motility, and regulating fermentation processes in the gut. It reduces the likelihood of undigested food fermenting in the colon, which can lead to gas production and bloating.
3. IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease)
- Reduces Inflammation in the Gut:
IBD, which includes conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, is characterized by chronic inflammation in the digestive tract. Lactobacillus rhamnosus has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce the chronic inflammation in the intestines. By modulating the immune response, it helps reduce the symptoms of IBD, such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding. - Supports Gut Barrier Function:
IBD weakens the gut barrier, leading to an increased permeability of the intestines (often referred to as "leaky gut"). Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps support the integrity of the intestinal barrier, which can help prevent the passage of harmful substances into the bloodstream and reduce inflammation. A healthy gut lining is essential for managing IBD symptoms. - Balances the Immune System:
IBD is often triggered or worsened by an overactive immune response. Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps regulate the immune system in the gut, preventing excessive inflammation and helping to manage IBD flare-ups. By balancing the immune response, it can reduce both the frequency and severity of symptoms. - Promotes Gut Healing:
In IBD, the digestive tract may suffer from ulcers or other forms of damage. Lactobacillus rhamnosus produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, which are essential for the health of intestinal cells and promote gut healing. These SCFAs support the regeneration of intestinal cells and reduce inflammation, contributing to the overall healing process in IBD. - Supports Nutrient Absorption:
One of the challenges with IBD is the impaired absorption of nutrients due to inflammation and gut damage. Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps improve the absorption of essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and amino acids, by enhancing the digestive process and reducing inflammation in the intestines.
IN SHORT USE - Summary of Benefits for GERD, IBS, and IBD:
- GERD:
- Restores gut microbiome balance
- Reduces gut inflammation
- Strengthens the gut lining
- Improves digestion and reduces gas
- IBS:
- Regulates gut motility
- Reduces inflammation and pain
- Promotes healthy bowel movements
- Balances gut flora and reduces gas/bloating
- IBD:
- Reduces chronic inflammation in the gut
- Supports gut barrier integrity
- Modulates immune response to prevent flare-ups
- Promotes gut healing and nutrient absorption
HOW LACTOBACILLUS RHAMNOSUS HELPS IN ACIDITY
Lactobacillus rhamnosus can be helpful in managing acidity or acid reflux, though it doesn't directly reduce stomach acid levels like antacids. Instead, it helps through a combination of mechanisms that promote overall digestive health, reduce inflammation, and support gut function.
1. Restores Gut Microbiome Balance
Acidity or acid reflux can be linked to an imbalance in the gut microbiome, where harmful bacteria may overgrow and contribute to digestive issues. Lactobacillus rhamnosus, as a probiotic, helps restore a healthy balance of good bacteria in the gut. This balance is crucial for preventing gastrointestinal disturbances, including those that may lead to increased acidity or acid reflux. By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, it helps manage the root causes of acidity.
2. Improves Digestion and Reduces Gas Production
Acidity and acid reflux can often result from poor digestion or delayed gastric emptying, which causes food and stomach acids to linger in the stomach or flow back into the esophagus. Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps improve digestion by supporting the production and activity of digestive enzymes, ensuring food is broken down efficiently and moves through the digestive tract without causing excessive fermentation or gas buildup. Reduced gas production leads to less bloating, which can alleviate some of the discomfort that often accompanies acidity.
3. Supports Healthy Gut Motility
Acidity can also be worsened by slow gut motility (or delayed gastric emptying), which can cause food and stomach acids to stay in the stomach for longer than necessary. Lactobacillus rhamnosus can help regulate gut motility, ensuring that food moves through the stomach and intestines at the right pace. This reduces the likelihood of acid reflux, where stomach acid moves into the esophagus, causing a burning sensation (heartburn).
4. Reduces Inflammation
Chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract can contribute to conditions like acid reflux and gastritis. Lactobacillus rhamnosus has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce gut inflammation, particularly in the stomach lining and esophagus. By lowering inflammation, it can help reduce the symptoms of acidity and prevent further irritation or damage to the stomach lining and esophagus.
5. Strengthens the Gut Lining
A strong, healthy gut lining is essential for protecting the stomach and intestines from excess acid. Lactobacillus rhamnosus supports the integrity of the intestinal barrier by producing lactic acid, which lowers the pH in the gut and fosters an environment where beneficial bacteria can thrive while harmful pathogens are suppressed. A robust gut lining reduces the risk of acid damage and may help reduce symptoms associated with acidity.
6. Improves Lactose Digestion
Lactose intolerance can lead to bloating and discomfort that may be mistaken for acid reflux or indigestion. Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps improve the digestion of lactose by promoting the activity of lactase, the enzyme that breaks down lactose. This can reduce the bloating and discomfort associated with dairy consumption, which may be mistaken for or exacerbate acidity symptoms.
7. Helps with Gastric Health and Prevents Overgrowth of Harmful Bacteria
An overgrowth of harmful bacteria, such as Helicobacter pylori (a bacteria linked to ulcers), can contribute to increased stomach acid and irritation of the stomach lining. Lactobacillus rhamnosus helps prevent the overgrowth of harmful bacteria and promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria, which supports healthy gastric function. This can reduce symptoms of acid reflux and gastritis by ensuring that the stomach environment remains balanced.
8. Reduces Stress and Anxiety
Stress is a known trigger for acid reflux and acidity, as it can lead to the overproduction of stomach acid. Lactobacillus rhamnosus has been shown to have a positive impact on mental health by modulating the gut-brain axis. It helps reduce the stress response in the body, which in turn may help decrease stress-induced acid reflux or increased acidity.
HOW LACTOBACILLUS SPOROGENES HELPS IN DIGESTION AND DETOXIFICATION
Lactobacillus sporogenes is a beneficial probiotic that plays a significant role in promoting digestion and detoxification in the body. This strain of Lactobacillus offers multiple health benefits, particularly by supporting a healthy gut microbiome, improving nutrient absorption, and helping the body eliminate toxins.
1. Supports Gut Microbiome Balance
Lactobacillus sporogenes helps maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria. A balanced microbiome is essential for optimal digestion because it promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria while suppressing harmful bacteria. When the gut is healthy, digestion functions more efficiently, and harmful microorganisms, which can produce toxins, are kept in check.
By supporting a balanced microbiome, Lactobacillus sporogenes helps to improve overall digestive function and prevent disruptions that could lead to issues like constipation, bloating, and indigestion.
2. Enhances Digestion and Nutrient Absorption
Lactobacillus sporogenes helps with the breakdown of food in the digestive tract, making it easier for your body to absorb nutrients. It enhances the activity of digestive enzymes, which are essential for breaking down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into smaller, absorbable components. When digestion is efficient, the body can better utilize the nutrients from food, promoting overall health.
Additionally, this probiotic helps digest complex carbohydrates and fiber in the colon, ensuring that there is minimal undigested food left to ferment, which could otherwise lead to bloating, discomfort, or irregular bowel movements.
3. Produces Lactic Acid
Lactobacillus sporogenes produces lactic acid as a byproduct of fermentation. This helps lower the pH in the intestines, creating an acidic environment that is favorable for the growth of beneficial bacteria while inhibiting the growth of pathogenic microorganisms. The low pH also aids in digestion by stimulating the production of stomach acid, which is necessary for the breakdown of proteins and other nutrients.
In addition, lactic acid helps maintain a healthy gut lining, supporting the integrity of the intestinal barrier, which is essential for proper digestion and absorption.
4. Detoxifies the Body by Supporting the Liver and Gut
Lactobacillus sporogenes plays an indirect role in detoxification by supporting the liver and digestive system:
- Improves Liver Function: The liver is the body's primary detoxification organ, processing toxins, waste products, and chemicals. Lactobacillus sporogenes may support liver health by promoting a healthier gut environment and improving the absorption of essential nutrients that help the liver detoxify more efficiently.
- Enhances Toxin Removal: A healthy gut is critical for eliminating toxins from the body, particularly those that enter the intestines from the food we eat or are produced during metabolism. Lactobacillus sporogenes helps improve intestinal motility, which promotes regular bowel movements and helps expel waste products and toxins from the digestive tract. By facilitating the removal of waste, it supports the detoxification process.
5. Reduces Inflammation in the Gut
Chronic inflammation in the gut can contribute to digestive problems and hinder the body's ability to properly detoxify. Lactobacillus sporogenes has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce gut inflammation, which can improve overall digestion and support the natural detoxification process. Inflammation often disrupts nutrient absorption and can lead to the overgrowth of harmful bacteria that may produce toxins. By reducing inflammation, Lactobacillus sporogenes helps maintain a healthier gut environment, supporting both digestion and detoxification.
6. Supports Healthy Bile Production
Bile is essential for the digestion of fats and the removal of certain waste products and toxins from the body. Lactobacillus sporogenes may help support healthy bile production by improving the gut environment, which in turn enhances fat digestion and the removal of fat-soluble toxins. Better bile production also aids in the digestion and absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (such as A, D, E, and K), which are vital for overall health.
7. Promotes Regular Bowel Movements
Lactobacillus sporogenes helps regulate intestinal motility, promoting regular bowel movements. Regular bowel movements are essential for eliminating waste products and toxins from the body. Without proper elimination, toxins can accumulate, leading to discomfort and potentially affecting overall health. By supporting a healthy digestive transit time, Lactobacillus sporogenes aids in the expulsion of waste, preventing constipation and promoting detoxification.
8. Detoxifies through Gut-Brain Axis Interaction
Lactobacillus sporogenes, like many probiotics, can influence the gut-brain axis, which links gut health to mental and emotional well-being. By helping regulate gut function and reducing systemic inflammation, Lactobacillus sporogenes indirectly aids in detoxifying the body by supporting overall health and reducing stress-related digestive issues. Stress and anxiety can impair digestion and detoxification, but by helping maintain a healthy gut, Lactobacillus sporogenes supports a calm and efficient digestive system, aiding detoxification.
9. Produces Beneficial Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
Lactobacillus sporogenes, as part of its fermentation process, produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, acetate, and propionate. These SCFAs provide several benefits for digestion and detoxification:
- Butyrate is particularly beneficial for gut health as it nourishes the cells of the gut lining, reducing inflammation and promoting a healthy gut barrier. It also plays a role in regulating immune function and detoxifying the body by supporting the elimination of toxins.
- Acetate and propionate also support gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibiting harmful bacteria, helping to maintain a balanced microbiome.
HOW LACTOBACILLUS SPOROGENES HELPS IN MAINTAIN ENZYME BALANCE

- Enhances Digestive Enzyme Production
Lactobacillus sporogenes plays a role in the overall digestive process by supporting the production of digestive enzymes. It helps stimulate the release of enzymes from the pancreas and intestinal cells that are responsible for breaking down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. By enhancing enzyme activity, Lactobacillus sporogenes ensures that food is properly digested, and nutrients are absorbed efficiently.
- Carbohydrases: These enzymes break down carbohydrates. Lactobacillus sporogenes can help balance the activity of these enzymes, ensuring effective digestion of starches, sugars, and other carbohydrates.
- Proteases: These enzymes break down proteins into amino acids. By promoting the secretion of proteases, Lactobacillus sporogenes ensures that proteins are adequately broken down for absorption.
- Lipases: These enzymes help digest fats. Lactobacillus sporogenes can improve the breakdown of fats, making them easier to absorb and utilize by the body.
- Supports Enzyme Activity in the Small Intestine
Lactobacillus sporogenes also helps maintain the enzyme balance in the small intestine, where a large portion of nutrient absorption occurs. The probiotics support the enzymatic breakdown of food, ensuring that nutrients are absorbed efficiently and reducing the chance of undigested food reaching the colon, which could lead to fermentation, bloating, or gas production.
- It can enhance the activity of brush-border enzymes (enzymes on the surface of intestinal cells), such as lactase (which breaks down lactose), maltase, and sucrase, that help break down disaccharides into simpler sugars for absorption.
- By improving the activity of these enzymes, Lactobacillus sporogenes supports the digestion of complex carbohydrates and other macronutrients, making the digestive process smoother and more effective.
- Reduces the Load on Digestive Enzymes
In cases of digestive distress or enzyme deficiencies, Lactobacillus sporogenes can relieve stress on the digestive system by improving the overall gut environment. When the gut microbiome is balanced, harmful bacteria or pathogens are less likely to overproduce gas-producing byproducts that could overwhelm digestive enzymes. A well-balanced gut microbiome improves enzyme activity by reducing the burden on these enzymes, allowing them to function more efficiently.
- Improved gut motility: Lactobacillus sporogenes promotes healthy motility of food through the digestive tract, which helps enzymes work at optimal efficiency. By maintaining appropriate transit time for food, it prevents enzyme overload or inefficiency due to delayed digestion.
- Supports Pancreatic Enzyme Secretion
The pancreas produces important digestive enzymes (amylase, lipase, proteases), which are necessary for breaking down food. Lactobacillus sporogenes can help maintain pancreatic function, ensuring that the pancreas releases these enzymes in adequate amounts. This support is particularly important for individuals with compromised digestion, as insufficient pancreatic enzyme secretion can result in poor nutrient absorption and gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Boosts Microbial Enzyme Production
As a probiotic, Lactobacillus sporogenes also helps produce beneficial enzymes itself through fermentation. This production of microbial enzymes aids in breaking down complex compounds in the gut, such as fiber, complex carbohydrates, and proteins. These enzymes further support digestion by reducing the need for the body to produce excess enzymes on its own. As a result, the digestive system functions more smoothly, with a balanced enzyme output that helps break down food more efficiently.
- Aids in Lactose Digestion
Lactose intolerance is caused by a lack of the enzyme lactase, which breaks down lactose (the sugar in milk) in the small intestine. Lactobacillus sporogenes can help improve lactose digestion by promoting the activity of lactase. In this way, it can help individuals with mild lactose intolerance by ensuring that lactose is broken down properly, reducing symptoms like bloating, gas, and discomfort.
- Improves Fiber Fermentation and SCFA Production
Lactobacillus sporogenes helps digest fiber and other complex carbohydrates in the colon by producing enzymes that ferment fiber into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as butyrate, acetate, and propionate. These SCFAs are essential for gut health because they:
- Nourish gut cells and support the intestinal lining.
- Help regulate pH in the colon, creating an environment that supports healthy bacteria.
- Promote the absorption of minerals like calcium, magnesium, and iron.
- Butyrate, in particular, also has anti-inflammatory effects and supports overall gut health.
- Regulates Enzyme Balance During Stress
Stress can disrupt digestion and enzyme production, leading to inefficiencies like slow digestion, acid reflux, or bloating. Lactobacillus sporogenes has been shown to positively affect the gut-brain axis, helping to reduce stress and its negative effects on digestion. By promoting a balanced microbiome and reducing gut inflammation, Lactobacillus sporogenes helps maintain a steady enzyme balance even during stressful conditions.
HOW LACTOBACILLUS SPOROGENES HELPS IN PROBIOTIC SUPPORT & REDUCES BLOATING

- Restores Balance in Gut Microflora
Lactobacillus sporogenes helps restore balance to the gut microbiome, which is essential for overall digestive health. An imbalance in gut bacteria (known as dysbiosis) can lead to overgrowth of harmful bacteria that produce gases, causing bloating, discomfort, and digestive distress. By increasing the population of beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus sporogenes, it helps to suppress the growth of harmful microbes that are responsible for producing excess gas and toxins. This balance promotes healthier digestion, reducing the symptoms of bloating.
- Improves Digestion and Nutrient Absorption
Lactobacillus sporogenes aids in breaking down food more efficiently. When food is properly digested, it prevents undigested food particles from fermenting in the gut, which is a common cause of bloating and gas production. Lactobacillus sporogenes also helps produce digestive enzymes, which further facilitate the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. This efficiency in digestion helps prevent gas buildup, which is often a contributing factor to bloating.
- Reduces Fermentation and Gas Production
When food sits undigested in the intestines, it begins to ferment, producing gases that can cause discomfort and bloating. Lactobacillus sporogenes helps accelerate the digestion process, reducing the time food remains in the digestive system and preventing excessive fermentation. By improving the overall gut environment and encouraging more efficient digestion, it helps prevent the overproduction of gas that can lead to bloating.
- Regulates Gut Motility
Gut motility refers to the movement of food through the digestive system. Slow motility can cause food to remain in the stomach or intestines for longer periods, leading to gas buildup and bloating. Lactobacillus sporogenes helps support healthy gut motility, ensuring that food moves through the digestive tract at the right pace. This regulation of gut motility helps reduce the risk of constipation, sluggish digestion, and bloating.
- Improves Lactose Digestion
Lactose intolerance, which is the inability to digest lactose (the sugar found in milk), often leads to bloating and gas production when dairy is consumed. Lactobacillus sporogenes produces lactase, the enzyme that breaks down lactose into simpler sugars that can be absorbed. By promoting lactose digestion, Lactobacillus sporogenes reduces the uncomfortable bloating and gas that many people with lactose intolerance experience.
- Supports Healthy Bile Production
Bile is necessary for the digestion and absorption of fats. Lactobacillus sporogenes supports healthy bile production in the liver and gallbladder. When bile is produced in the right amount, fats are properly digested and absorbed, reducing the likelihood of undigested fat causing bloating or discomfort in the gut. A better-digested fat also reduces fermentation and subsequent gas formation, contributing to less bloating.
- Alleviates Gut Inflammation
Inflammation in the gut can lead to gaseous bloating, abdominal discomfort, and other digestive issues. Lactobacillus sporogenes has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract. By calming inflammation, it helps improve gut health and reduces bloating associated with conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), gastritis, or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Supports the Gut-Brain Axis
Stress and anxiety are known to exacerbate digestive issues, including bloating. The gut-brain axis is the connection between the digestive system and the brain, meaning that stress can negatively affect gut function and contribute to bloating. Lactobacillus sporogenes has been shown to influence the gut-brain axis, promoting a more balanced and calm digestive system. By reducing stress and supporting mental well-being, it can help reduce stress-induced bloating and digestive discomfort.
- Prevents Overgrowth of Harmful Bacteria
Harmful bacteria in the gut can produce gases and toxins during digestion, contributing to bloating. Lactobacillus sporogenes helps maintain a healthy bacterial balance by inhibiting the growth of pathogenic or harmful bacteria. By creating an environment where beneficial bacteria thrive, it reduces the likelihood of harmful bacteria proliferating and producing gas or toxins, thereby reducing bloating.
- Improves Short-Chain Fatty Acid (SCFA) Production
Lactobacillus sporogenes also contributes to the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as butyrate, acetate, and propionate. These SCFAs play a crucial role in gut health by:
- Providing energy to colon cells.
- Supporting a healthy gut lining, preventing intestinal permeability or "leaky gut."
- Modulating the gut’s pH, creating an environment that is less conducive to gas-producing bacteria.
SCFAs also help reduce inflammation and improve digestion, both of which can help alleviate bloating.
HOW LACTOBACILLUS SPOROGENES HELPS IN GERD,IBS AND IBD MANAGEMENT

1. GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
GERD is characterized by the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, causing symptoms like heartburn, regurgitation, chest pain, and bloating. Lactobacillus sporogenes can help manage GERD in several ways:
a. Restores Gut Microbiome Balance
An imbalance in gut bacteria can contribute to GERD by promoting inflammation and impairing digestion. Lactobacillus sporogenes helps restore the balance of good bacteria in the gut. By supporting the growth of beneficial bacteria, it reduces the growth of harmful microbes that may contribute to increased acid production or gastrointestinal distress. A healthy microbiome helps maintain normal digestive function and minimizes symptoms like acid reflux.
b. Improves Digestive Function
Lactobacillus sporogenes improves overall digestion, particularly the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Efficient digestion reduces the risk of acid build-up in the stomach, which can lead to reflux. By optimizing the digestive process, it helps prevent the conditions that exacerbate GERD, such as slow gastric emptying or bloating.
c. Reduces Gut Inflammation
GERD is often associated with inflammation in the stomach and esophagus, which can aggravate acid reflux symptoms. Lactobacillus sporogenes has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract, including the stomach lining and esophagus. By calming inflammation, it helps alleviate GERD-related discomfort.
d. Improves Gut Motility
Lactobacillus sporogenes helps regulate gut motility, ensuring that food moves through the stomach and intestines at an appropriate pace. Slow motility can lead to delayed gastric emptying, increasing the risk of reflux. By promoting healthy motility, Lactobacillus sporogenes helps prevent the backflow of stomach contents into the esophagus, reducing GERD symptoms.
2. IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
IBS is a functional gastrointestinal disorder that causes symptoms like bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and/or constipation. Lactobacillus sporogenes offers several benefits in managing IBS:
a. Restores Gut Flora Balance
An imbalance in gut bacteria is often linked to IBS symptoms. Dysbiosis (an imbalance of harmful and beneficial bacteria) can lead to increased gas production, bloating, and gut inflammation. Lactobacillus sporogenes helps restore a healthy microbiome by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and suppressing the growth of harmful bacteria. This restores balance and can help reduce IBS symptoms, including bloating and gas.
b. Reduces Gut Inflammation
IBS is frequently associated with low-grade inflammation in the gut, which can contribute to abdominal pain and discomfort. Lactobacillus sporogenes has anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce inflammation in the intestines. This helps calm the gut and alleviate symptoms such as cramping, bloating, and discomfort that are common in IBS.
c. Improves Digestive Health
Lactobacillus sporogenes enhances the overall digestive process by improving the breakdown and absorption of nutrients. When digestion is more efficient, there is less undigested food available to ferment in the gut, which can cause bloating, gas, and discomfort. This improvement in digestion helps to prevent these IBS-related symptoms.
d. Regulates Bowel Movements
For individuals with IBS, irregular bowel movements (either diarrhea or constipation) are common. Lactobacillus sporogenes helps regulate bowel motility, ensuring that food moves through the digestive system at the right pace. By supporting regular bowel movements, it helps prevent both diarrhea and constipation, common symptoms of IBS.
e. Helps Manage Stress and Anxiety
IBS is often aggravated by stress, as the gut-brain axis links emotional stress with digestive health. Lactobacillus sporogenes has been shown to positively influence the gut-brain axis, reducing the stress response in the body. By promoting a more balanced and calm digestive system, it can help reduce stress-induced IBS flare-ups.
3. IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease)
IBD, which includes conditions like Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative Colitis, is characterized by chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. Lactobacillus sporogenes can aid in managing IBD in the following ways:
a. Reduces Intestinal Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of IBD. Lactobacillus sporogenes has anti-inflammatory effects that can help reduce inflammation in the gut lining. By suppressing inflammatory markers and promoting a healthier gut environment, it helps alleviate the pain, cramping, and discomfort that are common in IBD.
b. Promotes Gut Healing
Lactobacillus sporogenes supports the integrity of the intestinal barrier, which is often compromised in IBD. By strengthening the gut lining, it helps prevent intestinal permeability (often referred to as "leaky gut"), which is a common issue in IBD. This helps protect the digestive tract from further damage and supports healing.
c. Supports Immune Function
IBD involves an overactive immune response that attacks the digestive tract. Lactobacillus sporogenes helps modulate the immune system by supporting a balanced immune response in the gut. It can help reduce the overactive immune reaction, which may alleviate symptoms of IBD and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
d. Improves Gut Microbiome
A disrupted gut microbiome is linked to the development and progression of IBD. Lactobacillus sporogenes helps restore a healthy microbiome by encouraging the growth of beneficial bacteria and suppressing harmful bacteria. This balance supports gut health, reduces inflammation, and may contribute to the long-term management of IBD.
e. Enhances Digestion and Nutrient Absorption
In IBD, digestive function can be impaired, leading to malabsorption of nutrients and weight loss. Lactobacillus sporogenes improves overall digestion by promoting efficient nutrient breakdown and absorption. This helps ensure that the body receives essential nutrients, which is particularly important for individuals with IBD, who may struggle with nutrient deficiencies.
HOW LACTOBACILLUS SPOROGENES HELPS IN ACIDITY

1. Promotes Healthy Gut Microbiome
Acidity and acid reflux are often associated with an imbalance in the gut microbiome, known as dysbiosis. Dysbiosis can contribute to inflammation in the gut and disrupt normal digestion. Lactobacillus sporogenes is a beneficial probiotic that helps restore a healthy balance of good bacteria in the gut. By improving gut flora, it can reduce the growth of harmful bacteria that can contribute to excess acid production or irritate the stomach lining, thereby helping to maintain a normal pH level and reducing acidity.
2. Supports Healthy Digestion
Lactobacillus sporogenes aids in the efficient digestion of food, particularly proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. When digestion is slow or inefficient, food can remain in the stomach longer, which increases the likelihood of acid buildup and reflux. By improving the overall digestive process, Lactobacillus sporogenes helps reduce the likelihood of undigested food remaining in the stomach, thus preventing the overproduction of gastric acid. This can help alleviate gastritis and acid reflux symptoms.
3. Regulates Stomach pH
Lactobacillus sporogenes supports the production of lactic acid in the gut, which helps to maintain an optimal acidic environment in the stomach. When the stomach's acid level is balanced, it ensures proper digestion and reduces the chances of acid backing up into the esophagus, which causes acid reflux. In addition, the lactic acid helps promote a healthy gut lining, protecting it from damage that could lead to ulcers or irritation caused by excess stomach acid.
4. Reduces Gastric Inflammation
Excess acidity can lead to gastritis, an inflammation of the stomach lining, causing discomfort and pain. Lactobacillus sporogenes has anti-inflammatory properties that can help soothe the stomach lining and reduce inflammation. By reducing this inflammation, Lactobacillus sporogenes can help ease the discomfort caused by acidity and promote better stomach health.
5. Regulates Gastric Emptying
Slow gastric emptying can contribute to acidity, as food remains in the stomach longer, leading to acid reflux and bloating. Lactobacillus sporogenes helps support healthy gastric motility, ensuring that food moves through the digestive system at an appropriate pace. By preventing delayed gastric emptying, it helps reduce acid buildup and minimize the chances of acid reflux.
6. Supports the Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES) Function
The lower esophageal sphincter (LES) is a muscle that prevents stomach acid from flowing backward into the esophagus. Dysfunction of the LES is often associated with acid reflux and heartburn. Lactobacillus sporogenes may help maintain the health and function of the LES, ensuring that it remains tightly closed after food passes into the stomach. This reduces the chances of acid escaping into the esophagus and causing heartburn or discomfort.
7. Balances the Gut-Brain Axis
Stress and anxiety are common triggers for acidity and acid reflux. The gut-brain axis links emotional stress with digestive function. Lactobacillus sporogenes has been shown to positively influence the gut-brain axis, reducing the stress response and promoting a more relaxed digestive system. By managing stress and improving gut health, it can reduce the occurrence of acid reflux and the symptoms of acidity.
8. Reduces the Growth of Pathogenic Bacteria
Certain harmful bacteria in the gut, like Helicobacter pylori, are known to contribute to excess stomach acid and even lead to ulcers. Lactobacillus sporogenes helps maintain a healthy gut microbiome by inhibiting the growth of these harmful bacteria, which can reduce the risk of acid overproduction and related digestive issues like gastritis and acid reflux.
9. Supports Healthy Bile Secretion
Bile is important for the digestion and absorption of fats. Lactobacillus sporogenes helps regulate bile secretion, which supports the digestion of fats and reduces the likelihood of fatty acids causing acid reflux. When bile is properly secreted and utilized, it helps neutralize excess stomach acid and supports proper digestion, thus reducing acidity-related symptoms.
HOW BIFIDOBACTERIUM BIFIDUM HELPS IN DIGESTION AND DETOXIFICATION

Bifidobacterium bifidum is a beneficial probiotic that plays a crucial role in digestion and detoxification. It is one of the first bacteria to colonize the intestines in newborns and remains essential for maintaining gut health throughout life
- Improves Digestive Efficiency
Bifidobacterium bifidum helps enhance the breakdown and absorption of nutrients from food. It does this by producing enzymes that break down complex carbohydrates, fibers, and other nutrients that the human digestive system alone may not fully process. These enzymes help ferment fibers and oligosaccharides, allowing them to be broken down into smaller, more digestible components that the body can absorb more easily. This reduces undigested food in the gut, which can otherwise lead to discomfort, bloating, or poor nutrient absorption.
- Carbohydrate digestion: It helps break down certain carbohydrates, including complex sugars, into simpler sugars, improving overall digestive efficiency.
- Fiber fermentation: It ferments dietary fiber, which not only supports digestion but also produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as butyrate, which are beneficial for gut health.
- Balances Gut Microflora
Bifidobacterium bifidum contributes to the balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut, preventing the overgrowth of harmful bacteria and pathogens. A balanced microbiome is essential for proper digestion, as an imbalance can lead to conditions like dysbiosis (microbial imbalance) that may impair digestion. By promoting the growth of good bacteria and inhibiting harmful microorganisms, it helps maintain a healthy gut environment, which optimizes digestion and reduces symptoms like bloating, gas, and indigestion.
- Reduces Gas and Bloating
Bifidobacterium bifidum helps reduce gas production and bloating by improving the breakdown of food in the gut. When food is not properly digested, it ferments in the intestines, producing gas. By enhancing digestive efficiency, Bifidobacterium bifidum reduces the amount of undigested food that ferments in the gut, thus reducing gas production and bloating. This can help alleviate the discomfort associated with poor digestion and digestive disturbances.
- Enhances Lactose Digestion
For individuals with lactose intolerance, Bifidobacterium bifidum can help digest lactose, the sugar found in milk and dairy products. It produces lactase, the enzyme that breaks down lactose into simpler sugars, making it easier for individuals with lactose intolerance to digest dairy without experiencing symptoms like bloating, gas, or diarrhea.
- Supports Detoxification Processes
Bifidobacterium bifidum aids in detoxification by supporting the elimination of toxins from the gut and promoting the health of the liver, which plays a central role in detoxifying the body. By maintaining a healthy gut lining and promoting efficient digestion, it helps prevent the absorption of harmful substances from the digestive tract into the bloodstream.
- Metabolizing harmful substances: Bifidobacterium bifidum helps break down potentially harmful substances in food or the gut, such as toxins, excess bile acids, and ammonia. It prevents these substances from building up and potentially causing harm to the body.
- Supporting liver function: A healthy gut microbiome supported by Bifidobacterium bifidum can help improve liver function, as the liver is responsible for filtering toxins from the blood. A healthy gut reduces the toxic load on the liver, assisting the body in more efficient detoxification.
- Enhances Immune Function
The gut is a major player in immune function, and Bifidobacterium bifidum supports the immune system by modulating the gut's immune response. A healthy immune system is essential for detoxification, as it helps identify and eliminate harmful substances from the body. Bifidobacterium bifidum helps regulate the activity of the immune cells in the gut and strengthens the gut barrier, which prevents harmful pathogens from entering the bloodstream.
- Reduces Inflammation
Inflammation in the gut can interfere with proper digestion and detoxification. Bifidobacterium bifidum has anti-inflammatory effects, which help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract. By calming gut inflammation, it ensures better digestion, nutrient absorption, and detoxification. Reduced inflammation also contributes to better gut health overall, which is essential for long-term digestive wellness and effective detoxification.
- Supports Healthy Bowel Movements
Bifidobacterium bifidum promotes regular and healthy bowel movements by supporting gut motility (the movement of food through the intestines). This is crucial for detoxification because proper bowel movements ensure the regular elimination of waste and toxins from the body. By improving motility and preventing constipation, Bifidobacterium bifidum helps facilitate the regular excretion of waste products.
- Produces Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
When Bifidobacterium bifidum ferments fiber and other carbohydrates, it produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as butyrate, acetate, and propionate. These SCFAs serve as an energy source for the cells lining the colon and help maintain the health of the gut barrier. Butyrate, in particular, has anti-inflammatory properties and supports detoxification by reducing oxidative stress and promoting the repair of damaged tissues in the gut.
- Prevents Leaky Gut
Leaky gut syndrome, also known as increased intestinal permeability, allows toxins and harmful substances to leak into the bloodstream from the intestines, leading to systemic inflammation and toxin buildup. Bifidobacterium bifidum helps maintain the integrity of the intestinal lining, preventing the leakage of harmful substances and supporting the body’s detoxification processes. A healthy gut lining also ensures that nutrients are properly absorbed, and toxins are efficiently removed.
HOW BIFIDOBACTERIUM BIFIDUM HELPS IN MAINTAIN ENZYME BALANCE

Bifidobacterium bifidum plays a significant role in maintaining enzyme balance in the digestive system. Enzymes are essential for breaking down food into smaller components that the body can absorb and utilize. An imbalance or deficiency in digestive enzymes can lead to poor digestion, bloating, discomfort, and nutrient malabsorption.
- Enhances Digestive Enzyme Production
Bifidobacterium bifidum supports the production of digestive enzymes in the gut, such as those responsible for breaking down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. By promoting a healthy gut microbiome, it can encourage the expression and activity of enzymes that are essential for digestion.
- Amylase: It supports the breakdown of starches into sugars.
- Protease: Helps break down proteins into amino acids.
- Lipase: Breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
This balance of enzymes ensures that food is properly digested and absorbed, preventing indigestion and promoting overall digestive health.
- Supports Lactase Activity for Lactose Digestion
One of the critical digestive enzymes is lactase, which is responsible for breaking down lactose (the sugar found in dairy products) into simpler sugars. Some people have reduced lactase activity, leading to lactose intolerance, which can cause symptoms like bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
Bifidobacterium bifidum can help maintain or enhance lactase activity in the gut, improving the ability to digest dairy products. This is particularly important for individuals who have difficulty digesting lactose, as it helps restore balance in the digestive process.
- Breaks Down Complex Carbohydrates and Fiber
Bifidobacterium bifidum is involved in the fermentation of dietary fibers and prebiotic carbohydrates, which are often indigestible by human enzymes. It produces enzymes like cellulase, xylanase, and b-glucanase, which help break down complex carbohydrates and fiber into simpler forms, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, acetate, and propionate. These SCFAs are beneficial for gut health and play a role in maintaining a healthy microbiome.
This process of fiber fermentation not only helps balance the enzyme activity in the gut but also contributes to intestinal health, providing energy for gut cells and reducing inflammation.
- Improves Digestive Efficiency
By supporting the production and function of digestive enzymes, Bifidobacterium bifidum improves the overall efficiency of digestion. When digestion is efficient, fewer undigested food particles are left in the intestines to ferment and cause gas, bloating, or discomfort. A balanced enzyme system ensures that food is broken down properly and absorbed effectively, reducing digestive distress and supporting nutrient absorption.
- Modulates Enzyme Activity in the Small and Large Intestines
Bifidobacterium bifidum helps regulate the enzyme activity in both the small and large intestines. In the small intestine, it promotes enzymes that break down food for absorption, while in the large intestine, it helps with the fermentation of fiber, producing SCFAs. The balance between these two types of enzyme activity is crucial for overall digestive health. When there is an imbalance in enzyme production, it can lead to conditions like gastritis, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Reduces Undigested Food in the Gut
When enzymes are imbalanced, undigested food can remain in the stomach and intestines, leading to fermentation by harmful bacteria. This can cause gas, bloating, and other digestive issues. By maintaining enzyme balance and ensuring that food is properly digested, Bifidobacterium bifidum reduces the amount of undigested food that reaches the colon. This helps prevent excessive gas production and maintains a balanced microbiome, which is key for optimal enzyme activity.
- Supports Pancreatic Enzyme Activity
Bifidobacterium bifidum indirectly supports the function of pancreatic enzymes. The pancreas secretes enzymes like amylase, lipase, and protease to aid in digestion, but these enzymes can be impaired if the gut microbiome is not healthy. By maintaining a healthy gut environment, Bifidobacterium bifidum helps ensure that the pancreas continues to secrete sufficient enzymes for optimal digestion. It also supports the overall digestive process by regulating the pH of the gut, which is essential for the proper activation of these enzymes.
- Helps Prevent Enzyme Deficiency
In some conditions, such as malabsorption or enzyme deficiencies, the body may not produce enough of certain digestive enzymes. Bifidobacterium bifidum can help prevent or alleviate enzyme deficiencies by supporting the body’s natural enzyme production. For instance, in individuals who suffer from conditions like exocrine pancreatic insufficiency or lactose intolerance, Bifidobacterium bifidum may help compensate for the lack of certain enzymes, improving overall digestion and reducing symptoms.
HOW BIFIDOBACTERIUM BIFIDUM HELPS IN PROBIOTIC SUPPORT & REDUCES BLOATING

- Restores and Maintains Gut Microbial Balance
Bifidobacterium bifidum helps support a healthy balance of gut bacteria, promoting the growth of beneficial microbes while inhibiting harmful bacteria. A balanced gut microbiome is essential for optimal digestion, as an imbalance (dysbiosis) can lead to bloating, discomfort, and other digestive issues.
- Probiotic support: By introducing good bacteria into the gut, Bifidobacterium bifidum helps crowd out pathogenic bacteria and supports the growth of other beneficial probiotics like lactobacilli.
- Inhibition of harmful microbes: It produces substances like lactic acid that lower the pH of the gut, making it less hospitable to harmful bacteria that could lead to bloating and gas.
- Enhances Digestion of Complex Carbohydrates and Fiber
Bifidobacterium bifidum is involved in the fermentation of dietary fibers and other complex carbohydrates that human digestive enzymes cannot fully break down. This fermentation process produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, which are beneficial for gut health.
- Reduced bloating: When Bifidobacterium bifidum ferments these fibers, they are broken down into simpler components, reducing the chances of gas buildup in the intestines, which often causes bloating.
- Gut comfort: The production of SCFAs helps reduce inflammation in the gut and supports a healthier digestive environment, contributing to reduced bloating.
- Promotes Efficient Digestion
Bifidobacterium bifidum helps improve the efficiency of digestion by aiding in the breakdown of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. This ensures that food is fully digested and nutrients are absorbed properly, preventing undigested food from remaining in the intestines and fermenting, which is a common cause of bloating and discomfort.
- Reduced fermentation: When food is adequately digested, there is less fermentation in the colon, reducing the gas production that leads to bloating.
- Supports Regular Bowel Movements
Healthy gut motility (the movement of food through the digestive system) is key to preventing bloating. If food moves too slowly through the intestines, it can lead to constipation, which contributes to bloating and discomfort. Bifidobacterium bifidum helps improve gut motility, ensuring that food passes through the digestive tract efficiently.
- Prevents constipation-induced bloating: By promoting regular bowel movements, it helps prevent the buildup of gas and waste that can lead to bloating.
- Reduces Gas Production
Excessive gas and bloating are often caused by the fermentation of undigested food in the intestines, especially when food remains in the gut for too long. Bifidobacterium bifidum helps reduce this by ensuring that food is properly digested in the stomach and small intestine, leaving fewer undigested components to ferment in the colon.
- Efficient digestion: By improving digestion, Bifidobacterium bifidum helps minimize the production of gas caused by bacterial fermentation of undigested food in the intestines.
- Supports Lactose Digestion
People with lactose intolerance often experience bloating, gas, and discomfort when consuming dairy products. Bifidobacterium bifidum can help by producing lactase, the enzyme that breaks down lactose, making it easier to digest dairy and reduce symptoms like bloating.
- Reduces Inflammation
Inflammation in the gut can exacerbate bloating and digestive discomfort. Bifidobacterium bifidum has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce gut inflammation, supporting a more comfortable digestive process.
- Soothed gut lining: By reducing inflammation, Bifidobacterium bifidum helps prevent the irritation that can contribute to bloating.
- Enhances Gut Barrier Function
The gut lining is essential for preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream. A compromised gut barrier can lead to leaky gut syndrome, which can contribute to bloating and discomfort. Bifidobacterium bifidum helps strengthen the gut barrier, reducing the likelihood of harmful bacteria and toxins entering the bloodstream and causing gut issues like bloating.
- Helps with IBS Symptoms
Individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) often experience bloating, along with other symptoms like gas, diarrhea, and constipation. Bifidobacterium bifidum can help regulate gut motility and reduce gut inflammation, both of which are important for managing IBS symptoms. It helps restore a healthy balance in the gut, which can reduce bloating and discomfort in IBS patients.
HOW BIFIDOBACTERIUM BIFIDUM HELPS IN GERD, IBS & IBD

1. Bifidobacterium bifidum in GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
GERD occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing heartburn and other symptoms. Although probiotics like Bifidobacterium bifidum don't directly neutralize stomach acid, they offer indirect benefits in managing GERD:
- Gut health support: Bifidobacterium bifidum helps restore and maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which can improve overall digestion and reduce gut inflammation. This can prevent disruptions in the gut that may trigger or worsen GERD symptoms.
- Reducing gut dysbiosis: GERD is sometimes linked to imbalances in the gut microbiota. By promoting a healthy balance of good bacteria and reducing the growth of harmful bacteria, Bifidobacterium bifidum can help restore a healthier microbial environment, which may alleviate GERD symptoms.
- Lowering gut inflammation: Inflammation in the digestive tract can worsen GERD. Bifidobacterium bifidum has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce gut inflammation, including inflammation in the esophagus and stomach lining, which can reduce the severity of GERD symptoms.
- Supporting gut motility: Probiotics like Bifidobacterium bifidum can help regulate gut motility (the movement of food through the digestive system). Proper motility ensures that food moves efficiently through the stomach and intestines, preventing delayed gastric emptying (a common issue in GERD) and reducing acid reflux.
2. Bifidobacterium bifidum in IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
IBS is a common condition characterized by symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation. Bifidobacterium bifidum has several benefits for people with IBS:
- Improving gut microbiome balance: IBS is often associated with an imbalance of gut bacteria (dysbiosis). Bifidobacterium bifidum helps restore a healthy microbial balance, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and reducing the overgrowth of harmful bacteria, which can contribute to IBS symptoms.
- Reducing inflammation: Chronic inflammation in the gut is common in IBS. Bifidobacterium bifidum has anti-inflammatory effects that can help calm inflammation in the digestive tract, reducing symptoms like bloating, pain, and discomfort.
- Regulating gut motility: Bifidobacterium bifidum supports proper gut motility, which is essential in IBS management. It can help regulate bowel movements and prevent both constipation and diarrhea, two hallmark symptoms of IBS. It helps improve the smooth movement of food and waste through the intestines, reducing bloating and discomfort.
- Reducing gas and bloating: One of the common symptoms of IBS is bloating, often caused by the fermentation of undigested food in the gut. Bifidobacterium bifidum helps break down complex carbohydrates and fibers, reducing the amount of undigested food in the gut and, consequently, reducing gas and bloating.
- Supporting digestion: Bifidobacterium bifidum enhances the digestion of food and the absorption of nutrients, helping alleviate discomfort caused by maldigestion in IBS patients.
3. Bifidobacterium bifidum in IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease)
IBD, which includes conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, involves chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. Bifidobacterium bifidum can offer several benefits in managing IBD:
- Reducing inflammation: Bifidobacterium bifidum has significant anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce the chronic inflammation characteristic of IBD. It supports the healing of the intestinal lining by modulating immune responses, which is critical for reducing flare-ups in conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Restoring gut barrier function: In IBD, the gut lining is often compromised, leading to a condition known as "leaky gut," where harmful substances can pass into the bloodstream and trigger immune responses. Bifidobacterium bifidum helps maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier, reducing gut permeability and protecting against the absorption of harmful substances.
- Balancing the gut microbiome: Dysbiosis is often present in IBD, with an imbalance of beneficial and harmful bacteria. Bifidobacterium bifidum helps restore a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which can reduce inflammation and support overall gut health. It promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria while inhibiting the growth of harmful microorganisms.
- Reducing oxidative stress: Inflammation in IBD is often accompanied by oxidative stress, which can damage the intestinal lining. Bifidobacterium bifidum helps mitigate oxidative stress by producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, which nourish the gut lining and have anti-inflammatory effects. SCFAs also help regulate immune cell activity, further supporting IBD management.
- Supporting immune function: A significant component of IBD involves an overactive immune response. Bifidobacterium bifidum helps modulate the immune system, reducing excessive inflammation and promoting a balanced immune response that is less likely to cause intestinal damage.
4. General Benefits for Digestive Health
In addition to its specific effects on GERD, IBS, and IBD, Bifidobacterium bifidum provides general digestive health benefits that can help people manage these conditions:
- Improves digestion: Bifidobacterium bifidum enhances the digestion and absorption of food, which can alleviate many symptoms of gastrointestinal discomfort that overlap in GERD, IBS, and IBD, such as bloating, indigestion, and abdominal pain.
- Supports gut motility: It helps ensure that food and waste move through the digestive system at a normal pace, which is critical for reducing symptoms like constipation, diarrhea, and bloating in conditions like IBS and IBD.
HOW BIFIDOBACTERIUM BIFIDUM HELPS IN ACIDITY
- Promotes Gut Microbial Balance
Acidity, or acid reflux, can sometimes be linked to an imbalance in the gut microbiome, a condition known as dysbiosis. When harmful bacteria overgrow in the gut, they can disrupt normal digestion and contribute to symptoms like acid reflux. Bifidobacterium bifidum helps maintain a healthy balance of good bacteria in the gut, which can:
- Reduce harmful bacteria: By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibiting the growth of harmful microbes, Bifidobacterium bifidum can help maintain a balanced gut environment, which may indirectly reduce the factors that contribute to acid reflux and acidity.
- Improve digestion: A balanced gut microbiome is essential for effective digestion. When food is properly digested, there is less likelihood of excess acid production, which is often a factor in acid reflux.
- Improves Gut Motility
Acidity is sometimes aggravated by delayed gastric emptying or slow digestion, where food stays in the stomach for too long. This can increase pressure in the stomach, promoting acid reflux. Bifidobacterium bifidum supports gut motility, ensuring food moves efficiently through the stomach and intestines.
- Prevents acid backflow: By improving the movement of food and waste through the digestive system, Bifidobacterium bifidum can help prevent the buildup of stomach contents that may cause acid reflux.
- Speeds up digestion: Efficient digestion means food is processed and emptied from the stomach more quickly, reducing the chances of acid rising into the esophagus.
- Supports a Healthy Gut Barrier
The stomach lining and the esophagus are sensitive to stomach acid. In people with acidity, the protective mucosal lining of the stomach may be compromised, which can make the digestive system more prone to irritation from acid. Bifidobacterium bifidum helps strengthen the gut barrier, preventing harmful substances (including stomach acid) from penetrating the lining of the stomach and esophagus.
- Reduces inflammation: It also has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help soothe and protect the gut lining, potentially preventing the irritation that can lead to acid reflux.
- Reduces Inflammation
Acid reflux and chronic acidity are often associated with inflammation in the stomach and esophagus. Bifidobacterium bifidum has anti-inflammatory effects that can help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract, particularly in the stomach lining and esophagus. This helps soothe the discomfort and burning sensation associated with acidity.
- Soothing effect: By calming inflammation, Bifidobacterium bifidum may help reduce the frequency and severity of acid reflux episodes and the discomfort that accompanies acidity.
- Supports Digestive Efficiency and Reduces Gas Production
Sometimes, acidity is worsened by the fermentation of undigested food in the stomach or intestines, which can create excess gas and bloating. Bifidobacterium bifidum helps break down complex carbohydrates and fibers in food, promoting efficient digestion and reducing the chances of gas formation. When food is properly digested, there is less likelihood of pressure building up in the stomach, which can reduce the occurrence of acid reflux and acidity.
- Prevents bloating and pressure: Proper digestion reduces bloating, which can put additional pressure on the stomach and lower esophageal sphincter (LES), the valve that prevents stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus. This can reduce symptoms of acid reflux.
- Helps with Lactose Digestion
People who are lactose intolerant often experience digestive discomfort and acidity after consuming dairy products. Lactose intolerance can lead to bloating and excess gas, which may increase the pressure in the stomach and exacerbate acid reflux. Bifidobacterium bifidum helps with lactose digestion, allowing individuals who are lactose intolerant to digest dairy more effectively, which may help reduce acidity and discomfort.
- Modulates Immune Response
Acidity can sometimes be aggravated by an overactive immune response in the digestive tract, leading to inflammation and irritation. Bifidobacterium bifidum helps modulate the immune system, promoting a balanced immune response that reduces excessive inflammation in the gut. This may help prevent the irritation caused by acid reflux and chronic acidity.
- Reduces Stress-Induced Acidity
Stress is a well-known trigger for acid reflux and other digestive issues. Bifidobacterium bifidum supports gut health and helps modulate the body's stress response, potentially reducing the negative impact of stress on the digestive system and acidity levels.
HOW BIFIDOBACTERIUM LONGUM HELPS IN DIGESTION & DETOXIFICATION
- Enhances Digestion
Bifidobacterium longum is a key player in promoting digestive health by improving the breakdown and absorption of nutrients in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Fermentation of dietary fiber: One of the primary functions of Bifidobacterium longum is to ferment prebiotic fibers (such as oligosaccharides) in the large intestine. This process produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, acetate, and propionate, which not only provide energy for the cells of the colon but also support overall gut health.
- Butyrate, in particular, is important for maintaining the integrity of the intestinal lining and promoting gut motility, ensuring that food moves through the digestive system at a healthy pace.
- Aid in lactose digestion: Bifidobacterium longum can help individuals who are lactose intolerant by producing lactase, the enzyme that breaks down lactose (the sugar found in milk). This helps prevent the discomfort associated with lactose intolerance, such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea, by ensuring that lactose is properly digested in the small intestine.
- Digestive enzyme production: It may help stimulate the production of certain digestive enzymes, assisting the breakdown of food into nutrients that can be absorbed more easily by the body. This reduces the risk of indigestion and enhances nutrient absorption.
- Detoxification Support
Bifidobacterium longum plays a significant role in supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes by promoting the removal of waste products and toxins from the digestive system.
- Regulation of gut microbiota: A balanced gut microbiome is essential for detoxification, as an imbalance in gut bacteria can impair the body’s ability to process and eliminate toxins. Bifidobacterium longum helps maintain a healthy balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut, preventing the overgrowth of harmful bacteria that can produce toxins.
- Reduction of gut permeability (Leaky Gut): Bifidobacterium longum can help strengthen the intestinal barrier by supporting the integrity of the gut lining. This prevents harmful substances, including toxins and waste, from passing through the gut wall into the bloodstream—a condition known as "leaky gut." By maintaining a strong gut barrier, it supports the body’s natural defense against toxins and contributes to better detoxification.
- Production of SCFAs: The short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) produced by Bifidobacterium longum, especially butyrate, help maintain the health of the colon and support its ability to remove waste products effectively. SCFAs also help regulate the pH of the colon, creating an environment where harmful bacteria are less likely to thrive, thereby preventing the buildup of harmful substances in the gut.
- Liver detoxification support: While Bifidobacterium longum works primarily in the gut, it also has indirect effects on liver detoxification. The gut and liver are connected through the hepatic portal system, and a healthy gut microbiome can help reduce the burden on the liver by preventing the absorption of harmful substances into the bloodstream that would otherwise have to be processed by the liver.
- Reducing Inflammation
Chronic inflammation in the gut can hinder both digestion and detoxification. Bifidobacterium longum has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract and promote a more effective digestive process.
- Soothing gut inflammation: By reducing inflammation, it can help reduce discomfort, bloating, and other digestive issues, allowing for more efficient digestion and absorption of nutrients.
- Supporting a healthy immune system: The gut is home to a significant portion of the immune system, and Bifidobacterium longum helps regulate immune responses. A balanced immune system can prevent chronic inflammation, which can impair digestion and detoxification processes.
- Detoxification of Harmful Substances
Bifidobacterium longum contributes to the detoxification of harmful substances in the digestive system through a process called biotransformation. This process involves converting potentially harmful compounds into less toxic, more easily excretable forms.
- Reduction of harmful metabolites: Bifidobacterium longum can help break down harmful substances like ammonia, a toxic byproduct of protein digestion, into non-toxic forms that can be safely eliminated from the body. It also helps detoxify other waste products and metabolic byproducts in the digestive system, preventing their accumulation and harmful effects.
- Regulation of Bowel Movements
Bifidobacterium longum supports regular bowel movements by promoting healthy gut motility. By improving the movement of food through the digestive tract and supporting the natural elimination process, it helps prevent constipation, which can contribute to the buildup of waste and toxins in the gut.
- Relief from constipation: When bowel movements are regular, the body is better able to eliminate waste and toxins, supporting overall detoxification.
- Supporting Metabolism and Absorption
A well-functioning digestive system is essential for detoxification, as it ensures that nutrients are absorbed effectively and waste products are eliminated properly. Bifidobacterium longum supports metabolism by improving nutrient absorption and promoting a balanced digestive environment.
- Enhancing nutrient absorption: By supporting digestion, it ensures that essential nutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are absorbed effectively by the body. A well-nourished body is better equipped to support detoxification processes and overall health.
HOW BIFIDOBACTERIUM LONGUM HELPS IN MAINTAIN ENZYME BALANCE

- Stimulating Production of Digestive Enzymes
Bifidobacterium longum can support the production of digestive enzymes that are crucial for breaking down food and absorbing nutrients.
- Enhancing enzymatic activity: It helps promote the activity of key enzymes involved in the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. This includes enzymes like amylase (for starch breakdown), lipase (for fat digestion), and proteases (for protein digestion).
- Improving lactase production: Many people struggle with lactose intolerance due to a lack of the enzyme lactase, which breaks down lactose (the sugar in milk). Bifidobacterium longum helps by producing lactase, enabling better digestion of dairy products, reducing bloating and discomfort.
- Enhancing Breakdown of Complex Carbohydrates
Bifidobacterium longum aids in breaking down complex carbohydrates and fibers, which are otherwise difficult for the body to digest. This process occurs primarily in the large intestine, where the bacteria ferment the fiber and produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, acetate, and propionate.
- Fermentation of fibers: These SCFAs not only help nourish the cells of the colon but also contribute to better digestion and enzyme activity. They improve the overall digestive environment, making it more conducive to enzymatic breakdown.
- Reducing undigested food: By improving fiber fermentation, Bifidobacterium longum reduces the chances of undigested food particles reaching the colon, preventing bloating, gas, and discomfort. This also eases the workload on digestive enzymes, allowing them to work more efficiently.
- Modulating Gut pH
Bifidobacterium longum helps create an acidic environment in the gut, particularly in the large intestine, through the production of SCFAs. This lower pH enhances the activity of certain digestive enzymes.
- Optimal pH for enzymes: A slightly acidic environment in the gut supports the optimal functioning of many digestive enzymes, especially amylase and lipase, which are more effective in an acidic environment.
- Inhibition of harmful microbes: The acidic environment also inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria, which can interfere with digestion and enzyme function. By promoting a healthy gut ecosystem, Bifidobacterium longum ensures that digestive enzymes work efficiently.
- Supporting Digestive Enzyme Balance in the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome is made up of various microorganisms, including bacteria that can either promote or disrupt digestion. Bifidobacterium longum helps maintain balance in the gut microbiota, which is key to supporting the proper function of digestive enzymes.
- Preventing dysbiosis: Dysbiosis, an imbalance of gut bacteria, can impair enzyme production and overall digestive efficiency. Bifidobacterium longum helps keep the gut microbiome balanced by promoting beneficial bacteria and preventing the overgrowth of harmful bacteria. This balance ensures that digestive enzymes are functioning properly.
- Improving Bile Salt Metabolism
Bile salts are essential for the digestion of fats, and enzymes work in synergy with bile to break down fat molecules. Bifidobacterium longum helps regulate the metabolism of bile salts, enhancing the process of fat digestion and absorption.
- Regulating bile acid levels: By supporting bile salt metabolism, Bifidobacterium longum helps optimize the action of lipase and other fat-digesting enzymes, improving fat absorption and reducing discomfort, such as bloating and indigestion.
- Regulating Enzyme Production in the Pancreas
The pancreas produces enzymes like amylase, lipase, and proteases that are critical for digesting carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Bifidobacterium longum has been shown to support gut health and may indirectly promote healthy enzyme secretion from the pancreas.
- Gut-pancreatic communication: A healthy gut microbiome helps regulate the communication between the gut and pancreas, ensuring that appropriate levels of digestive enzymes are secreted when needed for optimal digestion.
- Reducing Inflammation in the Gut
Chronic gut inflammation can impair the function of digestive enzymes and disrupt digestion. Bifidobacterium longum helps reduce gut inflammation through its anti-inflammatory properties, supporting the optimal functioning of enzymes in the digestive tract.
- Protecting enzyme function: By reducing gut inflammation, Bifidobacterium longum helps maintain the integrity of the gut lining and prevents the damage or dysfunction of the enzymes responsible for digesting food.
- Supporting Protein Digestion
Bifidobacterium longum helps break down proteins and amino acids in the digestive system. It produces enzymes that support the fermentation of proteins into simpler forms, reducing the digestive burden on the body's own enzyme systems.
Protease activity: By supporting the fermentation and breakdown of proteins, Bifidobacterium longum can help ease the workload on proteolytic enzymes (proteases), aiding in efficient protein digestion and improving the absorption of amino acids
HOW BIFIDOBACTERIUM LONGUM HELPS IN PROBIOTIC SUPPORT

- Supports a Healthy Gut Microbiome
Bifidobacterium longum contributes to the overall health and balance of the gut microbiota by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria while inhibiting the growth of harmful microorganisms.
- Maintains a healthy balance of gut flora: By outcompeting harmful bacteria and pathogens for resources, Bifidobacterium longum helps ensure that the gut microbiome remains balanced. This balance is crucial for preventing the overgrowth of bad bacteria that can cause bloating and digestive discomfort.
- Strengthens gut barrier function: A healthy gut microbiome, supported by probiotics like Bifidobacterium longum, helps maintain the integrity of the gut lining. This prevents "leaky gut," which can contribute to inflammation and bloating. By promoting a strong gut barrier, Bifidobacterium longum indirectly reduces the occurrence of bloating.
- Enhances Digestion of Complex Carbohydrates
One of the main causes of bloating is the undigested food in the intestines, particularly complex carbohydrates that are difficult for the body to break down. Bifidobacterium longum helps improve digestion by fermenting these complex carbohydrates, including fiber and certain sugars, into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as butyrate, acetate, and propionate.
- Fermentation of fiber: This fermentation process not only provides energy for the gut lining cells but also helps prevent the buildup of gas and pressure in the intestines that can lead to bloating. The SCFAs produced help regulate gut motility and reduce the likelihood of digestive discomfort.
- Reduces gas production: By aiding in the fermentation of undigested carbohydrates, Bifidobacterium longum helps break down these substances before they ferment excessively in the colon, thereby reducing the excess gas and bloating associated with fermentation.
- Regulates Gut Motility
Slow digestion or intestinal motility issues can lead to bloating, as food and gas accumulate in the intestines. Bifidobacterium longum supports normal gut motility, ensuring that food and gas move efficiently through the digestive system.
- Promotes regular bowel movements: By improving motility, Bifidobacterium longum can help prevent constipation, which is often a contributing factor to bloating. When food moves too slowly through the digestive tract, it can create pressure and cause bloating.
- Reduces symptoms of constipation: With more regular bowel movements, there is less likelihood of food and gas accumulating, which reduces bloating and discomfort.
- Reduces Gut Inflammation
Inflammation in the digestive tract can contribute to bloating and discomfort, especially in conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Bifidobacterium longum has anti-inflammatory properties, which help soothe the gut and prevent excessive inflammation.
- Decreases intestinal inflammation: By calming inflammation in the gut, Bifidobacterium longum helps reduce the swelling and bloating that often accompany digestive issues like IBS and other inflammatory bowel conditions.
- Supports a healthy gut lining: Reducing inflammation also helps to protect the gut lining, which may prevent further irritation or sensitivity that can lead to bloating.
- Enhances the Breakdown of Lactose
Lactose intolerance is a common cause of bloating and digestive discomfort. Bifidobacterium longum produces lactase, the enzyme required to break down lactose, the sugar found in dairy products. For those with lactose intolerance, Bifidobacterium longum helps break down lactose into simpler sugars, reducing the symptoms of bloating and gas that often result from undigested lactose.
- Improves lactose digestion: By aiding the digestion of lactose, Bifidobacterium longum reduces the fermentation of lactose in the colon, which can otherwise produce gas, bloating, and discomfort.
- Balances the Immune System
Bloating can be exacerbated by an overactive immune response in the gut, leading to inflammation and discomfort. Bifidobacterium longum helps regulate immune function in the gut, promoting a balanced immune response that prevents excessive inflammation and bloating.
- Modulates gut immunity: It helps regulate immune cell activity in the gut, reducing the risk of excessive inflammation that can trigger bloating and discomfort.
- Promotes anti-inflammatory cytokines: Bifidobacterium longum encourages the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines that help balance immune responses and prevent the kind of chronic inflammation that contributes to bloating.
- Improves Intestinal pH
Bifidobacterium longum helps produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, which lower the pH in the intestines. This acidic environment helps regulate the growth of beneficial bacteria while inhibiting harmful bacteria that can contribute to digestive discomfort and bloating.
- Inhibits gas-producing bacteria: The acidic environment created by SCFAs makes it difficult for gas-producing bacteria to thrive. This helps prevent the excessive gas production that leads to bloating.
- Supports a healthy microbial ecosystem: A balanced gut pH supports the growth of beneficial bacteria like Bifidobacterium longum, which outcompetes harmful bacteria and prevents imbalances that could lead to bloating.
- Helps with Protein Digestion
Inadequate protein digestion can also contribute to bloating, as undigested protein may ferment in the gut, producing gas. Bifidobacterium longum supports the fermentation and digestion of proteins in the gut, helping to break them down into more digestible forms and reducing the likelihood of bloating.
Supports protease activity: By aiding the fermentation and breakdown of proteins, Bifidobacterium longum reduces the strain on digestive enzymes and ensures that proteins are properly digested, which minimizes fermentation and gas production
HOW BIFIDOBACTERIUM LONGUM HELPS IN GERD,IBS &IBD MANAGEMENT

1. Bifidobacterium Longum and GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
GERD is characterized by the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, leading to symptoms like heartburn, chest pain, and regurgitation. Bifidobacterium longum can help manage GERD in the following ways:
- Reducing gut inflammation: GERD can often be accompanied by inflammation in the esophagus and stomach lining. Bifidobacterium longum has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce this inflammation, potentially alleviating the discomfort and irritation caused by acid reflux.
- Supporting gut motility: One of the factors contributing to GERD is delayed gastric emptying or slowed motility in the digestive tract. By promoting normal gut motility, Bifidobacterium longum helps ensure that food moves efficiently through the stomach and intestines, reducing the risk of acid reflux.
- Strengthening the gut barrier: A healthy gut barrier prevents the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus. Bifidobacterium longum helps support the intestinal barrier, preventing the breakdown of the gut lining and promoting a more effective defense against acid reflux.
- Balancing gut microbiome: Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in the gut microbiome, can exacerbate GERD symptoms. Bifidobacterium longum helps balance the gut microbiota by promoting beneficial bacteria, which can prevent the overgrowth of harmful bacteria that may trigger or worsen GERD symptoms.
2. Bifidobacterium Longum and IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
IBS is a chronic digestive disorder characterized by symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation. Bifidobacterium longum offers several benefits for IBS management:
- Improving gut motility: One of the most common symptoms of IBS is altered gut motility, which can lead to both constipation and diarrhea. Bifidobacterium longum helps regulate gut motility, ensuring more regular bowel movements and reducing the discomfort associated with constipation and diarrhea.
- Reducing gut inflammation: IBS is often associated with low-grade inflammation in the digestive tract. Bifidobacterium longum has anti-inflammatory effects that help soothe the gut lining, reducing abdominal pain and discomfort.
- Modulating the gut-brain axis: IBS is thought to be influenced by the gut-brain axis, where stress and anxiety can exacerbate digestive symptoms. Bifidobacterium longum may help regulate the gut-brain axis by promoting a healthy balance of gut microbiota, which can positively influence mood and reduce stress-related digestive issues.
- Improving digestion and nutrient absorption: Bifidobacterium longum supports the digestion of complex carbohydrates and fiber, improving nutrient absorption and reducing bloating, gas, and other IBS-related symptoms.
- Reducing gas and bloating: IBS often results in excess gas and bloating due to fermentation of undigested carbohydrates. Bifidobacterium longum helps in the fermentation of fiber, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, which supports healthy gut function and reduces bloating and gas buildup.
3. Bifidobacterium Longum and IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease)
IBD, which includes conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, is characterized by chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, leading to symptoms like diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fatigue. Bifidobacterium longum can be beneficial in the management of IBD:
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Bifidobacterium longum has powerful anti-inflammatory properties, which are especially helpful in conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. It can help reduce the inflammation that causes the symptoms of IBD, potentially providing relief from pain, diarrhea, and other inflammatory symptoms.
- Supporting intestinal barrier function: In IBD, the gut lining is often compromised, leading to "leaky gut," where harmful substances can pass into the bloodstream, exacerbating inflammation. Bifidobacterium longum helps strengthen the intestinal barrier, preventing the leakage of harmful particles and promoting gut integrity.
- Restoring gut microbiome balance: IBD is often associated with an imbalance in the gut microbiome. Bifidobacterium longum helps restore the balance of beneficial bacteria, which can reduce the overgrowth of harmful bacteria that contribute to inflammation and disease flare-ups.
- Promoting SCFA production: The fermentation of fiber by Bifidobacterium longum produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, which have anti-inflammatory effects and provide energy to the cells lining the gut. Butyrate helps reduce gut inflammation and supports the healing of the intestinal lining in individuals with IBD.
- Supporting immune modulation: In IBD, the immune system is often dysregulated, leading to chronic inflammation. Bifidobacterium longum helps modulate the immune response in the gut, reducing the overactive immune response that contributes to inflammation and flare-ups.
- Reducing oxidative stress: Oxidative stress plays a role in the inflammation and tissue damage seen in IBD. Bifidobacterium longum may help reduce oxidative stress, which can contribute to the long-term management of IBD symptoms.
4. General Benefits for GERD, IBS, and IBD
In addition to the specific effects for each condition, Bifidobacterium longum provides some general benefits that help improve overall gut health, which can be beneficial for managing GERD, IBS, and IBD:
- Restoring gut flora balance: A balanced gut microbiome is key to maintaining digestive health. Bifidobacterium longum helps restore the balance of beneficial bacteria, which can support overall digestive function and reduce symptoms of digestive disorders.
- Strengthening gut immunity: A healthy immune system is crucial for managing inflammatory conditions like IBD and IBS. Bifidobacterium longum supports gut immunity, helping to maintain a balanced immune response and reduce excessive inflammation in the digestive tract.
- Protecting against harmful bacteria: By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, Bifidobacterium longum can help prevent the overgrowth of harmful bacteria that may contribute to gut dysbiosis, inflammation, and symptoms of GERD, IBS, and IBD.
HOW BIFIDOBACTERIUM LONGUM HELPS IN ACIDITY

- Reducing Inflammation in the Gut
Excess acidity in the stomach can lead to gastric irritation and inflammation, contributing to symptoms such as heartburn, acid reflux, and gastritis. Bifidobacterium longum has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce this inflammation:
- Soothes the gut lining: By reducing inflammation, Bifidobacterium longum can help protect the stomach lining from the erosive effects of stomach acid, reducing symptoms of acidity and discomfort.
- Supports healing: Bifidobacterium longum may also aid in the healing of the gut lining if it has been irritated by excess acid, promoting better overall digestive health and reducing the recurrence of acidity.
- Restoring Gut Microbiome Balance
An imbalance in the gut microbiome (dysbiosis) is often associated with digestive issues, including acidity. Bifidobacterium longum helps restore balance by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, which can counteract the harmful effects of acid-producing bacteria or pathogens.
- Improves gut flora balance: By restoring a healthy balance of gut bacteria, Bifidobacterium longum helps support the optimal functioning of the digestive system, reducing the likelihood of bacterial imbalances that may contribute to excess acidity or acid reflux.
- Supports digestion: A well-balanced gut microbiome supports more efficient digestion, reducing the chances of food fermenting in the stomach and causing bloating, discomfort, or acid production that leads to acidity.
- Improving Gut Motility
Slow or impaired gastric emptying can contribute to acid reflux and indigestion, as food stays in the stomach for longer, increasing the likelihood of acid backflow into the esophagus. Bifidobacterium longum helps regulate gut motility, promoting efficient movement of food and stomach contents.
- Promotes faster digestion: By improving motility, Bifidobacterium longum helps ensure that food moves through the digestive tract more efficiently, reducing the risk of delayed gastric emptying, which can lead to excessive acid production and discomfort.
- Reduces reflux: Better motility also means less chance for stomach contents, including acid, to back up into the esophagus, which reduces the likelihood of symptoms like heartburn and acid reflux.
- Strengthening the Intestinal Barrier
A compromised gut barrier (often seen in conditions like leaky gut) can exacerbate acidity symptoms and inflammation. Bifidobacterium longum helps strengthen the intestinal barrier, preventing harmful substances from leaking into the bloodstream and causing inflammation.
- Prevents leaky gut: By improving gut permeability, Bifidobacterium longum helps to ensure that harmful substances don’t trigger systemic inflammation, which can worsen acid reflux and acidity symptoms.
- Enhances gut protection: A strong intestinal barrier reduces the risk of gastric acid irritating the digestive tract, providing protection against conditions like gastritis and acid reflux.
- Regulating Gastric Acid Production
Bifidobacterium longum may also help regulate gastric acid secretion. While there is still some research needed in this area, the balance of gut bacteria has been shown to influence the production of stomach acid.
- Regulates pH levels: By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, Bifidobacterium longum helps maintain a balanced pH environment in the stomach. This balance can prevent excess acid secretion that may lead to acid reflux or irritation.
- Reduces overproduction of acid: A well-regulated gut microbiome can prevent the overstimulation of acid-producing cells in the stomach, reducing the likelihood of excessive acid buildup and the discomfort it causes.
- Reducing Gas and Bloating
Excess gas and bloating can exacerbate acidity symptoms by increasing pressure on the stomach, which can lead to acid reflux. Bifidobacterium longum helps reduce gas production by improving the digestion of complex carbohydrates and fiber in the gut.
- Prevents bloating: By supporting healthy digestion, Bifidobacterium longum reduces the chances of undigested food fermenting in the stomach, which can cause gas buildup and bloating. This, in turn, reduces the pressure on the stomach and the likelihood of acid reflux.
- Supports efficient digestion: Efficient digestion means that food doesn’t stay in the stomach too long, which helps prevent the overproduction of stomach acid that may lead to discomfort and acid-related symptoms.
- Supporting the Gut-Brain Axis
Acidity and digestive issues like heartburn can be exacerbated by stress and emotional factors. The gut-brain axis refers to the communication between the gut and the brain, and Bifidobacterium longum has been shown to support this connection. By promoting a healthy gut microbiome, Bifidobacterium longum may help reduce the stress response that contributes to digestive discomfort.
- Reduces stress-related acidity: By supporting a healthy gut and reducing inflammation, Bifidobacterium longum can help manage stress-related digestive issues, including acid reflux and gastritis, which are often triggered or worsened by stress.
- Enhancing Nutrient Absorption
Efficient digestion and nutrient absorption play a crucial role in maintaining overall digestive health. Bifidobacterium longum aids in the digestion of fiber and other nutrients, preventing undigested food from causing bloating or excess acid production.
- Improves nutrient absorption: By promoting the breakdown of carbohydrates and other nutrients, Bifidobacterium longum ensures that food is digested properly and absorbed efficiently. This reduces the likelihood of undigested food fermenting in the stomach, which can lead to excessive acid production and bloating.
HOW SACCHAROMYCES BOULARDII HELPS IN DIGESTION & DETOXIFICATION

How Saccharomyces Boulardii Supports Digestion
- Promotes Healthy Gut Flora
- Saccharomyces boulardii helps maintain a healthy balance of gut microbiota by supporting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the digestive system. It acts as a probiotic, helping to restore and maintain the natural balance of bacteria in the gut, especially after disruptions caused by antibiotics, stress, or infections.
- It helps prevent the overgrowth of harmful microorganisms (like pathogens or opportunistic bacteria) in the intestines, thus supporting better digestion and overall gut health.
- Enhances Digestive Enzyme Production
- Saccharomyces boulardii can help stimulate the production of digestive enzymes, which are essential for breaking down food into nutrients that the body can absorb. These enzymes help optimize the digestion of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
- By enhancing digestive enzyme activity, it improves the body's ability to absorb nutrients from food, which can lead to better energy levels and improved overall health.
- Supports Healthy Bowel Movements
- Saccharomyces boulardii has been shown to help maintain regular bowel movements by promoting healthy intestinal motility. It can help prevent diarrhea, especially antibiotic-associated diarrhea, and traveler's diarrhea by enhancing the gut’s ability to manage inflammation and restore normal gut function.
- It also helps reduce intestinal permeability (often referred to as "leaky gut"), preventing harmful substances and toxins from entering the bloodstream, which can disrupt digestion and lead to inflammation.
- Supports Gut Mucosal Integrity
- Saccharomyces boulardii helps strengthen the intestinal lining, reducing intestinal permeability and promoting a healthy gut barrier. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), or leaky gut syndrome.
- By improving gut barrier function, Saccharomyces boulardii helps to prevent the entry of harmful substances into the bloodstream, which could lead to immune system activation and digestive disturbances.
- Reduces Gastrointestinal Inflammation
- Saccharomyces boulardii has anti-inflammatory effects that help soothe inflammation in the gut. This is especially helpful in managing conditions like IBS, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis, where inflammation in the intestines can impair digestion.
- It reduces levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the gut and helps modulate the immune response, thus reducing symptoms like bloating, cramps, and discomfort.
- Supports Healthy Gut Motility
- This probiotic yeast helps support normal gut motility (the movement of food through the digestive tract). It can be particularly useful for individuals with constipation, as it helps stimulate peristalsis, the natural muscle contractions that push food through the intestines.
- Saccharomyces boulardii has been shown to improve both gastric motility and intestinal transit time, promoting more efficient digestion and waste elimination.
How Saccharomyces Boulardii Helps Detoxification
- Supports the Elimination of Toxins
- Saccharomyces boulardii helps remove harmful toxins from the body by promoting regular bowel movements and enhancing the overall function of the digestive system. The yeast binds to toxins in the gut, helping to prevent their absorption and aiding in their elimination through feces.
- It also helps to reduce the gut’s toxicity load by limiting the growth of pathogenic microbes (such as Candida and Clostridium difficile) that can produce harmful toxins.
- Restores Gut Flora After Antibiotics
- After a course of antibiotics, the gut microbiota can be significantly disrupted, leading to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria or yeast. Saccharomyces boulardii helps restore the natural balance of gut flora, supporting detoxification and preventing an overgrowth of harmful microorganisms like Candida albicans.
- By restoring a healthy microbial environment, Saccharomyces boulardii supports the detoxification process and ensures the gut remains effective at processing and eliminating waste products and toxins.
- Inhibits Harmful Pathogens
- Saccharomyces boulardii can bind to and inhibit the growth of harmful pathogens in the gut, such as Clostridium difficile and certain strains of Salmonella, which can produce toxins and disrupt digestion.
- It helps protect the gut from these toxins, reducing the overall toxin burden in the body, which supports the detoxification process and prevents gastrointestinal upset.
- Improves Liver Function
- The liver plays a key role in detoxifying the body by filtering out toxins from the bloodstream. Saccharomyces boulardii indirectly supports liver health by improving gut health, which reduces the burden on the liver. When the gut is functioning optimally, it reduces the overall load of toxins that need to be processed by the liver.
- By promoting a healthier digestive system and reducing the absorption of harmful substances, Saccharomyces boulardii helps the liver perform its detoxifying functions more efficiently.
- Reduces Endotoxemia
- Endotoxins, produced by harmful gut bacteria, can enter the bloodstream and cause inflammation throughout the body (a condition known as endotoxemia). Saccharomyces boulardii has been shown to help reduce the levels of endotoxins in the bloodstream by promoting a healthy gut barrier and preventing the passage of these toxins into the blood.
- By reducing endotoxemia, Saccharomyces boulardii helps reduce overall systemic inflammation, which supports the body’s detoxification pathways and overall health.
- Supports Immune Function
- Saccharomyces boulardii plays a role in supporting immune function by balancing the gut's immune response. A healthy gut is vital for the proper functioning of the immune system, which is essential for detoxification and fighting off infections.
- It helps regulate the production of immune cells and antibodies, ensuring the immune system responds appropriately to pathogens and other harmful agents, supporting the body's natural detoxification process
HOW SACCHAROMYCES BOULARDII HELPS IN ENZYME BALANCE

- Promotes Production of Digestive Enzymes
- Saccharomyces boulardii can stimulate the production of digestive enzymes in the gut. These enzymes, such as amylase, lipase, and protease, are essential for breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into smaller molecules that the body can absorb. By supporting enzyme production, Saccharomyces boulardii helps improve digestion and nutrient absorption.
- It particularly supports the activity of pancreatic enzymes, which are vital for the digestion of fats and proteins. This helps ensure that the digestive system functions optimally and that nutrients are properly processed and absorbed.
- Supports Gut Enzyme Activity
- Saccharomyces boulardii may help balance the activity of enzymes produced by the intestinal lining, such as lactase (the enzyme that breaks down lactose) and enzymes responsible for digesting other complex carbohydrates. This is especially helpful for individuals with lactose intolerance, as Saccharomyces boulardii can enhance the digestion of lactose by increasing lactase activity in the gut.
- The yeast also supports the proper functioning of brush-border enzymes (enzymes found on the surface of the small intestine) that help break down disaccharides (like sucrose and lactose) into simpler sugars for absorption.
- Improves Gut Health and Enzyme Function
- By restoring and maintaining a healthy balance of gut microbiota, Saccharomyces boulardii promotes overall gut health, which is essential for proper enzyme function. A balanced gut microbiome encourages the healthy expression of genes involved in enzyme production, ensuring that the enzymes needed for digestion are present in sufficient amounts.
- A healthy gut flora can also help protect against pathogenic bacteria and yeasts, which may otherwise interfere with the production and activity of digestive enzymes. Saccharomyces boulardii helps prevent the overgrowth of harmful microbes that could disrupt normal enzyme production and digestion.
- Reduces Inflammation and Improves Enzyme Efficiency
- Inflammation in the gut can impair the function of digestive enzymes and disrupt normal enzyme balance. Saccharomyces boulardii has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce gut inflammation. By calming inflammation, it ensures that digestive enzymes can work efficiently, thus promoting better digestion and absorption of nutrients.
- The yeast's ability to reduce inflammation also helps protect the enzymes themselves from oxidative stress, which could otherwise degrade their activity.
- Enhances the Digestion of Fiber and Complex Carbs
- Saccharomyces boulardii has been shown to improve the digestion of fiber by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria that assist in breaking down complex carbohydrates and fibers. This process relies on certain digestive enzymes produced by the gut microbiota, which Saccharomyces boulardii helps to support and balance.
- It may also improve the gut's ability to digest oligosaccharides and polysaccharides, which are more difficult to break down, by encouraging the activity of enzymes that help digest these carbohydrates.
- Helps Restore Normal Enzyme Function After Disruption
- Certain factors, such as antibiotic use, stress, or gastrointestinal infections, can disrupt the balance of gut microbiota and enzyme activity. Saccharomyces boulardii is especially beneficial after these disruptions as it helps restore normal enzyme function. By balancing the microbiome and supporting the gut lining, it promotes the return of optimal enzyme production and activity in the digestive system.
- Prevents Gut Dysbiosis-Induced Enzyme Imbalance
- Gut dysbiosis (an imbalance of gut bacteria) can impair the normal function of digestive enzymes and lead to digestive disorders. Saccharomyces boulardii helps restore microbial balance in the gut, thus preventing or correcting the enzyme imbalances associated with dysbiosis.
By enhancing the growth of beneficial bacteria and keeping harmful bacteria in check, Saccharomyces boulardii helps maintain the proper enzymatic environment in the gut, ensuring efficient digestion and nutrient absorption
HOW SACCHAROMYCES BOULARDII HELPS IN PROBIOTIC NEEDS

- Restores Gut Microbial Balance
- Saccharomyces boulardii helps restore the balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut, especially after disruptions caused by antibiotic use, infections, or stress. It acts as a probiotic by promoting the growth of beneficial microbes while inhibiting the overgrowth of harmful microorganisms.
- This yeast supports the gut’s microbiome by boosting the numbers of beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which are essential for maintaining digestive health, immune function, and overall wellbeing.
- Supports Gut Health During Antibiotic Use
- One of the primary applications of Saccharomyces boulardii is its ability to help prevent antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) and restore gut flora balance after antibiotics kill off both harmful and beneficial bacteria. Antibiotics often cause a disruption in the gut microbiota, leaving the digestive system vulnerable to imbalanced gut flora.
- Saccharomyces boulardii acts as a protective probiotic, helping to maintain gut health during antibiotic treatment and preventing the growth of opportunistic pathogens like Clostridium difficile that can lead to gut infections.
- Supports Immune Function
- As a probiotic, Saccharomyces boulardii plays a role in boosting the immune system. It helps regulate the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), which is responsible for a significant portion of the body’s immune response. By promoting the activity of immune cells in the gut, Saccharomyces boulardii helps the body defend against harmful microorganisms and infections.
- It also enhances the production of immunoglobulin A (IgA), an important antibody that protects the intestines from pathogens and supports overall immune function.
- Improves Intestinal Barrier Function
- Saccharomyces boulardii helps maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier, which prevents harmful substances, toxins, and pathogens from entering the bloodstream. It supports the mucosal lining of the gut, which is crucial for keeping the intestinal lining healthy and intact.
- By enhancing tight junctions between intestinal cells, it helps prevent leaky gut syndrome and improves gut permeability, thereby reducing the risk of systemic inflammation and food sensitivities.
- Reduces Inflammation in the Gut
- Chronic gut inflammation can disrupt the balance of the microbiome and lead to digestive issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and gastritis. Saccharomyces boulardii has anti-inflammatory properties that help soothe inflammation in the intestines.
- It reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and helps restore the balance of the immune system in the gut, ensuring that inflammatory responses do not overwhelm the digestive system.
- Fights Pathogens and Infections
- Saccharomyces boulardii can help protect the digestive system from harmful pathogens like Salmonella, Escherichia coli (E. coli), and Clostridium difficile. It works by binding to harmful pathogens in the gut and preventing them from adhering to the intestinal walls, which reduces the risk of infections.
- By supporting the gut's microbiome, Saccharomyces boulardii also limits the ability of harmful microbes to proliferate and cause damage to the intestinal lining.
- Regulates Gut Motility
- Saccharomyces boulardii plays a role in regulating gut motility, which is essential for the proper movement of food and waste through the digestive system. It helps improve intestinal transit time, supporting the digestion and absorption of nutrients while promoting regular bowel movements.
- For individuals with constipation or diarrhea, Saccharomyces boulardii can help maintain normal bowel function by promoting the proper movement of the intestines and balancing stool consistency.
- Protects Against Diarrhea and Gastrointestinal Distress
- Saccharomyces boulardii is effective in managing various types of diarrhea, including traveler's diarrhea and gastroenteritis. It helps by inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria and supporting the gut's healing processes.
- It is especially beneficial for individuals who experience diarrhea as a side effect of taking antibiotics, as it helps restore the normal balance of gut flora and prevent the overgrowth of opportunistic pathogens.
- Enhances Nutrient Absorption
- By maintaining a healthy gut environment and ensuring that the gut lining is intact, Saccharomyces boulardii enhances the absorption of nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and amino acids. This is crucial for overall health and wellbeing, as it ensures that the body can effectively absorb the nutrients from food.
- The yeast also supports the proper breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, making it easier for the body to digest and assimilate these macronutrients.
- Supports Overall Digestive Health
- Saccharomyces boulardii helps balance the gut microbiota, supporting digestive health and ensuring that the digestive system functions optimally. By preventing the growth of harmful microbes and promoting the health of beneficial bacteria, it contributes to improved digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function.
- This probiotic yeast also helps alleviate common digestive complaints such as bloating, gas, cramping, and indigestion, supporting overall gut comfort and function.
HOW SACCHAROMYCES BOULARDII HELPS IN GERD, IBS &IBD MANAGEMENT

- How Saccharomyces Boulardii Helps in GERD Management
GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) occurs when stomach acid or contents flow back into the esophagus, causing irritation, heartburn, and discomfort. Saccharomyces boulardii can help manage GERD through the following mechanisms:
- Promotes Gut Health and Microbial Balance
- GERD can be aggravated by an imbalance in the gut microbiome. Saccharomyces boulardii helps restore and maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which supports overall digestive health and helps reduce the frequency of acid reflux episodes.
- A balanced gut microbiota can improve the digestive process and prevent excessive gas production or bloating, which can exacerbate GERD symptoms.
- Reduces Gut Inflammation
- Chronic inflammation in the digestive tract can contribute to GERD. Saccharomyces boulardii has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, which may lead to a reduction in acid reflux and discomfort.
- By reducing gastric and esophageal inflammation, it can help soothe the irritation caused by acid reflux and promote healing in the esophagus.
- Supports Gastrointestinal Motility
- Saccharomyces boulardii can help support gastrointestinal motility, ensuring the smooth movement of food and gastric contents through the digestive system. This is important for people with GERD, as impaired motility can lead to delayed stomach emptying, which may exacerbate reflux.
- By promoting efficient gastric emptying, Saccharomyces boulardii may help reduce the occurrence of reflux episodes.
- How Saccharomyces Boulardii Helps in IBS Management
IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) is a functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation. Saccharomyces boulardii helps manage IBS by improving gut health, balancing the microbiome, and addressing inflammation:
- Reduces Inflammation in the Gut
- IBS is often associated with gut inflammation, particularly in the intestinal lining. Saccharomyces boulardii has anti-inflammatory effects that help reduce inflammation in the gut, which can alleviate symptoms like abdominal pain and bloating.
- By reducing gut inflammation, Saccharomyces boulardii can help reduce the severity and frequency of IBS flare-ups.
- Improves Gut Microbiota
- IBS is often linked to an imbalance in gut bacteria, known as dysbiosis. Saccharomyces boulardii helps restore balance to the microbiome by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria.
- A healthy microbiota can improve digestion, reduce gas production, and mitigate IBS symptoms, particularly bloating and abdominal discomfort.
- Supports Gut Motility
- Saccharomyces boulardii can help regulate gut motility, which is essential in managing IBS symptoms like diarrhea and constipation. By improving the movement of food through the intestines, Saccharomyces boulardii helps reduce the frequency of both diarrhea and constipation in IBS patients.
- The yeast also helps balance bowel movements, promoting regularity and reducing symptoms like bloating or urgency.
- Modulates the Immune System
- IBS is thought to be influenced by abnormal immune responses in the gut. Saccharomyces boulardii helps regulate the immune system in the gastrointestinal tract by enhancing the production of immunoglobulin A (IgA), an antibody that plays a role in mucosal immunity.
- By modulating the immune system, Saccharomyces boulardii may help reduce the immune-related inflammation that contributes to IBS symptoms.
- How Saccharomyces Boulardii Helps in IBD Management
IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease) includes conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, which are characterized by chronic inflammation in the intestines. Saccharomyces boulardii can be beneficial in managing IBD through the following mechanisms:
- Reduces Inflammation
- Saccharomyces boulardii has significant anti-inflammatory effects that can help alleviate the chronic inflammation seen in IBD. It helps modulate the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and promotes the healing of the intestinal lining, reducing inflammation in the gut.
- By calming the inflammation, it may help reduce symptoms like pain, diarrhea, and bloody stools, which are common in IBD flare-ups.
- Improves Intestinal Barrier Function
- IBD often involves a breakdown in the intestinal barrier, allowing harmful substances to leak into the bloodstream, leading to further inflammation. Saccharomyces boulardii helps strengthen the gut barrier, reducing intestinal permeability (also known as leaky gut).
- By maintaining the integrity of the intestinal lining, Saccharomyces boulardii helps prevent harmful substances from triggering inflammation and supports the healing of damaged intestinal tissues.
- Balances the Gut Microbiome
- Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in gut bacteria, is a key factor in the development and progression of IBD. Saccharomyces boulardii helps rebalance the gut microbiome by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria.
- A balanced microbiome supports better digestion, reduces the risk of infection, and helps manage IBD symptoms by keeping harmful bacteria in check.
- Supports the Immune System
- IBD is associated with an abnormal immune response in the gut, which causes ongoing inflammation. Saccharomyces boulardii helps modulate the immune response in the gut, preventing an overactive immune response that can contribute to IBD flare-ups.
- By boosting IgA production and promoting the health of immune cells in the gut, Saccharomyces boulardii helps regulate immune function, which can aid in controlling inflammation and supporting overall gut health.
- Improves Gut Motility
- In IBD, irregular gut motility can lead to symptoms like diarrhea, cramps, and constipation. Saccharomyces boulardii helps regulate gut motility, supporting the movement of food and waste through the digestive system.
- By promoting normal bowel movements, Saccharomyces boulardii helps reduce the frequency of diarrhea and manage the constipation that can sometimes occur in IBD.
HOW SACCHAROMYCES BOULARDII HELPS IN ACIDITY

- Reduces Inflammation in the Gut and Esophagus
- Chronic acidity or acid reflux can lead to inflammation in the esophagus and stomach lining, causing discomfort and pain. Saccharomyces boulardii has anti-inflammatory properties that can help soothe this inflammation.
- By reducing gastric and esophageal inflammation, it helps prevent the irritation that worsens symptoms of acidity, heartburn, and acid reflux. This can lead to less frequent or less severe episodes of acid reflux.
- Supports Gut Microbiota Balance
- An imbalance in the gut microbiome, known as dysbiosis, can contribute to digestive issues like gastric reflux and acid regurgitation. Saccharomyces boulardii helps restore a healthy balance of gut bacteria by promoting the growth of beneficial microbes while inhibiting harmful bacteria.
- A balanced gut microbiome aids in proper digestion and the optimal functioning of digestive enzymes, which can reduce the likelihood of indigestion, bloating, and excessive acid production that contribute to acidity.
- Improves Gastrointestinal Motility
- Delayed gastric emptying (when food stays in the stomach too long) can lead to acid reflux and increased stomach acidity, as the stomach produces more acid in an attempt to digest food. Saccharomyces boulardii can improve gut motility, ensuring that food moves efficiently through the digestive system.
- By promoting regular stomach emptying and normalizing the movement of food and acid, Saccharomyces boulardii helps reduce the likelihood of acid backing up into the esophagus.
- Enhances Intestinal Barrier Function
- Saccharomyces boulardii helps maintain a strong intestinal barrier by promoting the integrity of the gut lining. A strong gut barrier prevents harmful substances from leaking into the bloodstream, which can trigger inflammation and worsen digestive issues like acid reflux and gastritis.
- By supporting the mucosal layer of the intestines and stomach, it ensures that gastric acid stays where it belongs—within the stomach—rather than leaking into the esophagus.
- Regulates Immune Response in the Gut
- An overactive immune response in the digestive tract can contribute to acid reflux and other gastrointestinal conditions. Saccharomyces boulardii helps regulate the immune response in the gut by balancing pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines.
- This immune regulation can help prevent excessive inflammation and hypersensitivity of the stomach lining, which might otherwise contribute to acid overproduction or reflux symptoms.
- Supports Digestive Health and Nutrient Absorption
- Saccharomyces boulardii supports digestive health by improving the breakdown of food, which can reduce the chances of undigested food fermenting in the stomach or intestines, leading to gas production, bloating, and acid reflux.
- By ensuring that the digestive process works efficiently, Saccharomyces boulardii helps reduce excessive stomach acid that might be produced in response to undigested food or irritation.
- Helps Prevent Gastrointestinal Infections
- Some infections, such as Helicobacter pylori, can cause gastritis and peptic ulcers, which can lead to increased acidity and discomfort. Saccharomyces boulardii has been shown to inhibit the growth of harmful pathogens like H. pylori, which can aggravate acidity and lead to stomach ulcers.
By preventing or reducing harmful bacterial growth, Saccharomyces boulardii helps maintain a healthy environment in the digestive tract and may reduce the risk of acid- related complications
HOW STREPTOCOCCUS THERMOPHILUS HELPS IN DIGESTION & DETOXIFICATION

Streptococcus thermophilus is a beneficial bacteria commonly used as a probiotic and an ingredient in the fermentation of dairy products, such as yogurt. It plays an important role in supporting digestion and detoxification by contributing to the balance of gut microbiota, enhancing digestion, and supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
- Supports Lactose Digestion
One of the most well-known benefits of Streptococcus thermophilus is its ability to assist in lactose digestion. Lactose is the natural sugar found in milk, and some individuals are lactose intolerant, meaning their bodies cannot effectively digest this sugar due to a lack of the enzyme lactase.
- Streptococcus thermophilus produces lactase, which helps break down lactose into its simpler components, glucose and galactose, making it easier for the body to absorb and preventing common symptoms of lactose intolerance such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
- This makes it particularly useful for people who have difficulty digesting dairy, helping to improve digestion and reduce discomfort.
- Enhances Gut Health and Digestion
Streptococcus thermophilus is a probiotic that helps maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the gut microbiome. A balanced microbiome is essential for efficient digestion and overall gut health. Here's how it contributes to better digestion:
- Promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria: Streptococcus thermophilus helps support the growth of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria, which are essential for a healthy gut. These beneficial bacteria are involved in the digestion of food, fermentation of dietary fibers, and absorption of nutrients.
- Breaks down complex carbohydrates: Streptococcus thermophilus assists in breaking down certain types of complex carbohydrates, helping with their fermentation in the gut. This process produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are beneficial for the gut lining and digestive health.
- Improves nutrient absorption: By supporting the growth of beneficial bacteria and promoting healthy digestion, Streptococcus thermophilus can enhance the absorption of nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and proteins from food.
- Supports the Detoxification Process
Detoxification involves the body’s ability to eliminate harmful toxins, waste products, and metabolic byproducts. Streptococcus thermophilus contributes to detoxification through several mechanisms:
- Boosts gut barrier function: A healthy gut barrier is crucial for preventing harmful toxins from leaking into the bloodstream. Streptococcus thermophilus helps maintain the integrity of the intestinal lining, preventing leaky gut syndrome, which can contribute to inflammation and the spread of toxins throughout the body.
- Supports the elimination of toxins: By improving the health of the gut, Streptococcus thermophilus plays a role in supporting the body's natural detox processes. A well-functioning digestive system helps in the effective elimination of waste products, preventing toxins from building up and potentially harming the liver and other organs.
- Helps balance gut bacteria: Dysbiosis (an imbalance of gut bacteria) can contribute to toxin buildup, inflammation, and poor digestion. Streptococcus thermophilus helps balance the gut microbiome, which can help reduce the production of harmful toxins in the gut and support overall detoxification.
- Alleviates Bloating and Digestive Discomfort
Bloating and gas can occur when food is not properly digested or when harmful bacteria overgrow in the gut. Streptococcus thermophilus supports gut health by:
- Fermenting food properly: It helps ensure that food is properly fermented and broken down in the intestines, reducing the likelihood of undigested food fermenting and causing gas or bloating.
- Promoting a balanced microbiome: By encouraging the growth of beneficial bacteria, it helps prevent the overgrowth of pathogenic bacteria, which can contribute to digestive discomfort like bloating, indigestion, or gas.
- Supports Immune System Function
The gut plays a central role in the body's immune system, and Streptococcus thermophilus contributes to immune health by maintaining a healthy microbiome and supporting the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT):
- Enhances immune response: A balanced gut microbiota, supported by probiotics like Streptococcus thermophilus, helps modulate the immune response. This helps protect against infections and supports overall detoxification by ensuring that harmful microorganisms are kept in check.
- Reduces inflammation: Streptococcus thermophilus has anti-inflammatory effects that can help reduce gut inflammation, which is important for detoxification and maintaining optimal digestive function.
- Supports Metabolic Health
Streptococcus thermophilus may also support metabolic health by aiding digestion and improving nutrient absorption, both of which are essential for maintaining optimal metabolic function and supporting the body’s detoxification processes:
Regulates metabolism: By improving nutrient absorption and digestion, Streptococcus thermophilus may contribute to the proper metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates, ensuring that the body can efficiently process and eliminate waste products.
HOW STREPTOCOCCUS THERMOPHILUS HELPS IN ENZYME BALANCE

Streptococcus thermophilus plays a role in enzyme balance within the digestive system by contributing to the breakdown of food, enhancing the activity of digestive enzymes, and supporting a balanced gut microbiome.
- Enhancing Lactose Digestion through Lactase Activity
One of the most prominent roles of Streptococcus thermophilus is its ability to produce lactase, the enzyme responsible for breaking down lactose (the sugar found in milk). Lactose intolerance is caused by a deficiency in lactase production, leading to difficulty digesting dairy products. Streptococcus thermophilus helps restore enzyme balance by producing this important enzyme.
- Lactase production: Streptococcus thermophilus helps break down lactose into its simpler sugars, glucose and galactose, which are easier for the body to absorb. This is particularly helpful for individuals who may have low lactase activity, as it compensates for the body's lack of this digestive enzyme.
- Improving digestion of dairy: By producing lactase, Streptococcus thermophilus helps balance the digestive enzymes in the gut and improves the digestion of dairy products, making them more tolerable for those who may experience symptoms of lactose intolerance.
- Supporting the Digestive Enzyme Environment
Streptococcus thermophilus has a broader impact on the digestive environment by promoting the overall balance of gut microbiota, which indirectly affects the activity of other digestive enzymes:
- Microbial balance and enzyme production: A healthy gut microbiome, supported by beneficial bacteria like Streptococcus thermophilus, helps create an optimal environment for the activity of digestive enzymes. A diverse microbiome encourages the production of a variety of enzymes, including proteases, lipases, and amylases, which help break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, respectively.
- Fermentation and nutrient absorption: Streptococcus thermophilus aids in the fermentation of certain carbohydrates in the gut, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). SCFAs play a role in stimulating the release of digestive enzymes from the pancreas and other digestive organs, which further supports enzyme balance in the gut.
- Improving the Function of Pancreatic Enzymes
Streptococcus thermophilus may help improve the function and secretion of pancreatic enzymes, which are essential for the digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates:
- Enzyme stimulation: The presence of beneficial bacteria like Streptococcus thermophilus helps stimulate the secretion of pancreatic enzymes (e.g., amylase, lipase, and protease), which are necessary for breaking down complex macronutrients in the small intestine.
- Efficient digestion: By supporting the activity of these enzymes, Streptococcus thermophilus helps ensure that food is properly broken down and absorbed, reducing the workload on the pancreas and promoting efficient nutrient digestion.
- Balancing Enzyme Activity in the Small Intestine
The small intestine is the site of most enzymatic digestion and nutrient absorption. Streptococcus thermophilus contributes to enzyme balance in the small intestine by supporting the gut's natural processes:
- Gut microbiota regulation: A balanced microbiome with sufficient beneficial bacteria like Streptococcus thermophilus helps prevent an overgrowth of harmful bacteria that could disrupt the activity of digestive enzymes. A stable microbiota enhances the production and activity of enzymes like disaccharidases (which break down sugars), ensuring that digestion occurs smoothly.
- Gut barrier function: Streptococcus thermophilus helps maintain a healthy gut barrier, which is important for proper enzyme function. A strong intestinal lining ensures that digestive enzymes work efficiently and that they are not degraded by harmful substances or pathogens.
- Contributing to Protein Digestion and Absorption
Streptococcus thermophilus also plays a role in supporting the digestion of proteins:
- Peptidase activity: Streptococcus thermophilus can contribute to the breakdown of protein molecules into smaller peptides and amino acids. By doing so, it helps enhance the work of digestive enzymes like pepsin and trypsin, which are involved in protein digestion.
- Facilitating protein absorption: The improved digestion of proteins and peptides allows for more efficient absorption of amino acids, which are critical for body functions such as tissue repair, immune system function, and hormone production.
- Promoting Overall Digestive Health and Enzyme Activity
Finally, Streptococcus thermophilus supports overall digestive health by promoting the proper balance of enzymes throughout the digestive tract:
- Digestive tract balance: By creating a healthy microbial environment, Streptococcus thermophilus helps ensure that digestive enzymes can function properly across all sections of the digestive system, including the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine.
- Preventing enzyme dysfunction: A disrupted gut microbiome can lead to digestive issues like enzyme deficiencies or improper enzyme activity. Streptococcus thermophilus helps maintain microbial balance, which in turn supports the proper function of digestive enzymes, reducing the risk of digestive disorders.
HOW STREPTOCOCCUS THERMOPHILUS HELPS IN PROBIOTIC NEEDS

- Supports Gut Microbiota Balance
One of the primary functions of Streptococcus as a probiotic is its ability to support the balance of gut microbiota:
- Promotes beneficial bacteria: Streptococcus helps promote the growth of other beneficial gut bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which are important for digestive health. This balance is crucial for overall gut health, digestion, and immune function.
- Inhibits harmful bacteria: Streptococcus species can help prevent the overgrowth of pathogenic or harmful bacteria in the gut, such as Clostridium difficile and Escherichia coli, by producing organic acids and other antimicrobial substances that inhibit their growth.
- Enhances Digestion and Nutrient Absorption
Streptococcus probiotics contribute to better digestion and nutrient absorption, essential for overall health:
- Lactase production: Some strains of Streptococcus, like Streptococcus thermophilus, produce the enzyme lactase, which helps break down lactose (the sugar found in milk) into simpler sugars like glucose and galactose, making it easier for people with lactose intolerance to digest dairy products.
- Fermentation of carbohydrates: Streptococcus species assist in the fermentation of carbohydrates, especially fibers and complex sugars, in the gut. This fermentation process produces beneficial compounds, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are important for gut health and nutrient absorption.
- Supports the Immune System
The gut is a crucial part of the immune system, and Streptococcus species play a role in enhancing immune function:
- Boosts immune responses: Probiotics like Streptococcus help stimulate the production of immune cells in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). This enhances the body's ability to fight off infections and maintain immune health.
- Reduces inflammation: By supporting a healthy gut microbiome, Streptococcus can help modulate immune responses and reduce chronic inflammation, which is linked to various health issues, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and autoimmune conditions.
- Improves Gut Barrier Function
A strong intestinal barrier is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system and preventing harmful substances from leaking into the bloodstream. Streptococcus species contribute to this by:
- Strengthening the gut lining: Streptococcus species help maintain the integrity of the intestinal epithelium, which forms the gut barrier. A healthy gut lining prevents leaky gut syndrome, where harmful bacteria and toxins leak into the bloodstream, potentially causing inflammation and systemic health issues.
- Supporting mucosal immunity: Streptococcus helps promote the production of mucus, which forms a protective layer along the gut lining. This mucus barrier helps trap harmful pathogens and toxins, preventing them from reaching the gut wall.
- Alleviates Digestive Issues
Streptococcus probiotics are beneficial for people with digestive issues such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), gastrointestinal discomfort, and constipation:
- Improves gut motility: Some strains of Streptococcus, particularly Streptococcus thermophilus, can improve gut motility, making it easier for the digestive system to process food and prevent constipation.
- Relieves bloating and gas: By supporting the breakdown of food and the fermentation of fiber, Streptococcus can reduce the buildup of gas and bloating, which are common symptoms of digestive discomfort.
- Alleviates symptoms of IBS: Streptococcus species may help reduce symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), such as abdominal pain, bloating, and irregular bowel movements, by promoting gut health and reducing gut inflammation.
- Helps Detoxify the Body
Probiotics like Streptococcus can support detoxification processes in the body by:
- Enhancing gut health: A healthy gut is key to effective detoxification, as it helps eliminate waste products and toxins. Streptococcus aids in the removal of harmful substances by supporting digestion and improving bowel regularity.
- Producing beneficial metabolites: As Streptococcus species ferment fibers and carbohydrates in the gut, they produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as butyrate, which support gut health and play a role in the body’s detoxification pathways.
- Regulating the immune system: By maintaining gut health and preventing intestinal dysbiosis (imbalance of gut bacteria), Streptococcus helps reduce inflammation and supports the body's ability to eliminate toxins more efficiently.
- Helps with Lactose Intolerance
Streptococcus thermophilus, in particular, is known for its ability to break down lactose, making it easier for individuals with lactose intolerance to consume dairy products without experiencing discomfort:
- Lactase production: Streptococcus thermophilus produces the enzyme lactase, which breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose, reducing the digestive discomfort associated with lactose intolerance, such as gas, bloating, and diarrhea.
- Improves Overall Health and Well-Being
By maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, Streptococcus species support overall well-being:
- Supports metabolism: A balanced gut microbiome helps regulate metabolic processes, including the breakdown of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. This supports overall metabolic health and energy levels.
- Enhances nutrient absorption: Probiotics like Streptococcus can help improve the absorption of vitamins and minerals, contributing to better nutritional status and general health.
Promotes mental well-being: The gut-brain connection is well-documented, and maintaining a healthy gut microbiome has been shown to positively affect mental health , including reducing symptoms of anxiety, depression, and stress.
HOW STREPTOCOCCUS THERMOPHILUS HELPS IN GERD , IBS AND IBD MANAGEMENT

1. GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) Management
GERD is a digestive condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing symptoms like heartburn, chest pain, and regurgitation. While Streptococcus thermophilus is not a direct treatment for acid reflux, it can help alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation associated with GERD in the following ways:
Supporting Gut Motility
- Improved gastric motility: Streptococcus thermophilus can help promote the smooth movement of food through the digestive system, reducing the risk of delayed gastric emptying, which can worsen GERD symptoms. When food stays in the stomach for longer periods, it increases the risk of acid reflux.
- Normalizing digestive function: By enhancing overall digestive function, Streptococcus thermophilus supports regular stomach emptying and helps reduce the likelihood of acid regurgitation into the esophagus.
Promoting the Gut Microbiome Balance
- Gut bacteria balance: A healthy gut microbiome plays a key role in controlling inflammation and gut motility. Streptococcus thermophilus supports a balanced microbiota by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which can help soothe the gut and reduce acid reflux symptoms.
- Reducing inflammation: This probiotic strain may help reduce gut inflammation, which could lower the risk of GERD-related esophageal irritation.
2. IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) Management
IBS is a chronic condition that affects the large intestine, causing symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation. Streptococcus thermophilus helps manage IBS symptoms by improving digestion and gut health in several ways:
Enhancing Digestion
- Improved digestion of lactose: Many people with IBS suffer from lactose intolerance. Streptococcus thermophilus produces lactase, an enzyme that breaks down lactose. This helps people with IBS who have trouble digesting dairy products, reducing symptoms like bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
- Promoting efficient digestion: Streptococcus thermophilus supports the overall digestive process by enhancing the breakdown of food and improving the absorption of nutrients. A well-functioning digestive system reduces the likelihood of IBS flare-ups.
Reducing Bloating and Gas
- Fermentation of fibers: Streptococcus thermophilus can help ferment fibers in the gut, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate. SCFAs are beneficial for gut health, as they can reduce bloating and gas, common symptoms of IBS.
- Supporting gut motility: Probiotics like Streptococcus thermophilus can help maintain regular bowel movements and reduce the discomfort of constipation or diarrhea that often accompanies IBS.
Balancing the Gut Microbiome
- Restoring gut flora balance: IBS is often associated with an imbalance of gut bacteria (dysbiosis). Streptococcus thermophilus helps maintain a healthy balance of gut flora, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria that can restore normal bowel function and reduce IBS symptoms.
- Improved gut barrier: This probiotic supports the integrity of the gut lining, which is important for reducing IBS-related inflammation and preventing the passage of harmful substances into the bloodstream.
3. IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease) Management
IBD, which includes conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, involves chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. Streptococcus thermophilus can play a supportive role in managing IBD by reducing inflammation, promoting gut healing, and improving overall digestive health:
Reducing Inflammation
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Streptococcus thermophilus has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. It can help reduce the inflammation that is characteristic of IBD, thereby alleviating symptoms like pain, cramping, and diarrhea.
- Modulating immune function: As a probiotic, Streptococcus thermophilus can help regulate the immune response in the gut. A balanced immune response is crucial for managing the chronic inflammation seen in IBD and preventing flare-ups.
Supporting Gut Barrier Integrity
- Strengthening the gut lining: Streptococcus thermophilus supports the intestinal barrier, which is essential for protecting the digestive system from harmful substances. By improving the gut lining, this probiotic can help prevent the leakage of toxins that may exacerbate inflammation in IBD patients.
- Gut healing: By maintaining the health of the intestinal lining, Streptococcus thermophilus supports the healing process in individuals with IBD, promoting the restoration of the gut’s normal function.
Promoting Digestive Health
- Improved digestion and nutrient absorption: As with IBS, Streptococcus thermophilus helps optimize the digestion and absorption of nutrients. For IBD patients, who may struggle with nutrient deficiencies due to impaired digestion and inflammation, this support is crucial for overall health.
- Balancing gut microbiota: The imbalance of gut microbiota in IBD is a contributing factor to disease progression. Streptococcus thermophilus helps restore the balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which may play a role in reducing IBD flare-ups.
HOW STREPTOCOCCUS THERMOPHILUS HELPS IN ACIDITY

While Streptococcus thermophilus does not directly neutralize stomach acid, its beneficial effects on digestion and gut function can reduce the symptoms of acidity, such as heartburn and discomfort.
- Improves Digestive Health and Gut Motility
- Supports proper digestion: Streptococcus thermophilus helps enhance overall digestion by promoting the breakdown of food, especially lactose, and supporting the absorption of nutrients. Efficient digestion reduces the chances of undigested food fermenting in the stomach and causing excess acid production.
- Promotes gastric motility: By supporting normal stomach emptying and improving gut motility, this probiotic can help prevent delayed gastric emptying, which can contribute to acid reflux or bloating and, by extension, acidity. When food stays in the stomach for too long, it can trigger acid reflux and the subsequent discomfort of acidity.
- Helps with Lactose Digestion
- Lactase production: One of the key roles of Streptococcus thermophilus is producing lactase, an enzyme that breaks down lactose, the sugar in dairy products. For people who are lactose intolerant, undigested lactose can ferment in the stomach and produce gas, bloating, and discomfort, which may worsen acid reflux and contribute to acidity. By breaking down lactose, Streptococcus thermophilus can help reduce these symptoms and ease discomfort.
- Maintains a Balanced Gut Microbiome
- Restores gut balance: Acidity, heartburn, and acid reflux can sometimes be exacerbated by an imbalanced gut microbiome (dysbiosis), where harmful bacteria overgrow, leading to digestive disturbances. Streptococcus thermophilus promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria, helping restore a healthy balance in the gut. This balance improves digestion and reduces symptoms of acidity.
- Prevents harmful bacteria overgrowth: Streptococcus thermophilus may also help keep harmful bacteria in check by outcompeting them for space and resources, preventing an overgrowth of bacteria that could contribute to excess gas, bloating, and digestive discomfort associated with acidity.
- Strengthens the Gut Barrier and Reduces Inflammation
- Gut barrier integrity: The gut lining plays a critical role in protecting the digestive system from irritation and inflammation that can be triggered by excess stomach acid. Streptococcus thermophilus helps maintain the health of the intestinal lining, preventing leaky gut syndrome, where harmful substances can escape into the bloodstream and exacerbate symptoms of digestive discomfort.
- Anti-inflammatory properties: Streptococcus thermophilus has mild anti-inflammatory effects that can help soothe the gut lining, reducing inflammation that may be caused by excess stomach acid and acid reflux. By reducing gut irritation, this probiotic helps alleviate the discomfort associated with acidity.
- Supports Overall Gut Health
- Reduces bloating and gas: Streptococcus thermophilus aids in the fermentation of certain carbohydrates in the gut, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, which help maintain a healthy gut lining. This fermentation process also reduces the production of gas and bloating, which can often accompany acidity or acid reflux. By reducing these symptoms, Streptococcus thermophilus helps alleviate some of the discomfort caused by excessive stomach acid.
- Improves the pH Environment of the Gut
- Regulates gut pH: Streptococcus thermophilus can help maintain a balanced pH in the gut, ensuring that the digestive environment is optimal for digestion. A healthy gut pH helps prevent conditions that could lead to increased acidity, like indigestion or fermentation of undigested food.
HOW FRUCTOOLIGOSACCHARIDE HELPS IN DIGESTION AND DETOXIFICATION

1. Enhancing Digestion
FOS plays a key role in supporting digestive health in the following ways:
Promoting Beneficial Gut Bacteria Growth
- Feeding probiotics: FOS acts as food for beneficial gut bacteria like Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, encouraging their growth and activity. These beneficial bacteria are crucial for healthy digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Balancing gut microbiome: A balanced microbiome, supported by FOS, is vital for efficient digestion. By promoting the growth of good bacteria and inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria, FOS helps maintain an optimal environment in the gut for nutrient breakdown and absorption.
Improving Nutrient Absorption
- Better absorption of minerals: FOS has been shown to improve the absorption of essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and iron in the gut. This is especially important for maintaining overall health, as deficiencies in these minerals can negatively affect digestion and overall well-being.
Supporting Regular Bowel Movements
- Improving stool consistency: FOS helps increase stool bulk and moisture, which can promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation. By improving bowel transit time and stool consistency, FOS supports a healthy digestive process.
- Relieving constipation: As a prebiotic fiber, FOS draws water into the colon, softening stools and helping with constipation relief. It can also stimulate the colon to contract and move waste through the intestines.
2. Supporting Gut Detoxification
FOS contributes to detoxification in several ways:
Supporting the Elimination of Toxins
- Fermentation of FOS in the gut: FOS undergoes fermentation by beneficial gut bacteria, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as butyrate, acetate, and propionate. These SCFAs have various benefits, including nourishing the cells of the intestinal lining, supporting gut health, and helping to eliminate waste and toxins from the body.
- Detoxification of harmful substances: The SCFAs produced during FOS fermentation help maintain a healthy gut barrier, preventing toxins and harmful bacteria from entering the bloodstream. This ensures that waste products and harmful substances are efficiently eliminated from the body through regular bowel movements.
Promoting Liver Health
- Liver detoxification support: Some studies suggest that the SCFAs produced by FOS fermentation may play a role in supporting liver detoxification. The liver is the primary organ responsible for filtering toxins from the body, and maintaining a healthy gut microbiome can improve the liver's ability to detoxify effectively.
- Reducing toxic buildup: FOS helps reduce the toxic burden in the body by promoting the elimination of waste products. This can aid in detoxification by ensuring that toxins are effectively removed from the digestive system before they accumulate in the body.
3. Reducing Inflammation
- Gut inflammation reduction: A healthy gut microbiome, supported by FOS, helps reduce inflammation in the digestive tract. Chronic gut inflammation can hinder digestion and detoxification, but by fostering a balanced microbiome, FOS can help reduce this inflammation, making detoxification more effective.
- Supporting gut barrier function: FOS promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria that help maintain the integrity of the gut lining, which serves as a barrier to prevent harmful substances from leaking into the bloodstream. A strong gut barrier is essential for protecting the body from harmful toxins and inflammation.
4. Alleviating Digestive Discomfort
- Reducing bloating and gas: FOS can promote the fermentation of fibers in the gut, which produces beneficial short-chain fatty acids. These SCFAs help alleviate symptoms like bloating, indigestion, and gas, which are often associated with poor digestion and toxin buildup.
- Soothing the digestive tract: By encouraging the growth of beneficial bacteria and improving gut health, FOS can help alleviate digestive discomforts such as bloating, cramping, and excess gas, leading to smoother digestion and detoxification.
5. Enhancing Immune Function
- Boosting gut immunity: Since a significant portion of the immune system is located in the gut, promoting gut health with prebiotics like FOS can enhance overall immune function. A balanced microbiome helps the body better resist infections and inflammation, which is key in preventing the toxic overload that can occur when the immune system is compromised.
6. Weight Management and Detoxification
- Supporting weight loss: FOS has been shown to help regulate appetite and promote feelings of fullness. By supporting healthy digestion and helping control calorie intake, FOS may assist with weight management, which in turn supports detoxification by preventing the accumulation of toxins that can arise from metabolic imbalances.
Reducing fat storage: Some studies suggest that FOS can influence fat metabolism, which could help reduce the accumulation of fat in the body. By preventing the buildup of excess fat, FOS supports detoxification processes that are otherwise impaired by excess body fat.
HOW FRUCTOOLIGOSACCHARIDE HELPS IN ENZYME BALANCE

- Encouraging Growth of Beneficial Bacteria
- Prebiotic effect: FOS acts as food for beneficial gut bacteria such as Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli. These bacteria are important for the production of various digestive enzymes that help break down nutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. By promoting the growth of these bacteria, FOS helps ensure that there is an adequate supply of the enzymes needed for efficient digestion.
- Balancing gut microbiome: A healthy and balanced microbiome is essential for proper enzymatic function. When harmful bacteria or pathogens dominate, they can disrupt digestive enzyme activity, leading to issues like bloating, indigestion, and poor nutrient absorption. FOS helps maintain a balance of gut bacteria, indirectly ensuring that digestive enzymes are functioning optimally.
- Enhancing Enzyme Production
- Fermentation of FOS by gut bacteria: When FOS reaches the colon, it undergoes fermentation by the gut microbiota, particularly beneficial bacteria. This fermentation produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, propionate, and acetate, which contribute to the health of the gut lining. Healthy gut cells are essential for producing enzymes that aid digestion, so maintaining the integrity of the gut with FOS helps optimize enzyme production.
- Improving lactase activity: FOS can also help improve lactase activity in the gut. Lactase is the enzyme responsible for breaking down lactose (the sugar found in milk). Since FOS promotes the growth of Lactobacilli, which are involved in lactase production, this can help improve lactose digestion, especially in individuals who are lactose intolerant. By improving enzyme activity, FOS contributes to better digestion of dairy products.
- Supporting Pancreatic Enzyme Function
- Encouraging proper nutrient digestion: FOS helps maintain a healthy gut environment, which can support the pancreas in producing and releasing digestive enzymes such as amylase, lipase, and protease. These enzymes are critical for breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, respectively. By supporting the overall health of the digestive system, FOS helps ensure that these enzymes are produced in adequate amounts and function effectively.
- Improving enzymatic breakdown of fibers: FOS itself is a fiber, and when it is fermented by gut bacteria, it helps promote the breakdown of other dietary fibers in the digestive tract. This enhances the gut's ability to digest complex carbohydrates and other fibrous foods, ensuring a balance of enzymatic activity throughout the digestive process.
- Supporting Gut Motility and Enzyme Efficiency
- Improving gut motility: Healthy gut motility ensures that food moves smoothly through the digestive tract, providing enzymes enough time to work on breaking down food. FOS aids in maintaining healthy motility by supporting the gut microbiome, which in turn helps promote regular bowel movements and optimal digestive enzyme function.
- Reducing fermentation by harmful bacteria: By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, FOS can prevent an overgrowth of harmful bacteria that produce unwanted by-products (like gases) during fermentation. This imbalance can interfere with normal enzyme function. FOS helps maintain a balanced microbial environment that supports the proper functioning of digestive enzymes.
- Improving Enzyme Activity in the Small Intestine
- Optimizing digestive enzyme production: In addition to its effects on the gut flora, FOS can help optimize the enzyme activity in the small intestine, where most nutrient absorption takes place. By fostering the growth of beneficial bacteria, FOS supports enzyme systems like sucrase, maltase, and lactase, which are responsible for breaking down complex sugars and carbohydrates into simpler forms that can be absorbed by the body.
- Enhancing Detoxification Enzyme Function
Supporting liver detoxification: The liver is responsible for detoxifying the body, and FOS has been shown to support liver function. This indirectly affects the activity of liver enzymes involved in detoxification. By improving the health of the gut microbiome and promoting regular elimination of waste through bowel movements, FOS helps reduce the burden on detoxification enzymes in the liver.
HOW FRUCTOOLIGOSACCHARIDE HELPS IN PROBIOTIC NEEDS

Fructooligosaccharides (FOS) are a type of prebiotic fiber that plays a critical role in supporting probiotic needs by enhancing the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria in the gut
- Feeding Beneficial Gut Bacteria
- Fuel for probiotics: FOS acts as a food source for beneficial bacteria, particularly Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, which are important probiotics that help maintain a healthy gut microbiome. By promoting the growth and activity of these good bacteria, FOS helps support a balanced and diverse gut microbiome.
- Promotes probiotic colonization: When FOS is consumed, it travels through the small intestine without being digested and reaches the colon, where it serves as a substrate for fermentation by beneficial gut bacteria. This fermentation process helps increase the population of probiotic bacteria in the gut, enhancing their colonization and overall effectiveness.
- Boosting the Growth of Beneficial Bacteria
- Selective stimulation of probiotics: FOS selectively stimulates the growth of beneficial bacteria while inhibiting the growth of harmful or pathogenic bacteria. By providing the right nutrients for probiotics, FOS helps increase the abundance of these beneficial microbes in the gut, which is essential for maintaining digestive health and supporting immune function.
- Enhancing probiotic activity: When FOS encourages the growth of Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, these bacteria, in turn, produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as butyrate, acetate, and propionate, which have anti-inflammatory effects and contribute to gut health. These SCFAs also help improve the absorption of minerals, protect the intestinal lining, and support overall digestive function.
- Maintaining a Healthy Gut Microbiome
- Gut microbiome balance: A healthy gut microbiome is essential for overall health, including digestion, immune function, and mental well-being. FOS helps maintain this balance by feeding the beneficial probiotics that crowd out harmful bacteria, preventing dysbiosis (an imbalance between beneficial and harmful gut bacteria). The growth of beneficial bacteria promoted by FOS strengthens the gut microbiome and supports a healthy digestive system.
- Preventing pathogen overgrowth: FOS helps reduce the likelihood of pathogenic bacteria (harmful bacteria) overgrowing in the gut by promoting the growth of beneficial probiotics that outcompete harmful bacteria for nutrients and space. This reduces the risk of infections and digestive issues caused by harmful bacteria.
- Improving Probiotic Efficacy
- Synergy with probiotics: When consumed together with probiotics (such as in probiotic supplements or fermented foods), FOS enhances the effectiveness of the probiotics. This is because FOS provides the necessary nutrients for probiotics to thrive, allowing them to work more efficiently in promoting gut health.
- Supporting probiotic supplementation: FOS is often included in many probiotic supplements as a synbiotic—a combination of prebiotics and probiotics. This combination ensures that the probiotics have the optimal environment to flourish and provide their beneficial effects on the gut.
- Supporting Digestive Health and Immunity
- Promoting gut barrier function: By supporting the growth of beneficial bacteria, FOS helps enhance the gut barrier. A healthy gut barrier prevents harmful substances from leaking into the bloodstream and causing inflammation or immune system disruption. The beneficial bacteria fueled by FOS produce SCFAs, which help nourish the cells of the gut lining, strengthening the barrier function.
- Boosting immune function: Probiotics play a critical role in modulating the immune system. By promoting the growth of beneficial probiotics, FOS indirectly supports immune function, as a healthy gut microbiome is essential for proper immune responses. FOS helps ensure that probiotics can thrive and provide immune benefits, such as the production of antimicrobial substances that protect the gut from infections.
- Enhancing Metabolism and Gut Motility
- Improving digestive efficiency: FOS helps regulate gut motility and improve the efficiency of digestion by ensuring that beneficial bacteria are present to break down food and absorb nutrients properly. By supporting probiotics, FOS aids in maintaining smooth digestion and preventing issues like constipation, bloating, and gas.
- Regulating the digestive process: The beneficial bacteria promoted by FOS can also help with the fermentation of complex carbohydrates, producing SCFAs that contribute to overall gut health and metabolism. This fermentation process can help balance digestive enzyme activity and prevent indigestion.
HOW FRUCTOOLIGOSACCHARIDE HELPS IN GERD, IBS & IBD MANAGEMENT
- GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
GERD is characterized by the backflow of stomach acids into the esophagus, causing symptoms like heartburn, chest pain, and regurgitation. While FOS doesn’t directly affect acid production or reflux, it helps manage symptoms by promoting a healthier gut environment in several ways:
- Promotes healthy gut microbiome: FOS supports the growth of beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria. A balanced microbiome can help reduce gut dysbiosis (an imbalance of good and bad bacteria), which may contribute to GERD symptoms.
- Strengthening gut barrier: FOS contributes to the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), like butyrate, which nourish the cells of the intestinal lining, strengthening the gut barrier. A strong gut lining may help reduce gut inflammation, which can exacerbate GERD symptoms. When the gut barrier is intact, the likelihood of acid reflux and irritation from food or stomach acid decreases.
- Improves motility: FOS helps promote healthy gut motility, which may reduce the likelihood of slow digestion and food stagnation in the stomach—two potential contributors to GERD. When the digestive process runs smoothly, it may lessen the chances of acid backflow.
- Reducing inflammation: FOS helps reduce inflammation in the gut through the production of SCFAs, which are known to have anti-inflammatory effects. Inflammation is a common factor in GERD, and by reducing it, FOS can help alleviate symptoms.
- IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
IBS is a common condition characterized by symptoms like bloating, abdominal pain, constipation, and diarrhea. FOS may offer relief from these symptoms by promoting a healthy gut microbiome and supporting overall digestive function:
- Improves gut flora balance: FOS promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria such as Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, which play a key role in maintaining a healthy digestive system. A balanced microbiome can help reduce symptoms of IBS, including bloating and discomfort.
- Relieves constipation: FOS is a prebiotic fiber, which can help regulate bowel movements. It draws water into the colon and helps soften stool, easing constipation. For individuals with IBS-C (constipation-predominant IBS), FOS can help promote more regular and comfortable bowel movements.
- Reduces bloating and gas: In IBS, excessive gas production and bloating can be problematic. FOS encourages the fermentation of fiber by good bacteria, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like acetate and butyrate. These SCFAs help reduce bloating and gas buildup, improving overall digestive comfort.
- Supports gut motility: FOS can improve gut motility by fostering the growth of beneficial bacteria that regulate the movement of food through the digestive tract. Proper motility is essential for preventing the discomfort associated with IBS, particularly bloating and cramping.
- Reduces gut inflammation: The SCFAs produced during FOS fermentation also help reduce inflammation in the gut. This is especially beneficial for those with IBS-D (diarrhea-predominant IBS), where inflammation plays a role in disrupting normal bowel function.
- IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease)
IBD encompasses chronic inflammatory conditions of the gastrointestinal tract, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. FOS can be a valuable tool in managing IBD by supporting gut health and reducing inflammation:
- Reduces inflammation: As in IBS, FOS helps produce SCFAs, especially butyrate, which has strong anti-inflammatory properties. Butyrate nourishes the cells of the colon lining, helping to maintain the intestinal barrier and reduce inflammation. For IBD patients, reducing inflammation is a critical part of managing the condition.
- Supports gut barrier function: The gut barrier is often compromised in IBD, leading to “leaky gut,” where harmful substances can pass into the bloodstream, triggering immune responses. FOS helps improve gut barrier integrity by fostering the growth of beneficial bacteria that produce SCFAs. A healthier gut lining helps prevent the inflammatory response that exacerbates IBD.
- Promotes healthy gut microbiota: Dysbiosis (an imbalance between beneficial and harmful bacteria) is a common feature in IBD. FOS helps restore balance in the microbiome by encouraging the growth of beneficial bacteria, particularly Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, which play a role in managing inflammation and supporting immune health.
- Promotes regular bowel movements: For IBD patients, FOS can help regulate bowel movements. By promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria and improving gut motility, FOS can assist in normalizing stool consistency and reducing diarrhea, a common symptom of IBD.
- Supports overall digestive health: FOS helps support digestive health in IBD by maintaining a healthy balance of beneficial gut bacteria, supporting digestion, and aiding in nutrient absorption. A healthy gut microbiome can improve overall digestion and reduce flare-ups associated with IBD.
HOW FRUCTOOLIGOSACCHARIDE HELPS IN ACIDITY
Fructooligosaccharides (FOS), as a type of prebiotic fiber, can help manage acidity (commonly linked to acid reflux or heartburn) by supporting overall digestive health
- Supporting Healthy Gut Flora
- Promoting beneficial bacteria: FOS acts as food for beneficial gut bacteria like Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria. These good bacteria help balance the gut microbiome and promote optimal digestion. When the gut microbiome is healthy, the risk of gut dysbiosis (imbalance of bacteria) is reduced. Dysbiosis can contribute to gut inflammation and potentially worsen acidity by affecting how food is digested and absorbed, leading to discomfort.
- Improving digestion: The growth of beneficial bacteria supports the proper breakdown and absorption of food. This is important because poorly digested food in the stomach or intestines can contribute to excess acid production or slow digestion, which can aggravate symptoms of acidity.
- Reducing Inflammation
- Anti-inflammatory effects: One of the key benefits of FOS is the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate during its fermentation by gut bacteria. Butyrate has anti-inflammatory properties and helps to reduce inflammation in the digestive tract, including the stomach. This reduction in inflammation can be beneficial for individuals suffering from conditions that lead to acidity or reflux, as inflammation often worsens acid-related discomfort.
- Promoting gut healing: By reducing inflammation and supporting the integrity of the gut lining, FOS may help repair any damage to the mucosal lining of the stomach or intestines, which can reduce the risk of acid irritation and improve overall digestion. A healthy gut lining is better able to handle stomach acid without leading to excessive discomfort.
- Supporting Gut Motility
- Improving motility: FOS can promote regular gut motility, which ensures that food moves smoothly through the digestive tract. Proper motility can help prevent food stagnation in the stomach, which is one of the factors that can contribute to acid reflux or excessive acidity. When the stomach empties properly and efficiently, it reduces the chances of acid lingering in the stomach, thereby lowering the risk of acid backflow (reflux).
- Preventing bloating and discomfort: FOS helps alleviate bloating, which is another common symptom associated with acidity. By encouraging the growth of beneficial bacteria and supporting efficient digestion, FOS helps to reduce gas buildup and bloating, both of which can put additional pressure on the stomach and increase the likelihood of acid reflux.
- Enhancing the Production of SCFAs
- Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, acetate, and propionate are produced when FOS is fermented in the gut. SCFAs have several beneficial effects on digestion:
- Butyrate has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce irritation in the stomach and intestines, which can alleviate the discomfort caused by acidity.
- SCFAs help maintain gut barrier integrity, preventing harmful substances from leaking into the bloodstream and triggering immune responses that could aggravate symptoms of acidity or reflux.
- Improving the pH Balance in the Gut
- Modulating gut pH: The fermentation of FOS by beneficial bacteria results in the production of SCFAs, which can lower the pH of the colon. A lower pH helps create an environment that favors the growth of beneficial bacteria while discouraging the growth of harmful bacteria that can lead to dysbiosis and digestive issues, including acid reflux. A more balanced gut pH can help support normal digestive processes, reducing the likelihood of acidity symptoms.
- Enhancing Overall Digestion and Nutrient Absorption
- Supporting digestive efficiency: FOS aids in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients by nourishing beneficial gut bacteria that aid in digestion. When the body absorbs nutrients more efficiently, there is less likelihood of undigested food remaining in the stomach or intestines, which can cause fermentation, gas, and bloating that may aggravate acidity. FOS can, therefore, indirectly improve digestion and reduce acidity by supporting overall digestive function.
HOW ACTIVATED CHARCOAL HELPS IN DIGESTION & DETOXIFICATION

1. Detoxification: Adsorbing Toxins and Impurities
- Binding to toxins: One of the primary mechanisms by which activated charcoal works is its ability to adsorb toxins, chemicals, and impurities in the gastrointestinal tract. This means that activated charcoal can attract and bind to substances like harmful bacteria, heavy metals, toxins, chemicals, and drugs (both prescription and recreational). Once bound to these harmful substances, activated charcoal helps carry them out of the body through the digestive system.
- Detoxification of the gut: Activated charcoal may assist in the detoxification process by removing toxins from the digestive system before they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. This may be particularly useful in cases of food poisoning, overeating, or exposure to certain toxins. It binds to harmful substances in the stomach and intestines, preventing them from being absorbed by the body and thus aiding in detoxification.
- Helping with drug overdose or poisoning: Activated charcoal is sometimes used in medical settings to treat certain types of poisoning or drug overdoses, as it can bind to a wide range of toxic substances, limiting their absorption into the bloodstream.
2. Supporting Digestive Health by Reducing Bloating and Gas
- Reducing bloating: Activated charcoal can help reduce bloating and gas by binding to gases in the gastrointestinal tract. Gases like hydrogen and methane produced during the fermentation of food in the gut can cause bloating and discomfort. Activated charcoal adsorbs these gases, potentially leading to a reduction in bloating, discomfort, and flatulence.
- Relieving indigestion: Activated charcoal may also help alleviate discomfort associated with indigestion or gastrointestinal distress. It can help to adsorb food particles and gases that might be contributing to digestive issues like burping, acid reflux, or feeling overly full.
- Helping with food intolerance: In some cases, activated charcoal has been used as a way to help reduce discomfort associated with food intolerances or digestive issues that arise from consuming certain foods that can cause gas or bloating.
3. Neutralizing Harmful Substances in the Gut
- Removing excess acids: Although activated charcoal doesn’t directly neutralize stomach acid in the way that antacids do, its adsorptive properties may help to reduce the harshness of excessive acid in the stomach by binding to the food particles and potential irritants in the stomach. This may help alleviate some of the symptoms associated with acid reflux or indigestion.
- Binding to undigested food: Sometimes, foods that are not fully digested can ferment and produce harmful byproducts in the stomach. Activated charcoal helps by binding to these undigested food particles and preventing their further fermentation, which can help reduce the production of harmful gases and acids in the gut.
4. Helping with Inflammatory Conditions
- Potential support for IBS and IBD: Some studies suggest that activated charcoal may help reduce symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), such as bloating, pain, and gas. By adsorbing toxins and reducing irritation in the gut, it may help alleviate some of the digestive discomfort associated with these conditions.
- Soothing inflammation: While not a direct anti-inflammatory agent, activated charcoal’s ability to remove toxins and reduce gut irritation may help support gut health and reduce some of the inflammation or discomfort associated with digestive conditions.
5. Promoting Overall Digestive Cleanse
- Supporting the body's natural detox process: Activated charcoal can be used as part of a digestive cleanse to help clear the digestive system of accumulated toxins, undigested food particles, and harmful byproducts. By adsorbing these substances, activated charcoal assists in the body’s natural detox process, helping to improve overall digestive health and function.
- Improving nutrient absorption: By removing harmful substances that may interfere with nutrient absorption, activated charcoal may help optimize the body’s ability to absorb essential nutrients from food. While this is still a topic of some debate, reducing digestive toxins could help improve overall digestive function and nutrient uptake.
HOW ACTIVATED CHARCOAL HELPS IN ENZYME BALANCE

Activated charcoal primarily works through its adsorptive properties, meaning it binds to substances within the digestive system and helps eliminate them from the body.
- Reducing Toxin Load
- Detoxification: One of activated charcoal's key functions is to adsorb toxins, chemicals, and other harmful substances from the digestive tract. These toxins can disrupt the normal function of digestive enzymes by irritating the stomach and intestines or by interfering with the natural pH balance required for enzyme activity. By removing these harmful substances, activated charcoal may indirectly support the optimal functioning of enzymes.
- Preventing gut inflammation: Toxins and waste products can also lead to gut inflammation, which can hinder the proper secretion and activity of digestive enzymes. Activated charcoal may reduce this inflammation by adsorbing toxins, helping to restore an environment more conducive to enzyme activity.
- Promoting a Healthier Gut Microbiome
- Balancing gut bacteria: Although activated charcoal does not directly affect enzyme production, its ability to improve gut health indirectly supports enzyme balance. By adsorbing harmful substances that could promote the growth of bad bacteria, charcoal helps foster a more balanced microbiome. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for enzyme function, as gut bacteria often play a role in producing or activating certain digestive enzymes.
- Reducing fermentation byproducts: Some undigested food particles in the gut can ferment, producing harmful byproducts that may interfere with the activity of digestive enzymes. Activated charcoal binds to these byproducts, preventing them from disrupting enzyme function and allowing enzymes to work more efficiently.
- Supporting Digestive Efficiency
- Reducing digestive overload: By adsorbing excess food particles, gases, and toxins, activated charcoal may help prevent the digestive system from becoming overloaded. This allows the body to focus on digestion and better utilize its enzymes for breaking down nutrients. When the digestive system isn't overloaded with waste or harmful substances, enzymes can function more effectively and efficiently.
- Preventing bacterial imbalances: An imbalance in gut bacteria can lead to poor digestion, fermentation, and production of gases that may interfere with enzyme action. Activated charcoal helps remove some of the excess gases and undigested food particles that can disrupt digestion and potentially interfere with enzyme efficiency.
- Minimizing the Impact of Excessive Gas and Bloating
- Alleviating gas production: By binding to gas-producing substances, activated charcoal can reduce bloating and excess gas. This can prevent the stretching of the stomach and intestines, which can alter the pH and create an environment that is less favorable for enzymes to function properly. By reducing bloating, charcoal may help maintain an optimal environment for enzymes to work effectively.
- Helping With Indigestion and Improper Digestion
Supporting enzyme function indirectly: When indigestion occurs due to the presence of toxins or undigested food particles, the digestive process can become inefficient, affecting enzyme production and activity. Activated charcoal helps to clear the digestive system of these substances, supporting the body’s ability to digest food properly and allowing enzymes to break down food more efficiently.
HOW ACTIVATED CHARCOAL HELPS IN PROBIOTIC NEEDS

- Supporting Gut Detoxification
- Adsorbing Toxins and Harmful Substances: Activated charcoal has powerful adsorptive properties, meaning it binds to toxins, heavy metals, and other harmful substances in the gut. This detoxification process helps to cleanse the gastrointestinal system, creating a healthier environment for probiotics to thrive.
- Reducing Gut Inflammation: Harmful substances in the gut, such as toxins, excess gas, or waste, can lead to gut inflammation. Inflammation can disrupt the balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut, including probiotics. By removing these harmful substances, activated charcoal helps create a less inflamed and more balanced environment where probiotics can function more effectively.
- Supporting Digestive Health
- Reducing Digestive Discomfort: Activated charcoal can help alleviate common digestive issues like bloating, gas, and indigestion, all of which can impact the balance of gut bacteria, including probiotics. By reducing discomfort and improving overall digestion, activated charcoal helps the digestive system work more efficiently, allowing probiotics to better support digestive health.
- Minimizing Fermentation byproducts: Undigested food particles in the gut can ferment, producing gases and byproducts that may harm the gut microbiome. Activated charcoal adsorbs these byproducts, preventing them from harming beneficial bacteria, including probiotics.
- Promoting a Balanced Gut Microbiome
- Encouraging Probiotic Growth: By detoxifying the gut and clearing out harmful substances, activated charcoal can create an environment where healthy bacteria, including probiotics, can thrive. A cleaner gut with fewer toxins allows probiotics to perform their role in digestion and immune health more effectively.
- Supporting Symbiotic Relationships: Activated charcoal helps maintain a balance in the gut, which supports the overall health of both probiotics and prebiotics. Probiotics thrive in a balanced environment where harmful bacteria are kept in check, and activated charcoal plays a role in fostering such an environment.
- Improving Gut Barrier Function
- Reducing Toxic Load: Activated charcoal helps reduce the toxic load on the body by binding to harmful substances in the gut and aiding in their elimination. This allows the gut barrier to function more efficiently, which is essential for gut health and the survival and function of probiotics. A healthy gut barrier also prevents harmful bacteria from crossing into the bloodstream, promoting the overall health of the gut microbiome.
- Assisting with Digestive Cleansing
- Cleansing the Digestive System: Activated charcoal can be part of a digestive cleanse, removing accumulated toxins and waste that may interfere with the function of probiotics. By clearing out harmful substances, activated charcoal helps create an environment where probiotics can thrive, ensuring a healthier gut microbiome.
HOW ACTIVATED CHARCOAL HELPS IN GERD, IBS & IBD MANAGEMENT

- GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
Activated charcoal may provide relief from some of the symptoms associated with GERD by targeting the factors that contribute to discomfort and acid reflux.
- Binding to Gases: Activated charcoal is known to adsorb gases produced during digestion. This can help reduce bloating and excess gas, which may contribute to pressure on the stomach and the esophagus, potentially alleviating some GERD symptoms like heartburn and acid reflux.
- Reducing Bloating and Pressure: GERD symptoms can worsen when gas and bloating increase pressure on the stomach, potentially pushing stomach acid back into the esophagus. By reducing gas and bloating, activated charcoal helps to ease this pressure, possibly decreasing the likelihood of acid reflux.
- Absorbing Toxins and Byproducts: Charcoal helps in detoxifying the digestive system by binding to toxins and metabolic byproducts that can irritate the digestive tract. This may lead to reduced stomach irritation and, in turn, reduced acid reflux symptoms.
- IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
For people with IBS, activated charcoal may help manage symptoms like bloating, gas, and digestive discomfort.
- Reducing Bloating and Gas: One of the hallmark symptoms of IBS is bloating and excessive gas. Activated charcoal can bind to the gas and help reduce bloating, which often causes discomfort in individuals with IBS. By absorbing the gas, it can help prevent the excessive buildup of gas that leads to distension and discomfort.
- Alleviating Digestive Discomfort: IBS is often accompanied by symptoms such as abdominal pain, cramping, and irregular bowel movements. Activated charcoal may provide relief by adsorbing some of the harmful substances or irritants in the gut that contribute to inflammation and discomfort, potentially improving overall digestive comfort.
- Supporting Gut Detoxification: In people with IBS, the gut may become more sensitive to irritants or undigested food particles. Activated charcoal can help by adsorbing these irritants, leading to a cleaner digestive tract and less irritation, which could reduce IBS flare-ups.
- IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease)
For individuals dealing with IBD (like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis), activated charcoal may offer relief from certain symptoms, though it should be used under medical supervision, as IBD is a chronic and complex condition.
- Reducing Gas and Bloating: Just as in IBS, gas production and bloating can be significant problems for individuals with IBD. Activated charcoal helps by adsorbing the gas in the intestines, potentially reducing bloating and discomfort that can aggravate IBD symptoms.
- Detoxification and Reduction of Toxins: One of the primary benefits of activated charcoal is its ability to adsorb toxins, heavy metals, and metabolic byproducts. For individuals with IBD, the gut can become inflamed, and toxins may build up in the system. Activated charcoal helps detoxify the gut, potentially reducing inflammation and providing some relief from symptoms.
- Reducing Inflammation: While activated charcoal itself is not an anti-inflammatory agent, its ability to bind to harmful substances and reduce gut irritation may indirectly support the body’s efforts to reduce inflammation. By creating a less toxic environment in the gut, activated charcoal may help in managing the symptoms of IBD.
General Benefits of Activated Charcoal for GERD, IBS, and IBD
- Supporting Gut Health: Activated charcoal can help by clearing out harmful substances from the digestive system, promoting a healthier environment where the gut can function more efficiently.
- Absorbing Excess Acids and Gases: By binding to excess acids and gases, activated charcoal helps to reduce pressure and discomfort associated with digestive issues.
Reducing Irritation: Activated charcoal may help soothe the digestive tract by removing irritants and toxins, which is beneficial for individuals with sensitive digestive systems, especially those dealing with conditions like GERD, IBS, or IBD.
HOW ACTIVATED CHARCOAL HELPS IN ACIDITY

- Adsorbing Excess Gas and Reducing Bloating
- Bloating and Gas: When there's excess gas in the stomach and intestines, it can put pressure on the stomach and lead to acid reflux or worsen heartburn symptoms. Activated charcoal has adsorptive properties, which means it can bind to and help eliminate excess gas in the digestive system. By reducing bloating and discomfort, charcoal may help ease the pressure that can contribute to acid rising from the stomach into the esophagus.
- Reducing Pressure on the Stomach
- Pressure Relief: Acid reflux is often triggered when pressure in the stomach increases, pushing stomach acid up into the esophagus. By helping to reduce bloating and gas, activated charcoal may reduce the overall pressure on the stomach, potentially lowering the chances of acid reflux episodes.
- Absorbing Harmful Toxins
- Detoxification: Activated charcoal works by binding to toxins, chemicals, and waste products in the gut. Some of these substances may irritate the stomach lining and increase acid production, exacerbating acidity and discomfort. By adsorbing these irritants, activated charcoal can help reduce the inflammation in the stomach and esophagus that can contribute to acid-related symptoms.
- Supporting Digestive Comfort
- Promoting Better Digestion: Activated charcoal can help reduce the feeling of fullness or indigestion, common symptoms of acidity. By clearing out excess food particles and other substances, charcoal can help support smoother digestion, preventing the disruption of stomach acid levels that can lead to acidity.
- Absorbing Stomach Acid (Indirectly)
- While activated charcoal does not directly neutralize stomach acid, it can help bind to acids and some acidic byproducts in the stomach. This may offer some temporary relief by reducing the total acidic load in the stomach and potentially preventing irritation of the esophagus.
HOW FUNGAL AMYLASE HELPS IN DIGESTION AND DETOXIFICATION
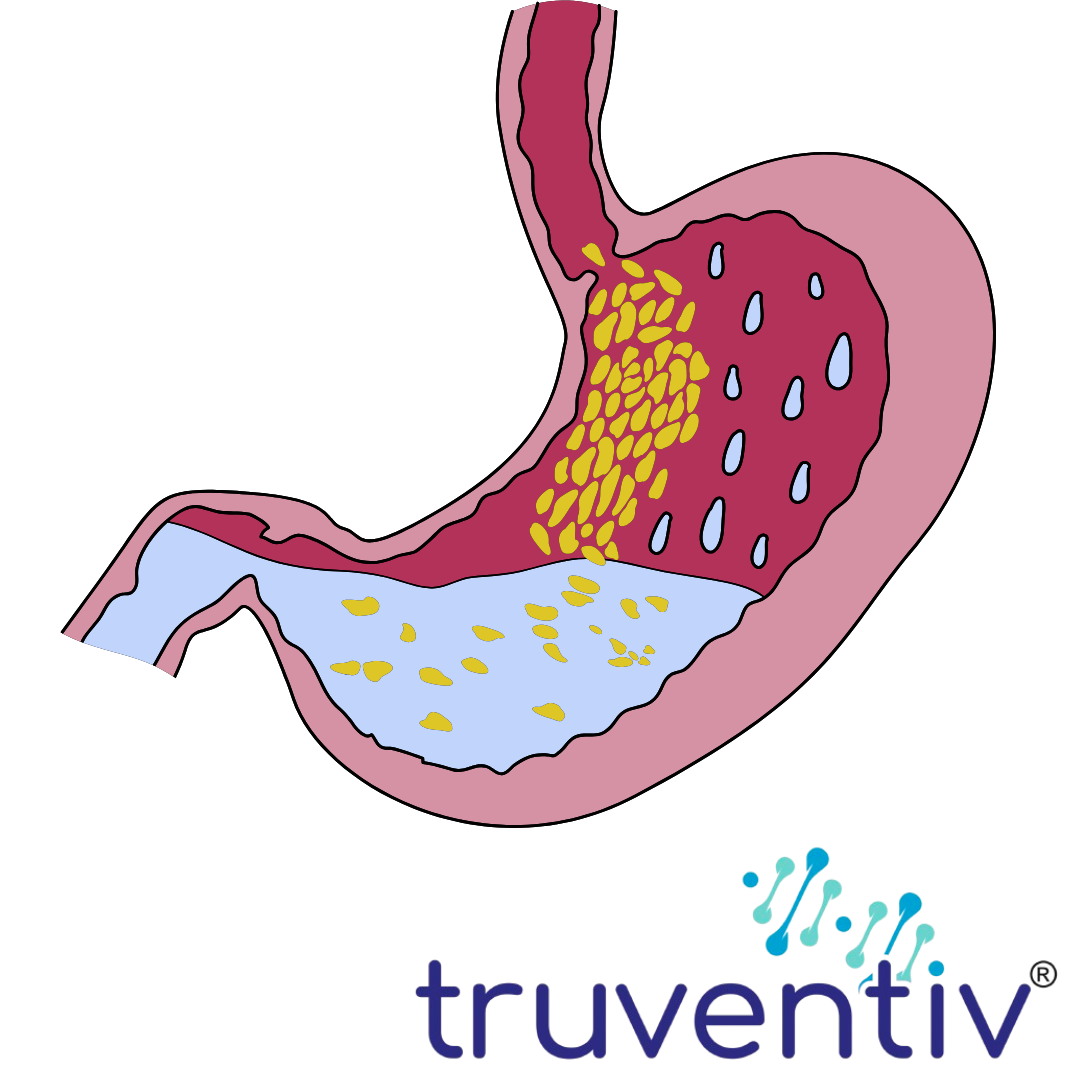
Fungal amylase is an enzyme derived from fungi, often used in digestive supplements to assist in breaking down complex carbohydrates, such as starches, into simpler sugars. This can help with the digestion and detoxification process in several important ways:
1. Aiding in Carbohydrate Digestion
- Breaking Down Starches: Fungal amylase helps break down complex carbohydrates (like starches) into simple sugars (like maltose and glucose), making them easier for the body to absorb. This is particularly helpful for individuals who may have difficulty digesting carbohydrates, ensuring better absorption of nutrients.
- Improving Digestive Efficiency: By aiding in the digestion of starchy foods, fungal amylase can improve overall digestive efficiency. This can help alleviate symptoms like bloating, gas, and discomfort that often arise from undigested carbohydrates fermenting in the gut.
2. Supporting Detoxification
- Reducing Toxin Build-up: When carbohydrates are not properly broken down and absorbed, they can ferment in the intestines, producing gases and byproducts that can contribute to digestive discomfort. This fermentation process can also lead to the build-up of harmful toxins. By breaking down starches more efficiently, fungal amylase can help reduce the fermentation of undigested carbohydrates and the subsequent toxin production.
- Supporting Gut Health: Efficient digestion and nutrient absorption support a healthier gut microbiome, which plays an important role in detoxification. A well-functioning digestive system allows the body to more effectively eliminate waste and toxins, reducing the load on the liver and other detoxifying organs.
3. Alleviating Bloating and Gas
- Preventing Fermentation: When starches and complex carbohydrates aren’t broken down properly, they can sit in the gut and ferment, leading to gas and bloating. Fungal amylase helps ensure that carbohydrates are digested before they can ferment, leading to less bloating and gas.
- Enhancing Digestive Comfort: By improving the digestion of complex carbohydrates, fungal amylase may reduce the uncomfortable symptoms associated with undigested food in the gut, such as bloating, cramping, and gurgling.
4. Improving Nutrient Absorption
- Better Absorption of Nutrients: As fungal amylase aids in the breakdown of carbohydrates, it enhances the absorption of glucose, which is a key energy source for the body. This also allows for better nutrient absorption overall, improving the efficiency of the digestive system and supporting optimal metabolic function.
- Detoxification Support: Proper digestion and absorption of nutrients can help maintain overall health, which supports the body’s natural detoxification processes. A properly functioning digestive system is crucial for eliminating waste and toxins from the body more effectively.
5. Potential Role in Gut Health and Immune Function
- Supporting a Healthy Gut Microbiome: By improving carbohydrate digestion, fungal amylase reduces the undigested food particles that may feed harmful bacteria or yeast in the gut. This can support a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which is important for detoxification and overall digestive health.
- Supporting Immune Function: A healthy digestive system and gut microbiome are closely linked to immune health. Efficient digestion, supported by fungal amylase, can help reduce inflammation in the gut and enhance the immune system’s ability to combat harmful pathogens.
HOW FUNGAL AMYLASE HELPS IN ENZYME BALANCE
- Complementing Natural Digestive Enzymes
- Amylase in the Body: The human body naturally produces salivary amylase and pancreatic amylase to break down carbohydrates into simple sugars. However, some people may not produce enough of these enzymes, which can lead to digestive discomfort, bloating, or difficulty processing complex carbohydrates. Fungal amylase acts as an additional source of amylase, helping to fill in any gaps and ensuring that carbohydrates are broken down more efficiently.
- Supporting Pancreatic Function: Fungal amylase can aid in the digestion of complex carbohydrates, especially if the body’s pancreatic enzyme production is insufficient. By providing an external source of amylase, it supports the overall enzyme activity in the digestive system, helping maintain balance and efficiency in digestion.
- Enhancing Digestive Efficiency
- Improved Carbohydrate Breakdown: Fungal amylase helps break down complex carbohydrates (like starches) into simpler sugars (such as maltose and glucose). This assists the body in absorbing these sugars more easily, reducing the workload of the digestive enzymes that are responsible for breaking down starches. By doing so, it contributes to a more balanced enzyme action throughout the digestive system.
- Preventing Overproduction of Certain Enzymes: When the body struggles to digest certain foods, it can sometimes produce an excess of digestive enzymes to compensate for the inefficiency. Fungal amylase helps by improving the breakdown of carbohydrates, which can prevent the overproduction of digestive enzymes and help maintain balance within the system.
- Supporting Enzyme Diversity
- Different Enzyme Activities: The digestive system relies on a variety of enzymes to break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Fungal amylase, being a plant-derived enzyme, works in harmony with other enzymes like lipase (fat-digesting enzyme) and protease (protein-digesting enzyme) to break down carbohydrates effectively without overwhelming the system. By providing more enzymatic diversity, fungal amylase supports overall enzyme balance in the digestive process.
- Ensuring Optimal pH Balance: Fungal amylase operates optimally in the slightly acidic environment of the stomach and intestines, complementing the body’s natural digestive processes without disrupting the pH balance of the digestive tract. This ensures that other enzymes, like pepsin (for protein digestion) and lipase, function properly as well.
- Supporting Gut Health
- Reducing Fermentation: When starches and complex carbohydrates are not broken down properly, they can ferment in the intestines, creating gas and potentially disrupting the balance of enzymes and gut bacteria. Fungal amylase helps break down these carbohydrates, preventing fermentation and thus reducing the risk of enzyme imbalance caused by excess gas production.
- Supporting the Microbiome: A healthy gut microbiome relies on a balance between different digestive enzymes and gut bacteria. By supporting the breakdown of carbohydrates, fungal amylase helps to maintain a healthy gut environment, reducing the chances of gut dysbiosis (an imbalance of gut bacteria) that could lead to digestive issues and enzyme-related imbalances.
- Balancing Digestive Enzyme Demand
Managing Digestive Load: During digestion, especially after consuming large or carbohydrate-heavy meals, the body can be stressed by the amount of work required to break down food. Fungal amylase helps ease the digestive load by assisting with carbohydrate digestion, which helps maintain enzyme balance in the digestive system. This means the pancreas and other digestive organs don’t need to produce as many enzymes to process food.
HOW FUNGAL AMYLASE HELPS IN PROBIOTIC NEEDS

- Supporting Carbohydrate Breakdown for Probiotic Growth
- Digestion of Complex Carbohydrates: Fungal amylase aids in breaking down complex carbohydrates (like starches) into simpler sugars such as maltose and glucose. These sugars can serve as food for beneficial gut bacteria (probiotics). By improving the digestion of carbohydrates, fungal amylase helps release nutrients that probiotics need to thrive and grow, supporting a healthy and balanced gut microbiome.
- Prebiotic Effects: Some of the simple sugars produced during carbohydrate digestion can act as prebiotics, compounds that selectively stimulate the growth or activity of beneficial microorganisms in the gut, including probiotics. Fungal amylase, by efficiently breaking down carbohydrates, may help generate prebiotic sugars that support probiotic activity.
- Reducing Undigested Carbohydrates in the Gut
- Minimizing Fermentation: When complex carbohydrates are not fully digested, they can ferment in the intestines, leading to gas production, bloating, and discomfort. This fermentation can create an unhealthy gut environment, potentially reducing the effectiveness of probiotics. By aiding in the breakdown of these carbohydrates, fungal amylase helps reduce the amount of undigested carbohydrates that reach the gut and ferment, promoting a more favorable environment for probiotics to flourish.
- Less Gas Production: Fungal amylase helps reduce gas and bloating by improving the efficiency of digestion. This creates less interference for probiotics, allowing them to perform their beneficial roles in the gut, such as aiding in digestion and supporting the immune system.
- Enhancing Nutrient Absorption for Probiotic Function
- Better Nutrient Availability: By assisting in the breakdown of complex carbohydrates, fungal amylase makes nutrients more available for absorption. This means that probiotics have more access to nutrients they need to support their activity and growth. A well-nourished probiotic community in the gut is more effective at performing its roles, including promoting digestion, supporting immune function, and maintaining a balanced gut microbiome.
- Promoting a Healthy Digestive Environment
- Balanced pH Levels: Fungal amylase helps break down carbohydrates more efficiently, reducing the likelihood of fermentation and the production of acidic byproducts that could disrupt the pH balance in the gut. Probiotics generally thrive in slightly acidic environments, so by reducing fermentation-related acidity, fungal amylase helps maintain an optimal environment for probiotics to survive and flourish.
- Reducing Inflammation: Efficient digestion and nutrient absorption support a healthy gut lining and reduce inflammation. Since probiotics help modulate inflammation, a more balanced and efficient digestive system allows probiotics to work more effectively, contributing to gut health and overall well-being.
- Supporting Gut Microbiome Diversity
- Enhanced Probiotic Activity: By breaking down carbohydrates more efficiently, fungal amylase helps prevent the overgrowth of harmful bacteria that feed on undigested food. This creates a healthier, more diverse gut microbiome, allowing probiotics to play a stronger role in maintaining digestive and immune health.
HOW FUNGAL AMYLASE HELPS IN GERD, IBS & IBD MANAGEMENT

- GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
GERD occurs when stomach acid flows backward into the esophagus, causing discomfort, heartburn, and damage to the esophagus. Fungal amylase can help alleviate GERD symptoms in the following ways:
- Reducing Bloating and Pressure: One common trigger for GERD is gas and bloating in the stomach. When carbohydrates are not fully digested, they can ferment in the gut, producing gas. This can increase pressure on the stomach and promote acid reflux. Fungal amylase helps break down complex carbohydrates into simple sugars, preventing fermentation and reducing gas, bloating, and the pressure that may contribute to reflux.
- Improving Digestion: By breaking down carbohydrates more efficiently, fungal amylase helps improve overall digestive function. This can prevent delayed stomach emptying and reduce the likelihood of acid reflux, helping manage GERD symptoms.
- Reducing Fermentation: Fungal amylase minimizes fermentation in the gut, which can contribute to discomfort and acid reflux. Reducing fermentation can help calm the digestive system and create a more stable environment that lessens the risk of GERD flare-ups.
- IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
IBS is characterized by symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation, often triggered by the way the body processes food. Fungal amylase can help manage IBS symptoms in the following ways:
- Alleviating Bloating and Gas: IBS patients often experience bloating and excess gas due to undigested carbohydrates fermenting in the gut. Fungal amylase helps digest complex carbohydrates, preventing fermentation and gas buildup, which can significantly reduce bloating and abdominal discomfort in IBS sufferers.
- Improving Digestion: Fungal amylase aids in breaking down carbohydrates into simpler sugars, which can help ease digestion and improve the overall efficiency of the digestive process. This reduces the chance of incomplete digestion, a key factor in IBS symptoms.
- Reducing Gut Inflammation: IBS is sometimes associated with low-grade gut inflammation. By improving digestion and reducing fermentation, fungal amylase can help reduce the irritation caused by undigested food particles in the gut, potentially helping with IBS-related inflammation.
- IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease)
IBD includes conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, which involve chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. While fungal amylase is not a direct treatment for IBD, it can support IBD management in the following ways:
- Supporting Digestive Function: Fungal amylase helps improve the digestion of complex carbohydrates, reducing the amount of undigested food that reaches the intestines. This is particularly helpful for individuals with IBD, who may have a compromised digestive system. Efficient digestion reduces the burden on the intestines and helps ease IBD-related symptoms like diarrhea and cramping.
- Reducing Gas and Bloating: Like IBS, gas and bloating are common complaints in IBD. Fungal amylase helps reduce these symptoms by ensuring that carbohydrates are digested properly before they have a chance to ferment in the gut. This can lead to less intestinal pressure and a reduction in bloating.
- Supporting Gut Health and Healing: While fungal amylase itself does not directly address the inflammation of IBD, its role in promoting better digestion can support overall gut health. By reducing the fermentation of food, fungal amylase helps maintain a less irritated and inflamed gut, which may support the healing process in IBD patients.
- Enhancing Nutrient Absorption: Since IBD can impair nutrient absorption, ensuring efficient digestion with the help of fungal amylase may help improve nutrient availability. This may be beneficial for people with IBD who often struggle with deficiencies due to poor absorption.
HOW FUNGAL AMYLASE HELPS IN ACIDITY

- Improving Carbohydrate Digestion
- Efficient Carbohydrate Breakdown: Fungal amylase helps break down complex carbohydrates (such as starches) into simpler sugars (maltose and glucose). When carbohydrates are not properly digested, they can remain in the stomach longer, causing fermentation and gas buildup. This can increase gas pressure in the stomach, pushing stomach acid into the esophagus, which leads to acid reflux or heartburn. By efficiently breaking down carbohydrates, fungal amylase can reduce this fermentation and gas buildup, which in turn reduces the risk of acid reflux and the discomfort associated with acidity.
- Preventing Excess Gas Production
- Reducing Fermentation: When undigested carbohydrates ferment in the stomach and intestines, they produce gases that can increase pressure on the stomach. This pressure can contribute to acid reflux, where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. Fungal amylase helps by ensuring carbohydrates are properly broken down before they reach the fermentation stage, which can help alleviate excessive gas production and reduce the risk of acidic backflow into the esophagus.
- Supporting Balanced Stomach pH
- Preventing Overproduction of Acid: In some cases, poor digestion—especially of carbohydrates—can lead to an increase in stomach acidity. The body may produce more acid to break down food that hasn’t been properly digested. Fungal amylase helps improve digestion, reducing the overproduction of gastric acid and potentially helping to maintain a more balanced stomach pH. This, in turn, can help reduce the discomfort of acidity and acid reflux.
- Reducing Bloating and Pressure
- Minimizing Stomach Distension: Fungal amylase improves carbohydrate digestion, which helps reduce bloating and distension of the stomach. Bloating can exacerbate acidity by increasing pressure on the stomach, which may push stomach acid into the esophagus. By reducing bloating, fungal amylase can help reduce the risk of acidic reflux.
- Improving Overall Digestion
Faster Food Processing: Fungal amylase speeds up the breakdown of carbohydrates, leading to more efficient digestion. When food moves more efficiently through the stomach and intestines, there’s less chance of delayed stomach emptying, which can trigger acidic indigestion or acid reflux. A smoother digestion process can help minimize symptoms of acidity and improve overall digestive health
HOW FUNGAL LIPASE HELPS IN DIGESTION & DETOXIFICATION

Fungal lipase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the digestion and detoxification processes by breaking down lipids (fats) into smaller molecules such as fatty acids and glycerol. This helps improve the digestion of fats and supports the body in eliminating waste and toxins.
- Enhanced Digestion of Fats
- Breaking Down Fats Efficiently: Fungal lipase helps break down dietary fats into fatty acids and glycerol. This is an essential step in the digestion process, as fats are complex molecules that require specific enzymes to be fully absorbed and utilized by the body. Efficient fat digestion ensures that the body can extract the necessary nutrients from fats, which are important for energy, cell function, and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (like vitamins A, D, E, and K).
- Improved Nutrient Absorption: By aiding in the breakdown of fats, fungal lipase ensures that essential fatty acids and other nutrients are more readily absorbed in the small intestine. This supports the overall nutritional status and helps the body function optimally.
- Reducing Digestive Discomfort
- Preventing Undigested Fats in the Gut: If fats are not properly digested, they can remain in the digestive tract, leading to symptoms such as bloating, indigestion, or diarrhea. These undigested fats may also disrupt the balance of gut microbiota and contribute to digestive discomfort. By efficiently breaking down fats, fungal lipase helps prevent these issues, promoting smoother digestion and reducing discomfort.
- Relieving Bloating and Gas: When fats are not digested properly, they can ferment in the intestines, contributing to gas production and bloating. Fungal lipase helps ensure fats are broken down before they reach the fermentation stage, reducing the chances of bloating and excess gas.
- Detoxification Support
- Breaking Down Stored Fats: One of the key aspects of detoxification is the elimination of toxic substances that are stored in fat cells. Fat-soluble toxins, such as heavy metals, pesticides, and environmental chemicals, can accumulate in the body’s fat stores. Fungal lipase helps break down stored fat, which can indirectly help release and mobilize these toxins, allowing them to be processed and eliminated by the body's detoxification systems, such as the liver.
- Supporting Liver Function: The liver plays a central role in detoxifying the body. When fats are broken down efficiently, the liver can process the resulting fatty acids and other byproducts more effectively. This supports the liver’s ability to detoxify the body by allowing it to focus on processing fat-soluble toxins and waste products, rather than being overwhelmed by undigested fats.
- Supporting Bile Production: Fat digestion stimulates the production of bile in the liver, which is important for emulsifying fats and helping with their digestion and absorption. Bile also plays a role in detoxification, as it helps eliminate waste products and toxins from the body through the digestive system. By breaking down fats, fungal lipase indirectly supports healthy bile production, enhancing detoxification.
- Balancing Cholesterol Levels
- Healthy Fat Metabolism: Efficient fat digestion can help regulate cholesterol levels in the body. Fungal lipase aids in the breakdown of dietary fats, including those that may contribute to high cholesterol when improperly processed. By supporting healthy fat metabolism, fungal lipase can help maintain balanced cholesterol levels, which supports overall cardiovascular health and detoxification processes.
- Supporting Gut Health
- Reducing Toxin Buildup: Inadequate digestion of fats can lead to the buildup of undigested food particles and toxins in the digestive tract, which can negatively impact gut health and promote an unhealthy gut microbiome. Fungal lipase helps prevent this buildup by breaking down fats more efficiently, which not only promotes better digestion but also helps maintain a cleaner and healthier gut environment.
- Reducing Inflammation: By improving the digestion of fats and reducing the amount of undigested food in the intestines, fungal lipase can help reduce intestinal inflammation. This may benefit overall gut health and potentially reduce the inflammation associated with conditions like IBS or IBD, which can be exacerbated by poor fat digestion.
HOW FUNGAL LIPASE HELPS IN ENZYME BALANCE
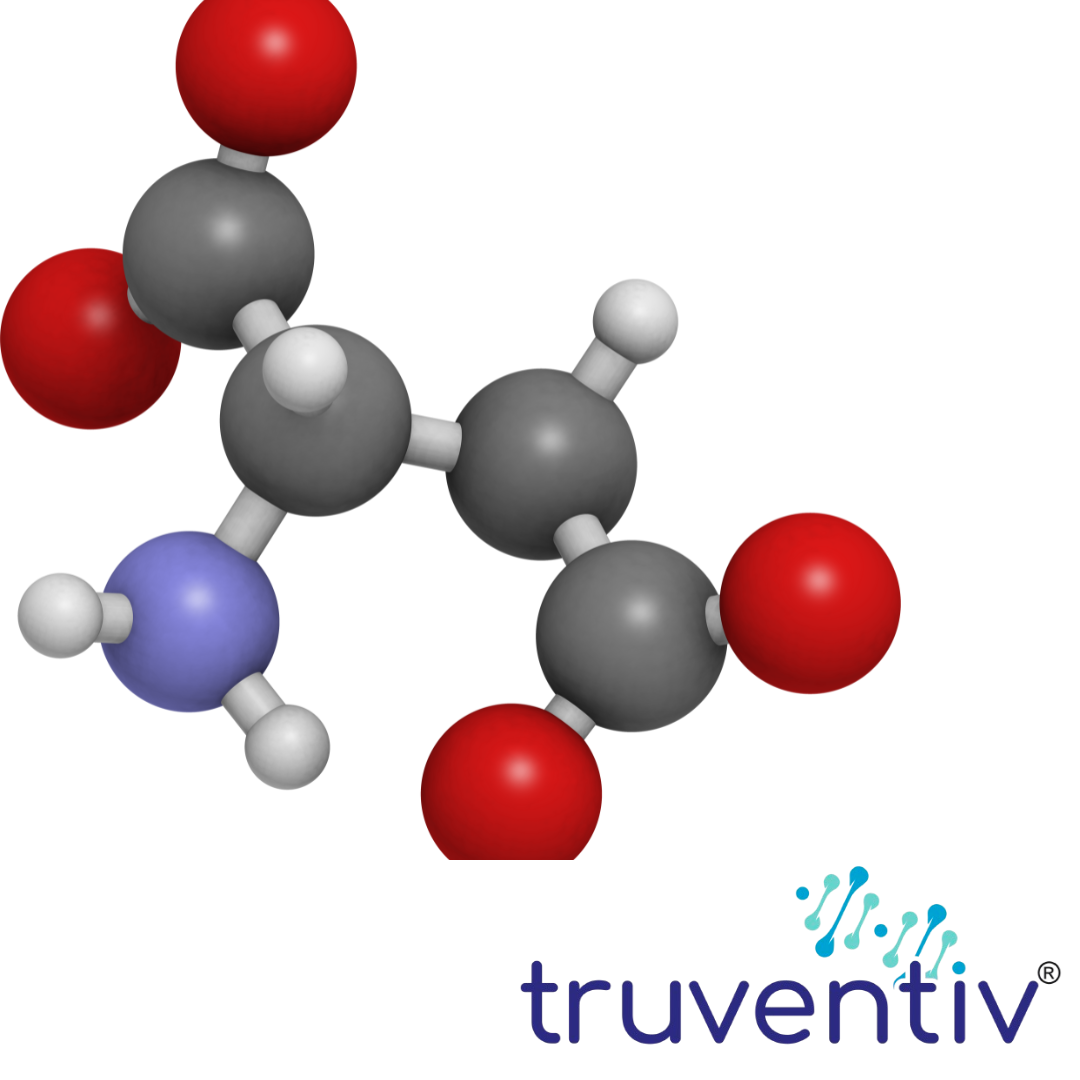
Fungal lipase contributes to enzyme balance in the digestive system by facilitating the efficient breakdown of dietary fats, supporting overall digestive processes, and preventing imbalances caused by undigested fats.
- Supporting Efficient Fat Digestion
- Optimal Digestion of Fats: Lipase is the key enzyme responsible for breaking down fats (lipids) into smaller components like fatty acids and glycerol. Fungal lipase helps ensure that fats are properly digested in the stomach and small intestine, preventing undigested fats from accumulating in the digestive system. This balance prevents a backlog of undigested food that could otherwise overburden the digestive system, allowing other digestive enzymes (such as proteases and amylases) to work efficiently without being overwhelmed.
- Enzyme Complementarity: In the digestive system, multiple enzymes work together to break down different food groups. Fungal lipase works in harmony with other digestive enzymes (such as amylase for carbohydrates and protease for proteins). By efficiently breaking down fats, it ensures that the focus of other enzymes, like amylases and proteases, remains on carbohydrates and proteins, creating a balanced enzyme environment in the gut for overall digestion.
- Preventing Digestive Overload
- Prevents Overproduction of Digestive Enzymes: When fats are not broken down properly, the body may overcompensate by producing more digestive enzymes to handle the undigested food. This could lead to an imbalance in the digestive system. By supporting the breakdown of fats, fungal lipase helps maintain proper enzyme activity levels, preventing the overproduction of lipase and other digestive enzymes.
- Reduces Fermentation of Fats: If fats are not digested properly, they may ferment in the gut, leading to the production of gases and discomfort. This fermentation process can also disrupt the balance of digestive enzymes, as the body may increase its production of enzymes to compensate for the incomplete digestion. Fungal lipase helps to prevent this by ensuring that fats are fully broken down, promoting a more balanced digestive enzyme environment.
- Improving Nutrient Absorption and Reducing Enzyme Overload
- Efficient Absorption of Fat-Soluble Nutrients: Fats are essential for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). Fungal lipase plays an essential role in breaking down dietary fats, ensuring that these nutrients are absorbed properly. This prevents deficiencies and eliminates the need for the body to overproduce enzymes to try and digest unabsorbed fats. A well-balanced enzyme system ensures the body has adequate access to these vital nutrients without stress.
- Enzyme Activity Balance: The presence of undigested fats can increase the workload on other enzymes in the digestive system, such as amylase and protease. By breaking down fats more efficiently, fungal lipase helps reduce the burden on other enzymes, promoting a more balanced and harmonious enzymatic function throughout the digestive process. This can lead to improved digestion and absorption of all types of nutrients, not just fats.
- Maintaining Healthy Gut Flora
- Balance in Gut Microbiota: Undigested fats in the gut can cause an imbalance in the gut microbiome, leading to overgrowth of harmful bacteria and yeast that thrive on undigested food. This imbalance can affect the function of digestive enzymes and disrupt overall gut health. By aiding in the digestion of fats, fungal lipase helps maintain a healthier gut flora, which in turn supports optimal enzyme function. A balanced gut microbiome also helps in regulating the production of enzymes for digestion, ensuring that the right enzymes are present in the right amounts.
- Reducing Gut Inflammation: Undigested food can lead to gut irritation and inflammation, which may negatively affect enzyme production and function. Fungal lipase’s role in improving fat digestion can help reduce such inflammation, which supports a healthy environment for digestive enzymes to work effectively.
- Preventing Enzyme Imbalances Linked to Fat Malabsorption
Fat Malabsorption: In cases where fats are not broken down properly (such as in pancreatic insufficiency or lipase deficiency), the body may attempt to compensate by overproducing digestive enzymes. This can lead to enzyme imbalances. Fungal lipase supports proper fat digestion, preventing the need for the body to overcompensate and produce excessive amounts of enzymes, thus maintaining a healthy balance of digestive enzymes
HOW FUNGAL LIPASE HELPS IN PROBIOTIC NEEDS

Fungal lipase plays a supportive role in probiotic needs by enhancing digestion, promoting gut health
- Supporting Fat Digestion and Absorption
- Efficient Fat Breakdown: Fungal lipase helps break down dietary fats into smaller molecules like fatty acids and glycerol, which are then absorbed and utilized by the body. When fats are digested properly, it helps prevent undigested fat from lingering in the intestines, where it can interfere with the gut microbiome. Efficient digestion of fats allows the gut to better absorb nutrients, creating an environment conducive to the growth and maintenance of healthy probiotics.
- Balancing Gut pH: The breakdown of fats helps to maintain a balanced pH in the gut. An optimal pH level is important for the survival of probiotics, as many beneficial bacteria prefer slightly acidic conditions for growth. By aiding fat digestion, fungal lipase indirectly helps in maintaining a pH balance that supports the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Reducing Gut Inflammation
- Preventing Bloating and Gas: If fats are not properly digested, they can ferment in the gut, producing gases that lead to bloating, discomfort, and gut inflammation. This inflammation can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, as harmful bacteria may thrive in an inflamed gut environment. Fungal lipase helps prevent this by breaking down fats efficiently, reducing bloating, and helping maintain a more balanced gut flora, which provides a healthier environment for probiotics to flourish.
- Promoting Healthy Gut Microbiota: Undigested fats can contribute to an imbalance in the gut microbiome, favoring the overgrowth of harmful bacteria or yeast. By ensuring proper fat digestion, fungal lipase supports a balanced gut microbiome, which is crucial for maintaining an optimal environment for probiotics to thrive. A balanced microbiome supports not only probiotics but also overall gut health, immune function, and digestion.
- Enhancing Nutrient Absorption for Probiotics
- Improving Nutrient Availability: Fungal lipase helps the body absorb essential fatty acids and fat-soluble vitamins (like vitamins A, D, E, and K), which are important for overall health, including the health of the gut lining and the probiotics within it. When nutrients are more efficiently absorbed, probiotics benefit from a well-nourished environment that supports their growth and function.
- Fat-Soluble Vitamin Absorption: Many probiotics rely on specific nutrients (including fat-soluble vitamins) for proper function. Fungal lipase helps the body absorb these essential nutrients, thereby supporting the metabolism and function of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- Facilitating Bile Production and Secretion
- Stimulating Bile Release: The digestion of fats stimulates the release of bile from the liver. Bile helps emulsify fats, which aids in their digestion and absorption. Additionally, bile has been shown to have antimicrobial properties that can help maintain the proper balance of gut bacteria. By supporting fat digestion, fungal lipase helps promote bile production and secretion, which in turn supports the growth and maintenance of probiotics by ensuring a healthy balance between beneficial and harmful microorganisms in the gut.
- Enhancing Gut Permeability and Protection
- Maintaining Healthy Gut Barrier Function: Fat digestion also plays a role in maintaining the integrity of the intestinal lining, which is crucial for gut health and the function of probiotics. When fats are properly digested and absorbed, it helps prevent intestinal permeability (also known as “leaky gut”), which can lead to inflammation and disrupt the gut microbiome. Fungal lipase helps ensure that fats are digested properly, which supports the integrity of the gut lining, creating a favorable environment for probiotics.
- Protecting Against Harmful Bacteria: By aiding in fat digestion, fungal lipase helps maintain a stable environment in the intestines. This helps prevent conditions that might allow harmful bacteria or pathogens to thrive, thus ensuring that beneficial probiotics can outcompete these harmful organisms for space and resources.
HOW FUNGAL LIPASE HELPS IN GERD, IBS AND IBD MANAGEMENT

1. GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
GERD is a condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, leading to symptoms like heartburn, regurgitation, and chest discomfort. Proper digestion, especially of fats, can help alleviate some of the triggers of GERD symptoms.
- Improved Fat Digestion: Fats that are not digested properly can slow down the stomach’s emptying process, increasing the risk of acid reflux. By helping to break down fats more efficiently, fungal lipase aids in faster gastric emptying and reduces the pressure that could otherwise lead to acid reflux. This helps minimize the potential for reflux episodes.
- Reducing Gastric Acid Production: When fats are not digested properly, the body may increase gastric acid production to compensate, which can worsen GERD symptoms. Efficient fat digestion by fungal lipase reduces the need for excessive gastric acid secretion, potentially minimizing irritation in the esophagus and stomach.
2. IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
IBS is a chronic gastrointestinal disorder characterized by symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constipation. Fungal lipase can help with IBS symptoms in several ways:
- Reducing Bloating and Gas: Poor fat digestion can lead to bloating, excessive gas, and discomfort. Fungal lipase helps break down fats more effectively, reducing the risk of fermentation in the gut and minimizing bloating and gas production. This can be especially beneficial for individuals with IBS who are sensitive to bloating and gas.
- Reducing Diarrhea and Constipation: Inefficient fat digestion can contribute to diarrhea in some individuals with IBS, as undigested fats can irritate the intestines. By improving fat digestion, fungal lipase can help reduce this irritation, potentially alleviating diarrhea. Similarly, constipation in IBS may be alleviated by improving overall digestion, ensuring that stool is not too hard or difficult to pass.
- Balancing Gut Microbiota: IBS is often associated with gut dysbiosis (an imbalance of gut bacteria). By aiding in digestion and promoting a healthier gut environment, fungal lipase helps maintain a balanced gut microbiome, which may help reduce IBS flare-ups and improve overall gut health.
3. IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease)
IBD, which includes conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, involves chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, leading to symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fatigue. Fungal lipase may help in IBD management by:
- Reducing Inflammation: One of the key benefits of fungal lipase is its ability to improve fat digestion. Undigested fats can contribute to inflammation in the gut, which is a hallmark of IBD. By supporting better digestion of fats, fungal lipase helps reduce the load of undigested food in the intestines, which may decrease overall gut inflammation.
- Supporting Nutrient Absorption: IBD can impair nutrient absorption, especially the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). Fungal lipase helps break down fats, ensuring that these essential vitamins are properly absorbed. This can help improve nutritional status, which is critical for managing IBD and promoting healing in the digestive tract.
- Supporting Gut Healing: In IBD, the gut lining can become damaged due to chronic inflammation. By improving fat digestion and reducing inflammation, fungal lipase helps create a more favorable environment for gut healing. This can help in reducing flare-ups and potentially enhancing recovery during remission periods.
- Preventing Malabsorption: Malabsorption of fats is a common issue in individuals with IBD, leading to the passage of undigested fats in the stool (steatorrhea). Fungal lipase helps prevent this malabsorption by ensuring fats are broken down and absorbed properly, which can alleviate symptoms like fatty stools, bloating, and diarrhea.
HOW FUNGAL LIPASE HELPS IN ACIDITY

- Improving Fat Digestion and Reducing Gastric Pressure
- Efficient Fat Breakdown: One of the primary functions of fungal lipase is to break down fats into smaller molecules (fatty acids and glycerol). When fats are not digested properly, they can slow down the digestive process and increase gastric pressure. This pressure can contribute to acid reflux, as undigested food, including fats, can push stomach acid into the esophagus.
- Reducing Gastric Distention: When fats are broken down properly by fungal lipase, it helps reduce bloating and distention in the stomach. This prevents the stomach from becoming too full, which can trigger acid reflux and lead to a feeling of heaviness or discomfort, a common issue in people suffering from acidity.
- Reducing Overproduction of Stomach Acid
- Preventing Overproduction of Acid: In the case of undigested fats, the stomach may increase acid production in an attempt to break down the food, especially if fats are not being adequately processed. This can lead to excess stomach acid, which can increase the likelihood of acid reflux and heartburn. By supporting the efficient digestion of fats, fungal lipase helps prevent the overproduction of stomach acid and reduces the risk of acidity symptoms.
- Balanced Gastric Environment: Fungal lipase aids in creating a more balanced digestive environment by ensuring that fats are digested properly. A well-functioning digestive system reduces the need for the stomach to produce excessive amounts of acid, thus promoting a more balanced stomach environment and reducing acidity.
- Reducing Fermentation and Gas Production
- Preventing Fermentation of Fats: When fats are not fully digested, they can ferment in the intestines, producing gas and contributing to discomfort and bloating. The buildup of gas can cause pressure on the stomach and lead to acid reflux or indigestion. Fungal lipase helps break down fats efficiently, reducing the likelihood of fermentation, gas production, and the associated bloating that can worsen acidity symptoms.
- Supporting a Healthy Gut Microbiome
- Balancing Gut Flora: Acidity and acid reflux can be aggravated by an imbalance in the gut microbiome, with the overgrowth of harmful bacteria or yeast that thrive on undigested food. Fungal lipase helps maintain a balanced gut microbiota by aiding in the digestion of fats, ensuring that food is properly broken down before reaching the intestines. A balanced microbiome supports digestive health and reduces the risk of acidity, as it prevents fermentation and other digestive issues that can lead to excess acid production.
- Promoting Nutrient Absorption
- Improved Absorption of Nutrients: Undigested fats can lead to poor nutrient absorption, including essential vitamins and minerals. When fats are broken down effectively by fungal lipase, it promotes better nutrient absorption and overall digestive health. Proper digestion and absorption help maintain a healthier digestive system, which can reduce the likelihood of developing symptoms like acidity and heartburn.
- Supporting Digestive Enzyme Balance
Optimal Enzyme Function: Fungal lipase works alongside other digestive enzymes, such as amylase for carbohydrates and protease for proteins. When fats are properly digested, it helps maintain an optimal balance of enzymes in the digestive tract. This balance is important for preventing digestive issues like acidity, as it ensures that the digestive system is working efficiently and effectively, without overburdening the stomach or producing excess acid.
HOW FUNGAL DIASTASE HELPS IN DIGESTION & DETOXIFICATION
Fungal diastase, an enzyme derived from fungi like Aspergillus oryzae, primarily helps in the breakdown of starches into simpler sugars during digestion. It plays a crucial role in supporting the digestive process and detoxification by improving nutrient absorption, facilitating the breakdown of carbohydrates, and supporting overall digestive health.
- Enhances Digestion of Carbohydrates
- Breakdown of Starches: Fungal diastase helps break down complex carbohydrates (starches) into simpler sugars like maltose and glucose, which are easier for the body to absorb. When carbohydrates are properly broken down, the digestive system works more efficiently, and the body is able to utilize the nutrients more effectively.
- Improves Digestion Efficiency: Starch-rich foods, such as grains, vegetables, and legumes, are often difficult to digest without proper enzymatic action. By aiding in starch breakdown, fungal diastase ensures that the body can access the energy and nutrients stored in these foods, making digestion smoother and more efficient.
- Reduces Digestive Discomfort
- Prevents Bloating and Gas: When starches are not fully digested in the stomach or small intestine, they can ferment in the colon, producing gas and leading to bloating. This can cause discomfort and digestive upset, especially in people with sensitive stomachs. Fungal diastase helps break down starches more effectively, reducing the risk of fermentation and minimizing symptoms like bloating, gas, and indigestion.
- Helps with Food Intolerances: People who struggle with digesting certain starches or have mild food sensitivities may benefit from fungal diastase, as it supports more thorough digestion and absorption of starches, reducing discomfort associated with food intolerances.
- Facilitates Nutrient Absorption
- Improved Absorption of Carbohydrates: Proper breakdown of starches allows for the absorption of simpler sugars like glucose into the bloodstream, providing the body with much-needed energy. This is essential for maintaining healthy metabolic function and overall energy levels.
- Supports the Absorption of Other Nutrients: A well-functioning digestive system supports the absorption of not just carbohydrates but also other nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and fats. Efficient digestion of carbohydrates through the action of fungal diastase improves overall nutrient absorption, which is vital for overall health and detoxification.
- Supports Detoxification
- Prevents Toxin Buildup: When undigested starches remain in the gut, they can ferment and create harmful byproducts like gases, ammonia, and other toxins. By helping break down starches efficiently, fungal diastase prevents this fermentation and toxin buildup, which can otherwise contribute to digestive issues and general body toxicity.
- Supports Healthy Gut Flora: A healthy gut microbiome is essential for detoxification, and a balanced microbiome can help break down harmful substances and assist in detoxification. When starches are properly digested, it reduces the chances of an imbalance in gut bacteria, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria that support overall health and detoxification.
- Aids in the Breakdown of Dietary Toxins
- Assists in Toxin Breakdown: While fungal diastase is primarily focused on carbohydrate digestion, an efficient digestive system helps the body better process and eliminate toxins from the diet. The more effectively the body breaks down and absorbs nutrients, the less work it has to do to rid itself of excess toxins and waste products. This allows for smoother detoxification processes.
- Improves Overall Gut Health
- Supports Digestive Enzyme Balance: By enhancing the breakdown of carbohydrates, fungal diastase helps maintain the balance of digestive enzymes in the gut, which is crucial for the overall digestion process. A healthy digestive enzyme balance prevents conditions like indigestion and promotes a cleaner, healthier gut environment, which in turn aids in better detoxification.
- Relieves Digestive Stress: If starches and carbohydrates are not adequately digested, they can irritate the gut lining and lead to inflammation. Fungal diastase can help reduce this strain on the digestive system, leading to healthier gut function and fewer digestive issues that could impede the detoxification process.
HOW FUNGAL DIASTASE HELPS IN ENZYME BALANCE
Fungal diastase plays a vital role in maintaining enzyme balance in the digestive system. By breaking down starches and facilitating the digestion of carbohydrates, it helps optimize the functioning of other digestive enzymes and contributes to overall digestive harmony.
- Optimizes Carbohydrate Digestion
- Proper Starch Breakdown: Fungal diastase is primarily responsible for breaking down complex carbohydrates (starches) into simpler sugars like maltose and glucose. When starches are efficiently broken down, it prevents excess food from lingering in the digestive tract. This allows other digestive enzymes to function optimally, without being overloaded.
- Reducing the Workload of Other Enzymes: By effectively handling starch digestion, fungal diastase reduces the burden on other digestive enzymes such as amylase (another enzyme that breaks down starches) and maltase (which further breaks down maltose). This allows all digestive enzymes to work in balance, leading to better digestion overall.
- Supports the Activity of Other Digestive Enzymes
- Promoting Optimal Enzyme Action: Digestive enzymes work in a coordinated manner to break down food into absorbable nutrients. When fungal diastase efficiently digests starches, it helps maintain the optimal pH and digestive conditions in the stomach and intestines, creating a favorable environment for other enzymes (proteases, lipases, etc.) to function effectively.
- Complementary Enzyme Roles: Digestive enzymes often act in sequence. For instance, amylase breaks down starch into smaller molecules, and then diastase takes over to further break those down into simple sugars. By ensuring starches are thoroughly digested in the proper stages, fungal diastase supports the smooth operation of the entire enzyme system, allowing each enzyme to perform its role without interference.
- Prevents Enzyme Imbalance
- Reducing Digestive Overload: If certain types of food, especially starchy foods, aren’t properly digested, the digestive system may attempt to overproduce digestive enzymes to compensate. This can lead to an imbalance, resulting in conditions like bloating, indigestion, or acid reflux. Fungal diastase helps prevent this by breaking down starches efficiently, so the body doesn't need to overproduce enzymes in response to undigested food.
- Maintaining Digestive Efficiency: When the right enzymes (such as fungal diastase) break down specific food components, it allows the other enzymes to focus on their designated tasks, preventing digestive congestion and enzyme overload. This balance leads to better overall digestive health and more efficient absorption of nutrients.
- Aiding in Nutrient Absorption
- Facilitating Nutrient Release: Efficient carbohydrate digestion by fungal diastase ensures that nutrients are released from food in a manner that allows for better absorption by the intestines. This efficient digestion supports the effective functioning of enzymes that are involved in absorbing the released nutrients (like lipases for fats or proteases for proteins). This creates a harmonious interaction between different types of enzymes, facilitating better absorption of all nutrients.
- Improving Gut Microbial Environment
- Supporting Healthy Gut Flora: Proper digestion with the help of fungal diastase prevents the overgrowth of harmful bacteria or yeast in the gut, which could otherwise disrupt the activity of digestive enzymes. By ensuring starches are broken down and absorbed effectively, fungal diastase helps maintain a balanced microbiome, creating a favorable environment for the enzymes to perform optimally.
- Promoting Healthy Fermentation: The breakdown of carbohydrates with fungal diastase prevents excessive fermentation in the gut. Fermentation of undigested starches by gut bacteria can lead to gas production, bloating, and discomfort, which can interfere with enzyme balance. By preventing this, fungal diastase helps maintain a harmonious gut environment where digestive enzymes can work effectively.
- Enhancing Overall Digestive Health
Regulating Digestive System pH: Fungal diastase contributes to regulating the pH of the stomach and small intestine, which is essential for optimal enzyme function. A balanced pH environment ensures that enzymes such as pepsin (which breaks down proteins) and lipases (which digest fats) can work efficiently without being hindered by excessive acidity or alkalinity. This creates a balanced digestive process, supporting all types of digestive enzymes.
HOW FUNGAL DIASTASE HELPS IN PROBIOTIC NEEDS

Fungal diastase, primarily known for its role in breaking down carbohydrates (especially starches)
- Promotes a Healthy Gut Environment for Probiotics
- Supports Digestive Health: By efficiently breaking down starches and other complex carbohydrates, fungal diastase helps create a more favorable environment in the gut for probiotics (beneficial bacteria). When the body digests food properly, it reduces the likelihood of harmful bacteria or yeast overgrowth, making it easier for probiotics to thrive.
- Reduces Inflammation and Gas: Undigested starches and carbohydrates can ferment in the gut, causing bloating, gas, and digestive discomfort. This creates an imbalance in gut microbiota, potentially suppressing the growth of beneficial probiotics. Fungal diastase helps reduce this fermentation by breaking down starches more effectively, reducing gut inflammation and discomfort, and promoting a healthier environment for probiotics to flourish.
- Enhances the Availability of Prebiotics
- Prebiotic Action: Fungal diastase helps break down complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars, which can serve as food for beneficial gut bacteria (prebiotics). Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers and sugars that feed probiotics, helping them grow and multiply. By aiding in the breakdown of certain carbohydrates, fungal diastase may indirectly contribute to the production of beneficial prebiotics that promote the health of probiotics.
- Stimulating Probiotic Growth: By helping to release simple sugars and fibers from starches, fungal diastase provides beneficial nutrients that probiotics can use for nourishment. This enhances the overall gut microbiome by supporting the growth of health-promoting probiotic strains.
- Improves Nutrient Absorption
- Nutrient Availability for Probiotics: Efficient digestion facilitated by fungal diastase means that more nutrients are absorbed in the intestines, providing essential elements for probiotics to thrive. A well-nourished digestive system supports the health of beneficial bacteria and enables them to perform their functions more effectively.
- Supports a Balanced Microbiome: By improving digestion and nutrient absorption, fungal diastase helps maintain a balance between beneficial and harmful bacteria in the gut. A balanced microbiome is crucial for probiotics to work effectively and support digestive, immune, and metabolic health.
- Aids in Gut Flora Balance
- Prevents Pathogen Growth: When starches are not properly digested, they can ferment in the gut, feeding harmful bacteria, pathogens, and yeast. This can suppress the activity of probiotics. By breaking down starches more efficiently, fungal diastase helps prevent fermentation in the gut, reducing the growth of pathogens and providing a healthier environment for beneficial probiotics.
- Enhances Probiotic Effectiveness: A well-balanced gut flora, with a flourishing colony of probiotics, can contribute to enhanced digestion, immune function, and overall health. Fungal diastase helps keep the digestive environment in balance by reducing inflammation and the overgrowth of harmful microorganisms, creating the ideal conditions for probiotics to perform optimally.
- Helps Prevent Digestive Issues That Disrupt Probiotics
- Reduces Digestive Stress: Without proper digestion, undigested food particles may irritate the gut lining, potentially causing discomfort and inflammation that negatively affects the probiotics. Fungal diastase ensures that starches are properly digested, reducing the stress on the digestive system and helping maintain a healthy gut environment for probiotics to thrive.
- Prevents Dysbiosis: Dysbiosis refers to an imbalance in the gut microbiome, where harmful bacteria overtake the beneficial ones. By supporting the breakdown of starches and preventing gut issues like fermentation, fungal diastase plays a role in preventing dysbiosis, which can interfere with the functioning of probiotics.
- Works Synergistically with Probiotics
- Promotes Digestive Efficiency: When used alongside probiotics, fungal diastase enhances the effectiveness of these beneficial bacteria. Efficient digestion of carbohydrates allows probiotics to have the necessary nutrients and a supportive environment to thrive. This synergistic effect leads to better gut health overall.
- Supports Probiotic Colonization: A well-functioning digestive system ensures that probiotics are able to reach their intended destination in the gut (such as the small intestine and colon) where they can colonize and exert their benefits. Fungal diastase helps create this optimal environment, promoting the successful colonization of beneficial bacteria.
HOW FUNGAL DIASTASE HELPS IN GERD, IBS & IBD MANAGEMENT

1. GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
GERD occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing symptoms like heartburn, regurgitation, and discomfort. Fungal diastase can assist in the management of GERD in the following ways:
- Enhances Digestive Efficiency: Fungal diastase helps break down complex carbohydrates more effectively, which reduces the overall burden on the stomach. When carbohydrates are not properly digested, they can ferment in the stomach and produce excess gas. This excess gas can put pressure on the stomach, increasing the likelihood of acid reflux. By improving carbohydrate digestion, fungal diastase minimizes gas production, reducing pressure and lowering the risk of acid reflux.
- Reduces Stomach Overload: Inefficient carbohydrate digestion can lead to indigestion, which can trigger GERD symptoms. By assisting in the breakdown of starches, fungal diastase reduces the workload of the stomach, preventing indigestion and promoting smoother digestion, which may help reduce GERD symptoms.
2. IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
IBS is a functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by symptoms like bloating, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain. Fungal diastase supports IBS management by:
- Reducing Bloating and Gas: One of the most common symptoms of IBS is bloating, often caused by undigested carbohydrates fermenting in the intestines. Fungal diastase breaks down starches and complex carbohydrates more efficiently, helping to prevent fermentation in the gut. This reduces gas production, bloating, and discomfort commonly experienced by those with IBS.
- Improving Overall Digestion: IBS is often linked to slow or irregular digestion. Fungal diastase helps improve carbohydrate digestion, which can aid in normalizing digestive function. By facilitating better digestion of starches, it supports smoother bowel movements and reduces the likelihood of symptoms like diarrhea or constipation associated with IBS.
- Supporting Gut Health: Efficient digestion with fungal diastase helps maintain a balanced gut microbiome. IBS is often linked to an imbalance in gut bacteria, and improved digestion can help support the growth of beneficial bacteria while reducing the overgrowth of harmful microorganisms. This balance can lead to symptom relief and improved gut health over time.
3. IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease)
IBD, which includes conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, involves chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, leading to symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, fatigue, and weight loss. Fungal diastase can aid in the management of IBD in several ways:
- Reduces Digestive Stress: Inflammation in the intestines can interfere with normal digestion and increase gut permeability. Fungal diastase helps break down carbohydrates efficiently, which reduces stress on the digestive system. Properly digested food can help soothe inflamed intestinal walls, potentially reducing symptoms of IBD, such as cramping and discomfort.
- Supports Nutrient Absorption: IBD can impair nutrient absorption due to the inflammation of the intestines. By promoting the breakdown of carbohydrates and supporting efficient digestion, fungal diastase helps ensure that nutrients are absorbed effectively, which is especially important for individuals with IBD who may suffer from malabsorption issues.
- Reduces Fermentation and Gas: Fermentation of undigested food in the intestines can exacerbate symptoms of IBD, such as bloating, pain, and diarrhea. By breaking down starches and carbohydrates more efficiently, fungal diastase reduces fermentation in the gut, leading to less gas and bloating, which can alleviate discomfort in people with IBD.
Supports Gut Microbiome Balance: IBD is often associated with an imbalance in the gut microbiome. Fungal diastase helps prevent the overgrowth of harmful bacteria by promoting the digestion of carbohydrates and preventing undigested food from fermenting in the intestines. This helps maintain a more balanced gut microbiome, which is crucial for managing IBD symptoms
HOW FUNGAL DIASTASE HELPS IN ACIDITY

Fungal diastase, an enzyme that primarily breaks down starches into simpler sugars, can play an indirect but supportive role in managing acidity
- Improves Digestion and Reduces Gastric Stress
- Efficient Starch Breakdown: Fungal diastase aids in the digestion of carbohydrates by breaking down starches into simple sugars. When carbohydrates are not fully digested, they can ferment in the stomach or intestines, producing gas. This gas increases stomach pressure, which may contribute to acid reflux or acidity. By ensuring that starches are properly broken down in the stomach, fungal diastase reduces gas production and helps prevent excess pressure on the stomach, which in turn can lower the likelihood of acid reflux or heartburn.
- Reduces Stomach Overload: When carbohydrates aren’t properly digested, they can create a heavy, bloated feeling, putting added strain on the digestive system. This strain can trigger acid reflux symptoms. Fungal diastase helps alleviate this by ensuring a smoother, more efficient digestion process, which can reduce the workload on the stomach and prevent unnecessary acid production.
- Prevents Fermentation and Gas Production
- Reduces Fermentation: Starches and carbohydrates that are not properly digested can ferment in the digestive tract, especially in the stomach, which produces gases like carbon dioxide. This excess gas can cause the stomach to become bloated and put pressure on the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), leading to acid reflux. By breaking down carbohydrates more effectively, fungal diastase helps prevent this fermentation and excess gas production, thus reducing pressure on the stomach and mitigating acid reflux symptoms.
- Balances Stomach pH
- Enhances Stomach's Digestive Function: Fungal diastase’s role in helping break down carbohydrates more effectively can indirectly contribute to a more balanced stomach pH. If digestion is not efficient, food may remain in the stomach longer than necessary, leading to overproduction of stomach acid. By speeding up digestion, fungal diastase helps ensure food passes through the stomach efficiently, preventing excessive acid buildup and thus alleviating acidity.
- Reduces Gastric Reflux Triggered by Slow Digestion
- Prevents Backflow of Stomach Acid: Inadequate digestion can lead to food staying in the stomach too long, causing it to mix with stomach acid and potentially leading to acid reflux. The slow digestion of carbohydrates can also worsen acid reflux symptoms. Fungal diastase speeds up carbohydrate digestion, reducing the chances of food stagnation and the subsequent risk of stomach acid flowing back into the esophagus, thus preventing acidity and heartburn.
- Supports Overall Digestive Health
Promotes Efficient Digestion: By breaking down starches and complex carbohydrates more effectively, fungal diastase helps optimize the digestive process, improving overall digestive health. This results in less irritation and inflammation in the stomach lining, which is often aggravated by acid reflux and acidity. When digestion works smoothly, it supports better overall gut health , preventing the conditions that lead to acid overproduction and acidity.
HOW PAPAIN HELPS IN DIGESTION & DETOXIFICATION

Papain, an enzyme derived from papaya, is highly regarded for its digestive and detoxification benefits. It aids in the breakdown of proteins and supports overall digestive health
1. Supports Protein Digestion
- Protein Breakdown: Papain is a protease enzyme, meaning it helps break down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids. This aids in protein digestion by making it easier for your body to absorb nutrients from protein-rich foods. When proteins are properly digested, it prevents undigested protein from fermenting in the gut, which can cause bloating, gas, and digestive discomfort.
- Improved Absorption of Nutrients: By enhancing protein breakdown, papain ensures that the body can absorb more essential nutrients, including amino acids, vitamins, and minerals. This improved nutrient absorption contributes to better overall health and digestion.
2. Helps Break Down Complex Foods
- Efficient Digestive Process: In addition to breaking down proteins, papain helps break down other complex food molecules, like carbohydrates and fats, making digestion more efficient. This can reduce the burden on the digestive system and prevent feelings of heaviness or indigestion after meals.
- Reduces Digestive Discomfort: With papain's support, food passes through the digestive system more easily, reducing the chances of experiencing bloating, indigestion, or discomfort, which can often occur when food is not fully broken down.
3. Improves Gut Health
- Enhances Gut Motility: Papain can help improve the motility of the digestive tract, meaning it helps food move smoothly through the intestines. This is crucial for maintaining regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Healthy bowel function is essential for overall digestive health and well-being.
- Balances Gut Flora: Papain can promote a healthy balance of bacteria in the gut by improving digestion and reducing the chances of harmful bacteria proliferating due to undigested food. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for proper digestion, immune function, and overall health.
4. Detoxification Support
- Aids in Toxin Removal: One of the key ways papain supports detoxification is by helping to break down waste and toxins in the digestive tract. When food is properly digested, it moves efficiently through the intestines, allowing the body to expel harmful toxins more effectively. This aids in detoxification and helps to maintain a clean digestive system.
- Enhances Liver Function: As the liver plays a central role in detoxifying the body, papain's ability to support digestion can also indirectly benefit liver health. Proper digestion reduces the burden on the liver, enabling it to more effectively process and eliminate toxins.
- Supports Healthy Skin: By aiding in digestion and detoxification, papain helps flush toxins from the body, which can reduce skin problems such as acne, eczema, or irritation caused by internal imbalances or toxin build-up.
5. Reduces Inflammation
- Anti-Inflammatory Benefits: Papain has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with digestive conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), where inflammation often plays a central role in symptoms. Reducing inflammation in the digestive system promotes better digestion and overall gut health.
- Healing Digestive Tissues: Papain's anti-inflammatory and digestive properties can also help heal tissues in the stomach and intestines that may have been irritated by poor digestion, toxins, or inflammation. This can aid in the healing process and reduce discomfort from conditions like gastritis or ulcerative colitis.
HOW PAPAIN HELPS IN ENZYME BALANCE
- Supports Protein Digestion
- Breakdown of Proteins: Papain is a protease enzyme, which means its primary function is to break down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids. By aiding in protein digestion, papain ensures that other digestive enzymes involved in protein metabolism (like pepsin and trypsin) are not overburdened. This balance helps maintain overall enzyme activity in the digestive process.
- Relieves Enzyme Overload: If proteins aren’t efficiently broken down, the body may rely on other digestive enzymes to compensate, which can cause an imbalance. Papain ensures that proteins are properly digested, thus preventing an overload of other enzymes that could be overworked.
- Reduces Digestive Strain
- Relieves Digestive Enzymes: When proteins and other nutrients are not properly digested, the digestive system can become strained, and the body may need to produce additional enzymes to assist with digestion. By efficiently breaking down proteins and other complex foods, papain helps to reduce the strain on other enzymes, thus helping to maintain an overall balance in the digestive process.
- Prevents Enzyme Deficiency: If the digestive system is not functioning properly, certain enzymes may not be produced in sufficient amounts, leading to digestive issues. Papain helps optimize protein digestion, ensuring that the stomach’s natural enzymes (like pepsin) can work more efficiently. This helps prevent enzyme deficiencies and supports overall digestive enzyme activity.
- Regulates Carbohydrate and Fat Digestion
- Supports Digestive Enzymes for Carbohydrates and Fats: Although papain is primarily a protease, it also contributes indirectly to carbohydrate and fat digestion by improving overall digestive efficiency. When papain helps break down proteins efficiently, it ensures that the digestive system works in harmony, allowing other enzymes responsible for breaking down carbohydrates (amylase) and fats (lipase) to work properly. This ensures a balanced digestive enzyme activity throughout the system.
- Enhances the Action of Other Digestive Enzymes
- Synergistic Action: Papain works synergistically with other digestive enzymes in the stomach and intestines. For example, it helps in the initial breakdown of proteins, allowing other proteolytic enzymes (like pepsin) to perform their roles more effectively. When papain breaks down proteins into smaller peptides, these peptides are easier for other enzymes to further process, improving overall enzyme activity and ensuring digestive balance.
- Promotes Healthy Gut Microbiome
- Supports Gut Flora: A balanced enzyme system aids in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. By breaking down food more effectively, papain helps ensure that harmful bacteria do not have a chance to thrive due to undigested food. A healthy gut microbiome, in turn, promotes balanced enzyme production, as the gut flora plays a role in enzyme secretion. This balance contributes to a more harmonious digestive process.
- Maintains Digestive System Homeostasis
Prevents Enzyme Imbalance: If the digestive system is overwhelmed with undigested food, certain enzymes can become excessively active, which may lead to digestive discomfort, bloating, or indigestion. Papain helps keep the digestive process running smoothly, reducing the need for the body to overproduce digestive enzymes and promoting a balanced, efficient digestive system
HOW PAPAIN HELPS IN PROBIOTIC NEEDS

1. Improves Protein Digestion and Gut Health
- Enhanced Digestion: Papain breaks down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids, which helps alleviate the burden on the digestive system. Efficient digestion reduces digestive stress, preventing issues like bloating, gas, or constipation that can disrupt the gut microbiome. A well-balanced digestive system creates an environment that is more favorable for probiotics to thrive, supporting overall gut health.
- Reduces Undigested Food in the Gut: When proteins are not properly broken down, they can ferment in the gut, leading to an imbalance of gut flora. This imbalance can promote the growth of harmful bacteria and hinder the effectiveness of probiotics. By breaking down proteins efficiently, papain helps prevent this fermentation, creating a more favorable environment for beneficial probiotic bacteria.
2. Helps Maintain a Healthy Gut Flora
- Support for Beneficial Bacteria: Papain helps to break down and eliminate undigested food particles that could otherwise feed harmful bacteria. By ensuring that food is properly digested and nutrients are absorbed, papain supports the growth of beneficial probiotic bacteria, which rely on a clean and well-functioning digestive system to flourish.
- Balancing Gut Microbiome: A healthy gut microbiome is essential for the proper functioning of probiotics. Papain helps maintain this balance by aiding in digestion, supporting the absorption of nutrients, and reducing the chance of pathogenic bacteria taking over. This creates a better environment for probiotics to perform their role in maintaining digestive health and immunity.
3. Boosts Probiotic Effectiveness
- Facilitates Probiotic Colonization: When digestion is efficient and the gut environment is optimized, it becomes easier for probiotics to colonize the intestines. Papain’s ability to break down food quickly and effectively reduces bloating and fermentation, which can cause discomfort and hinder probiotic growth. As a result, the probiotics you ingest have a better chance of surviving and thriving in the gut, leading to improved digestive health and immunity.
- Reduces Digestive Discomfort: Conditions like bloating, indigestion, or gas can be a result of inefficient digestion, and these symptoms can make it harder for probiotics to be effective. By supporting better protein and food digestion, papain helps to alleviate these symptoms, creating a more hospitable environment for probiotics to function properly.
4. Supports Immune System Health
- Promotes Immune System Function: Since the majority of the body’s immune system is housed in the gut, a healthy gut microbiome plays a key role in overall immune health. Papain helps maintain gut health by supporting digestion, reducing inflammation, and allowing probiotics to flourish. In turn, this bolsters the immune system, helping the body fight off harmful pathogens and supporting overall health.
- Reduces Inflammation: Inflammation in the gut can inhibit the growth of beneficial bacteria and compromise probiotic function. Papain has natural anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce digestive tract inflammation, ensuring that the environment remains favorable for probiotics to thrive and maintain gut health.
5. Aids in Detoxification
- Supports Detox Processes: Papain helps break down and detoxify proteins and other food particles, reducing the buildup of harmful substances in the digestive tract. This detoxification process helps prevent toxicity in the gut, creating a more balanced environment that supports the growth of beneficial probiotics. A clean, detoxified gut is essential for maintaining the efficacy of probiotics.
- Flushes Out Toxins: By improving digestion and promoting healthy bowel movements, papain helps in the removal of waste and toxins from the digestive system. A toxin-free gut is more likely to support the survival and activity of probiotics, helping them maintain a healthy balance of gut flora.
HOW PAPAIN HELPS IN GERD, IBS AND IBD MANAGEMENT

- GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
- Improves Protein Digestion: One of the causes of GERD can be poor digestion, which leads to undigested food particles in the stomach. These particles can contribute to acid reflux. Papain helps break down proteins more efficiently, ensuring that food is fully digested and reducing the chance of undigested food irritating the stomach lining and esophagus, which can trigger GERD symptoms.
- Reduces Bloating and Gas: GERD is often aggravated by bloating and excess gas in the stomach. Papain helps reduce bloating by improving protein digestion and preventing undigested food from fermenting in the stomach. This can help alleviate bloating and prevent the pressure that might contribute to acid reflux.
- Reduces Inflammation: GERD can cause inflammation in the esophagus. Papain has natural anti-inflammatory properties that may help soothe inflammation in the digestive tract, easing the discomfort associated with GERD.
- Supports Smooth Digestion: Papain helps ensure food moves through the digestive system more efficiently. This can prevent the delayed digestion that sometimes contributes to acid reflux, promoting a smoother digestive process and reducing the likelihood of GERD flare-ups.
- IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
- Promotes Better Digestion: IBS is often linked to digestive inefficiency, where food moves too quickly or too slowly through the gut, leading to symptoms like bloating, diarrhea, and constipation. Papain helps break down proteins and other complex foods, which reduces the load on the digestive system and helps regulate bowel movements, making digestion more efficient and less likely to cause IBS flare-ups.
- Reduces Gas and Bloating: One of the key symptoms of IBS is bloating, which can cause discomfort and pain. By improving protein digestion and reducing the occurrence of undigested food in the gut, papain helps alleviate bloating and reduce the production of excess gas. This can provide relief for individuals dealing with the bloating and discomfort common in IBS.
- Supports Gut Health: IBS can cause an imbalance in the gut microbiome. By promoting the efficient breakdown of food, papain helps maintain a healthy gut environment, supporting the growth of beneficial bacteria while reducing the overgrowth of harmful microbes. A balanced microbiome is essential for managing IBS symptoms effectively.
- Reduces Inflammation: Inflammation is a common issue in IBS, and papain’s anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce gut inflammation, easing symptoms like abdominal pain and discomfort.
- IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease, including Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis)
- Reduces Inflammation: IBD is characterized by chronic inflammation in the digestive tract, leading to pain, diarrhea, and other symptoms. Papain has natural anti-inflammatory properties that may help soothe inflammation in the intestines, potentially reducing flare-ups and alleviating discomfort associated with IBD.
- Supports Healing of the Gut Lining: Papain has been shown to promote wound healing, which could be helpful for those with IBD, where the lining of the intestines is often damaged. By supporting tissue repair, papain may aid in the recovery of the gut lining, helping to alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of complications from IBD.
- Improves Digestion and Nutrient Absorption: IBD can impair digestion and the absorption of nutrients. Papain’s role in breaking down food more efficiently may help enhance nutrient absorption and reduce the stress on the digestive system. This ensures that individuals with IBD are better able to absorb essential nutrients, which is important for overall health.
- Helps Alleviate Diarrhea: In some cases, individuals with IBD experience diarrhea due to poor digestion. Papain can help regulate the digestive process by improving food breakdown and reducing the likelihood of undigested food causing irritation in the intestines, which may help alleviate diarrhea symptoms.
HOW PAPAIN HELPS IN ACIDITY

- Improves Protein Digestion
- Efficient Breakdown of Proteins: One of the key contributors to acidity and acid reflux is improper digestion, especially of proteins. When proteins are not broken down properly, they can sit in the stomach longer, ferment, and contribute to the production of stomach acid. Papain helps break down proteins more efficiently, reducing the burden on the stomach and preventing the excessive production of stomach acid.
- Prevents Undigested Food: Papain helps break down food thoroughly, preventing large chunks of undigested food from staying in the stomach and causing irritation, which can trigger acidity.
- Reduces Bloating and Gas
- Minimizes Digestive Stress: Indigestion, bloating, and the build-up of gas can lead to discomfort and pressure in the stomach, exacerbating acid reflux and acidity. Papain aids in the efficient digestion of food, particularly proteins, and reduces bloating and gas. By improving overall digestion, papain helps prevent the discomfort that often accompanies acidity.
- Lessens Gas Formation: Since papain helps proteins digest more efficiently, it reduces the fermentation of undigested food in the stomach, which can lead to the production of gas and contribute to the discomfort of acidity.
- Regulates Stomach pH Levels
- Supports Proper Digestion: By breaking down proteins effectively, papain helps the stomach operate more efficiently and prevents the overproduction of acid. When food is digested properly and in a timely manner, the stomach doesn’t need to produce excessive acid to break down food, which can otherwise contribute to acidity.
- Reduces Inflammation
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Acidity can cause irritation and inflammation in the stomach lining and esophagus. Papain has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce this inflammation. By soothing the digestive tract, papain helps prevent further irritation caused by the acidic environment, thereby providing relief from symptoms of acidity and acid reflux.
- Supports Gut Health and Balance
- Improves Gut Function: Acidity is sometimes linked to gut dysbiosis (an imbalance in gut bacteria). Papain helps maintain a healthy digestive system by improving food breakdown and supporting overall digestive function. This balance can help ensure that the digestive system works efficiently and that acidity is kept in check.
- Reduces the Pressure that Leads to Acid Reflux
- Prevents Reflux: When food is not properly digested, it can create pressure in the stomach, contributing to acid reflux. Papain helps the stomach break down food more quickly and efficiently, reducing this pressure and lowering the likelihood of acid being pushed up into the esophagus (reflux), which causes heartburn and acidity.
HOW FUNGAL CELLULASE HELPS IN DIGESTION & DETOXIFICATION
Fungal cellulase, an enzyme derived from fungi, plays a crucial role in the digestion and detoxification process.
- Aids in Breaking Down Cellulose
- Cellulose Digestion: Humans cannot naturally digest cellulose because we lack the necessary enzymes. However, fungal cellulase helps break down this tough, fibrous compound found in many plant-based foods. This enables better digestion and absorption of nutrients from vegetables, fruits, and other plant materials that are rich in fiber.
- Improves Nutrient Absorption: By breaking down cellulose, fungal cellulase allows the body to access more nutrients locked inside plant cell walls, ensuring that vital vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants are absorbed more efficiently during digestion.
- Enhances Fiber Utilization
- Supports Digestive Health: Fiber plays a key role in digestion by promoting regular bowel movements and adding bulk to stool. Fungal cellulase helps break down the complex fibers that our bodies cannot easily digest, making fiber more useful in supporting digestive processes.
- Prevents Constipation: As fungal cellulase breaks down cellulose, it supports smoother digestion and regular bowel movements, helping to alleviate constipation or irregular stool patterns often caused by undigested fiber.
- Promotes Gut Health
- Reduces Gas and Bloating: Fiber that isn’t properly broken down can ferment in the gut, leading to gas, bloating, and discomfort. Fungal cellulase helps digest these fibers more thoroughly, reducing the likelihood of fermentation, and thereby preventing bloating and excess gas.
- Supports Healthy Gut Microbiota: By aiding in the breakdown of fiber, fungal cellulase ensures that the gut microbiome (the balance of beneficial bacteria in the intestines) remains healthy. Proper digestion of fiber allows beneficial bacteria to thrive, while reducing the growth of harmful bacteria that may contribute to gut issues.
- Detoxification and Cleansing
- Eliminates Toxins: Fungal cellulase helps in the detoxification process by breaking down plant fibers that may contain toxins or other harmful compounds. When these fibers are digested properly, toxins that may otherwise stay in the body are more effectively eliminated.
- Binds to Heavy Metals: Some studies suggest that cellulase can aid in binding and removing certain heavy metals from the digestive system, preventing them from being absorbed into the body. This assists in detoxifying the gut and cleansing it from harmful substances.
- Supports Digestive Enzyme Balance
- Improves Overall Digestive Efficiency: Fungal cellulase contributes to the overall balance of digestive enzymes in the body. By breaking down cellulose and complex plant fibers, it complements the function of other enzymes (like amylase, lipase, and proteases) in the digestive process, helping ensure that the entire digestive system operates smoothly.
- Helps with Fats and Sugars Digestion
- Aids in Complete Digestion: While fungal cellulase primarily targets fiber, its role in breaking down plant cell walls can also help make other nutrients (like fats and sugars) more accessible to digestive enzymes. This supports the overall digestive process and helps in the more complete breakdown of various food components.
HOW FUNGAL CELLULASE HELPS IN ENZYME BALANCE

Fungal cellulase plays an important role in maintaining enzyme balance in the digestive system by complementing and enhancing the activity of other digestive enzymes.
- Supports the Breakdown of Cellulose and Fiber
- Specialized Enzyme Activity: Fungal cellulase is specifically designed to break down cellulose, a type of complex carbohydrate (fiber) found in plants. Unlike human digestive enzymes, which can't break down cellulose on their own, fungal cellulase helps convert these tough fibers into simpler sugars. This enables the digestive system to process fibrous foods more effectively.
- Works in Tandem with Other Enzymes: As fungal cellulase breaks down cellulose, it supports the overall digestive process by reducing the work that other digestive enzymes (like amylase, protease, and lipase) have to do. The simpler forms of nutrients, such as sugars, can be more easily processed by these other enzymes, leading to more efficient digestion.
- Improves the Efficiency of Digestive Enzymes
- Reduces Digestive Load: When complex fibers and plant cell walls aren’t properly broken down, they can create a heavy load on the digestive system, requiring more work from digestive enzymes. Fungal cellulase helps lighten this load by breaking down these hard-to-digest fibers, ensuring that digestive enzymes can focus on their specific tasks (like breaking down proteins, fats, and starches) without being overburdened.
- Optimizes Nutrient Breakdown: By breaking down plant fibers, fungal cellulase allows other digestive enzymes to work more effectively. For example, amylase can then more efficiently digest starches, and protease can focus on breaking down proteins. This synergy between enzymes ensures smoother and more effective digestion.
- Prevents Overuse of Other Enzymes
- Balances Digestive Function: When certain types of fiber remain undigested in the gut, they can cause fermentation, leading to gas, bloating, and digestive discomfort. In such cases, the digestive system may produce more acid or additional enzymes to cope with the excess fiber. Fungal cellulase helps prevent this by breaking down fiber before it causes problems, thus reducing the need for excessive production of digestive acids or enzymes. This ensures a balanced and efficient enzyme response.
- Helps with Digestive Disorders
- Supports Healthy Enzyme Action: In cases where there’s a deficiency in digestive enzymes (like in IBS, GERD, or other digestive disorders), the body might struggle to process certain foods. Fungal cellulase can help improve digestion, particularly of plant-based foods, by breaking down complex fibers that the body would otherwise have trouble processing. This reduces the strain on the body’s enzyme system and helps restore a more balanced digestive process.
- Regulates Digestive Efficiency and Gut Health
- Prevents Digestive Disruptions: When food isn't adequately broken down, it can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and the digestive process. Fungal cellulase ensures that complex fibers are properly digested, minimizing the risk of digestive disruptions that could throw off the balance of other enzymes or gut bacteria.
- Supports Healthy Microbiome: By aiding in the breakdown of cellulose, fungal cellulase helps maintain a balanced gut microbiome. When fibers are digested efficiently, it prevents bacterial overgrowth or imbalances, ensuring that digestive enzymes are operating at their best. This also prevents symptoms like bloating or indigestion that can result from undigested food fermenting in the gut.
- Enhances Overall Enzyme Activity
Improves Enzyme Synergy: The digestive system relies on a wide variety of enzymes working together in harmony. Fungal cellulase, by assisting in fiber breakdown, ensures that other enzymes (like lipase, protease, and amylase) can do their jobs more effectively. This improves the overall enzyme activity and digestive efficiency, promoting better digestion and nutrient absorption.
HOW FUNGAL CELLULASE HELPS IN PROBIOTIC NEEDS
promoting gut health, and Fungal cellulase plays a key role in supporting probiotic needs by enhancing digestion, fostering a balanced microbiome.
- Improves Digestive Efficiency
- Breaks Down Fiber: Fungal cellulase helps break down cellulose, a complex fiber found in plant cell walls. While humans cannot digest cellulose without enzymes, fungal cellulase facilitates its breakdown, making nutrients in fiber-rich foods more accessible. By improving the digestion of fiber, fungal cellulase helps optimize the overall digestive process, ensuring that probiotics (beneficial bacteria) have a healthier environment in which to thrive.
- Prevents Undigested Food in the Gut: Undigested fibers can ferment in the gut, leading to discomfort like bloating, gas, and indigestion, which can harm the balance of beneficial bacteria. Fungal cellulase helps prevent this by efficiently breaking down fiber, ensuring that probiotics aren't disrupted by fermenting food in the digestive tract.
- Supports Healthy Gut Microbiota
- Promotes a Healthy Microbial Environment: A healthy gut microbiome relies on proper digestion and the availability of prebiotics (like fiber). By breaking down complex plant fibers, fungal cellulase creates a better environment for beneficial bacteria to thrive. This is particularly important because probiotics rely on a rich, fiber-rich environment to grow and proliferate.
- Enhances Prebiotic Action: Certain fibers act as prebiotics, which are food sources for probiotics. By breaking down plant cell walls, fungal cellulase helps release prebiotics from the fiber matrix, allowing them to support and feed the beneficial bacteria in your gut.
- Reduces Bloating and Gas
- Minimizes Fermentation: When fiber isn't broken down properly, it can ferment in the gut, producing gas and causing bloating, discomfort, and indigestion. This fermentation can also disrupt the balance of the gut microbiota by creating an environment in which harmful bacteria thrive. Fungal cellulase helps mitigate this by breaking down fiber properly, reducing bloating, gas, and discomfort that could otherwise negatively affect the health of your gut microbiome.
- Supports Healthy Fermentation: By assisting in the breakdown of complex fibers, fungal cellulase helps ensure that fermentation in the gut occurs in a controlled, healthy manner. This not only prevents harmful bacteria from overgrowing but also provides a stable environment for probiotics to function effectively.
- Promotes a Balanced Digestive System
- Helps in Probiotic Colonization: For probiotics to be effective, they need to have an appropriate environment to colonize and thrive. Fungal cellulase promotes a more balanced digestive system by breaking down fibers and allowing nutrients to be better absorbed. This balanced environment fosters the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria, which helps maintain a healthy gut microbiome.
- Improves Nutrient Absorption: Fungal cellulase improves the breakdown of complex fibers, ensuring that the gut can absorb essential nutrients more efficiently. This provides better nourishment for the probiotics, contributing to their growth and activity in the gut.
- Supports Gut Motility and Regularity
- Regulates Bowel Movements: Since fungal cellulase helps break down fibrous materials, it contributes to smoother digestion and regular bowel movements. Regular digestion prevents constipation, which can disrupt the balance of your gut microbiota. By improving motility and reducing digestive discomfort, fungal cellulase helps maintain a healthy environment for probiotics.
- Detoxifies and Cleanses the Gut
- Enhances Detoxification: Fungal cellulase also plays a role in the detoxification process. As it breaks down plant fibers, it helps eliminate toxins and waste from the digestive tract, creating a cleaner, healthier environment for probiotics. This can help reduce the buildup of harmful substances that could negatively impact gut health and probiotic function.
HOW FUNGAL CELLULASE HELPS IN GERD, IBS & IBD MANAGEMENT

- GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
- Reduces Bloating and Gas: GERD symptoms are often exacerbated by bloating and excessive gas, which can create pressure on the stomach and contribute to acid reflux. Fungal cellulase helps break down complex fibers from plant-based foods, reducing the likelihood of fermentation and gas buildup in the stomach. This can alleviate bloating and lessen the frequency and severity of reflux episodes.
- Improves Digestion: By helping the body more effectively digest fibrous foods, fungal cellulase supports smoother digestion, ensuring that food moves more easily through the stomach and intestines. This reduces the overall burden on the digestive system, helping prevent pressure buildup in the stomach, which can lead to acid reflux in GERD patients.
- Prevents Undigested Food in the Stomach: When complex fibers and carbohydrates aren’t properly broken down, they can cause digestive discomfort, bloating, and the potential for food to remain in the stomach too long. This can increase the risk of acid reflux. Fungal cellulase helps to break down these fibers, reducing the chances of food being undigested and providing relief from GERD-related symptoms.
- IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
- Reduces Gas and Bloating: One of the main symptoms of IBS is bloating, which is often caused by the fermentation of undigested food in the gut. Fungal cellulase helps break down fiber, reducing the chances of fermentation and the resultant gas. This can alleviate bloating and discomfort commonly associated with IBS.
- Improves Fiber Digestion: People with IBS often struggle to digest certain types of fiber, particularly insoluble fiber. Fungal cellulase is effective at breaking down cellulose, a major component of insoluble fiber, which can improve overall fiber digestion in IBS patients. This helps reduce symptoms like abdominal cramping, diarrhea, and constipation.
- Supports a Healthy Gut Environment: Fungal cellulase helps create a more balanced digestive system by ensuring that fiber is properly broken down and absorbed. This reduces irritation and discomfort in the gut, which can be especially beneficial for people with IBS, who often experience heightened sensitivity in their digestive tract.
- IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease)
- Reduces Inflammation: While fungal cellulase doesn't directly reduce inflammation, by supporting the breakdown of fiber and improving digestion, it can help reduce the burden on the gut. When fiber isn't properly digested, it can irritate the gut lining and exacerbate inflammation in conditions like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, which are common forms of IBD. Fungal cellulase helps prevent this by improving fiber breakdown and promoting smoother digestion.
- Supports Digestive Health: IBD often leads to difficulty digesting certain foods, particularly those that are high in fiber. Fungal cellulase helps the body break down plant fibers that might otherwise aggravate the intestines. This reduces digestive discomfort, such as bloating, cramping, and gas, and promotes better nutrient absorption. This can be especially helpful for IBD patients, whose intestines are often more sensitive to dietary fibers.
- Improves Gut Motility: IBD patients often experience disrupted gut motility, leading to either diarrhea or constipation. Fungal cellulase can help regulate motility by improving the breakdown of fiber and easing the passage of food through the intestines. This can help maintain more regular bowel movements and reduce the frequency of flare-ups.
Promotes Gut Health and Symptom Relief: Proper digestion and nutrient absorption are crucial in IBD management. Fungal cellulase can assist in breaking down complex fibers, which can be particularly beneficial for people with IBD, who may find fiber to be a challenge. By making digestion more efficient, fungal cellulase helps maintain gut health and reduce symptoms like cramping, diarrhea, and bloating
HOW FUNGAL CELLULASE HELPS IN ACIDITY

Fungal cellulase can help in managing acidity or acid reflux by improving digestion and reducing factors that contribute to digestive discomfort.
- Improved Digestion and Nutrient Absorption
- Breaks Down Fiber: Fungal cellulase helps break down cellulose, a type of fiber found in plant cell walls. Inadequate digestion of fiber can lead to undigested food particles lingering in the stomach, which may cause discomfort, bloating, and acid production. By helping to break down these fibers more effectively, fungal cellulase ensures that the stomach doesn't become overly full of undigested food, thus reducing the likelihood of acid reflux or indigestion.
- Reduces Fermentation: When fibers are not properly broken down, they can ferment in the gut, producing gases that create pressure and discomfort. This can trigger acid reflux, as the increased pressure forces stomach acid to move upward into the esophagus. Fungal cellulase improves fiber digestion, thus reducing fermentation, bloating, and gas buildup that could contribute to acidity.
- Prevents Stomach Overload
- Efficient Breakdown of Fibers: Fungal cellulase helps break down plant fibers that can otherwise sit in the stomach and contribute to bloating or discomfort. The stomach doesn’t have to work as hard to digest fibrous foods, which can reduce the overall pressure in the stomach, lessening the chances of acid reflux or heartburn that results from the buildup of undigested food.
- Reduces Bloating and Gas
- Alleviates Pressure on the Stomach: Bloating and excess gas are common causes of increased stomach pressure, which can lead to acid reflux. Fungal cellulase aids in breaking down complex plant fibers, preventing the fermentation process that leads to gas buildup. By reducing bloating and gas, it minimizes the risk of acid moving into the esophagus, helping to manage acidity.
- Supports a Balanced Digestive System
- Normalizes Digestion: Fungal cellulase helps normalize digestion by promoting the breakdown of fibrous materials in foods, ensuring that the digestive process flows more smoothly. When digestion is more efficient and there’s less undigested food in the stomach, the likelihood of acid backup and reflux is reduced. This can help reduce symptoms of acidity over time.
- Reduces Digestive Discomfort
- Improves Motility: Efficient digestion of fiber means food moves more effectively through the digestive system, reducing stagnation or delays that might contribute to excessive acid production in the stomach. By promoting healthy gut motility, fungal cellulase helps prevent the digestive discomfort that often leads to acidity.
HOW PEPSIN HELPS IN DIGESTION & DETOXIFICATION

Pepsin is a powerful digestive enzyme that plays a crucial role in the breakdown of proteins in the stomach.
- Role of Pepsin in Digestion
- Protein Digestion: Pepsin is primarily responsible for breaking down proteins into smaller peptides in the acidic environment of the stomach. It is secreted as an inactive precursor called pepsinogen, which gets activated by stomach acid (hydrochloric acid) into active pepsin. This enzyme then begins the process of protein digestion, which is vital for the absorption of amino acids, the building blocks for muscle, tissue repair, and other bodily functions.
- Facilitates Nutrient Absorption: The breakdown of proteins into smaller peptides by pepsin is crucial for nutrient absorption. Once the proteins are broken down, they are further digested in the small intestine, where the amino acids can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Proper digestion of proteins by pepsin helps the body obtain the necessary nutrients to maintain overall health.
- Supports Other Digestive Enzymes: Pepsin helps prepare proteins for further digestion by other enzymes like trypsin and chymotrypsin in the small intestine. By starting the process of protein digestion in the stomach, it ensures that subsequent digestive processes are more efficient.
- Role of Pepsin in Detoxification
- Breaks Down Harmful Substances: Pepsin can also help in breaking down some potentially harmful proteins or substances that enter the stomach, including those from contaminated food. By digesting these proteins, pepsin helps reduce the potential for toxins to enter the bloodstream, supporting the body’s detoxification process.
- Improves Gut Health: Proper digestion facilitated by pepsin helps prevent the build-up of undigested food particles and proteins in the gut, which could lead to gut dysbiosis (an imbalance in the gut microbiota). This imbalance could contribute to issues like leaky gut or inflammation. By promoting efficient digestion, pepsin aids in maintaining a healthy gut environment, supporting overall detoxification by preventing the accumulation of toxins.
- Aids in the Breakdown of Environmental Toxins: In some cases, pepsin may also play a role in breaking down certain environmental toxins that enter the body through food. Toxins, when not properly digested or detoxified, could accumulate in the digestive tract and lead to inflammation or other health issues. Pepsin assists in breaking down larger toxin molecules, making them easier for the liver and kidneys to process and eliminate.
- Supports Healthy pH Balance: Pepsin requires an acidic environment to function effectively, and the stomach's natural acidic environment (due to hydrochloric acid) aids in digestion and detoxification. A proper pH balance in the stomach ensures that harmful microorganisms or pathogens present in food are neutralized, further supporting the detoxification process.
- Pepsin's Contribution to Overall Digestion and Detoxification
- Enhances Protein Breakdown: Efficient breakdown of dietary proteins means that harmful pathogens or toxins associated with these proteins are less likely to stay in the stomach or intestines, preventing their absorption into the body.
- Supports Gut Microbiota Balance: By aiding digestion and ensuring proteins are broken down properly, pepsin helps maintain a balanced gut microbiota. This balance is critical for gut health and the body’s ability to effectively detoxify and eliminate waste.
- Reduces Digestive Stress: Proper digestion of proteins by pepsin reduces the overall stress on the digestive system, preventing the accumulation of undigested food or harmful substances that could cause inflammation or toxicity. This allows the body's natural detoxification systems (like the liver and kidneys) to function more efficiently.
HOW PEPSIN HELPS IN ENZYME BALANCE
1. Initiates Protein Digestion
- Activation of Other Enzymes: Pepsin is one of the first digestive enzymes activated when food enters the stomach. It starts the digestion of proteins by breaking them down into smaller peptides. The proper function of pepsin ensures that proteins are digested correctly, providing a smooth transition for other digestive enzymes (like trypsin and chymotrypsin) in the small intestine to continue the breakdown process. This sequential enzymatic activity maintains balance in the digestive system.
- Optimal pH for Enzyme Function: Pepsin requires an acidic environment (low pH) to work effectively. The presence of stomach acid (hydrochloric acid) not only activates pepsin but also creates the ideal environment for other digestive enzymes to work. A balanced, acidic pH in the stomach ensures that enzymes like pepsin and those in the small intestine function efficiently, which is essential for overall digestive health.
2. Supports Enzyme Activity Throughout the Digestive System
- Prepares Food for Further Digestion: Pepsin breaks down complex proteins into smaller peptides, making it easier for other enzymes in the small intestine (like pancreatic enzymes) to continue breaking down these peptides into amino acids for absorption. This coordinated enzymatic activity helps maintain enzyme balance by ensuring that each digestive enzyme works effectively in its designated phase of digestion.
- Facilitates Absorption of Nutrients: By starting the protein breakdown process, pepsin aids in the overall absorption of nutrients. Proper digestion by enzymes at each stage ensures that the body gets the necessary nutrients from food, and this balanced digestion also reduces the likelihood of overburdening any single enzyme.
3. Ensures Efficient Digestive Processes
- Prevents Undigested Food Build-Up: If food is not broken down properly in the stomach, it can lead to undigested particles entering the small intestine, where they may interfere with the action of other digestive enzymes. Pepsin ensures that proteins are sufficiently broken down before they reach the small intestine, helping to prevent congestion or enzyme overload in the digestive system.
- Maintains Optimal Enzyme Levels: By initiating the digestion of proteins in the stomach, pepsin ensures that the digestive system doesn’t overproduce enzymes in an attempt to break down undigested food. It helps balance enzyme production by allowing enzymes to perform their duties efficiently and without excess.
4. Protects Against Overuse of Digestive Resources
- Helps Regulate Enzyme Release: Proper protein digestion via pepsin can help regulate the release of digestive enzymes. Without adequate protein digestion in the stomach, the pancreas may release excess digestive enzymes in the small intestine, which could strain the system. Pepsin helps by breaking down proteins early, so the pancreas doesn’t have to release more enzymes than necessary.
- Prevents Overactive Enzymatic Action: Overactive enzyme activity in the digestive system can lead to discomfort, such as bloating, indigestion, or acid reflux. Pepsin ensures that protein digestion is handled in a controlled manner, helping to maintain enzyme activity within a balanced range.
5. Enhances Overall Digestive Coordination
- Optimizes Enzyme Timing: Digestive enzymes are released at different stages of digestion. Pepsin’s role in the stomach prepares proteins for further digestion by enzymes in the small intestine. This balance allows for the proper sequencing of enzyme activity, so each enzyme works at the right time in the digestive process, enhancing the overall efficiency of digestion.
Regulates pH for Enzyme Balance: The acidic environment in the stomach, which is required for pepsin to function, also influences the activity of other enzymes. A balanced pH ensures that not only pepsin but also other enzymes (like amylase in the mouth and lipase in the pancreas) work at their optimal levels, leading to more effective and coordinated digestion.
HOW PEPSIN HELPS IN PROBIOTIC NEEDS

Pepsin is an enzyme that plays a key role in the digestion of proteins, primarily in the stomach. While it’s not a probiotic itself, pepsin can support the overall digestive process, which indirectly benefits the gut environment for probiotics to thrive.
- Breaking Down Proteins: Pepsin helps break down proteins into smaller peptides, which aids the digestive process. A more efficient digestion process creates a better environment for probiotics to grow and function properly in the intestines.
- Creating an Optimal pH: Pepsin works best in an acidic environment, which the stomach naturally provides (pH of around 1.5 to 2.5). A well-functioning stomach with proper acid levels supports the survival of probiotics as they pass through the stomach into the intestines, where they can flourish.
- Supporting Gut Health: Healthy digestion, including protein breakdown facilitated by pepsin, can reduce bloating, indigestion, or other gastrointestinal issues. This allows probiotics to work more effectively in maintaining a healthy balance of gut bacteria.
While pepsin doesn’t directly provide the benefits that probiotics do (like restoring or maintaining a healthy gut microbiome), it supports a healthy digestive system, which is an essential foundation for probiotics to do their job.
HOW PEPSIN HELPS IN GERD, IBS & IBD MANAGEMENT

1. GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
- Pepsin's Role in GERD: GERD is caused by acid reflux, where stomach acid, including pepsin, flows back into the esophagus. This can cause inflammation, discomfort, and damage. Pepsin itself doesn’t directly treat GERD, but understanding its role is important for treatment. Pepsin can survive in the acidic environment of the stomach and reflux into the esophagus, where it can cause harm. However, pepsin inhibitors or medications that lower stomach acid production (like proton pump inhibitors) are often used to reduce the impact of pepsin in the esophagus.
How it Helps: Reducing excess acid production may indirectly help manage GERD by preventing pepsin from moving up into the esophagus and causing damage. Additionally, some people with GERD have low stomach acid (hypochlorhydria), and taking supplements to increase acid production can help the digestive process, potentially reducing reflux.
2. IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
- Pepsin's Role in IBS: IBS is characterized by symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and irregular bowel movements (diarrhea or constipation). The connection between pepsin and IBS isn’t direct, but pepsin helps break down proteins in the stomach, which aids digestion overall. Poor digestion can exacerbate IBS symptoms, so improving digestive efficiency with pepsin can help.
How it Helps: In some cases, individuals with IBS may have incomplete digestion due to low stomach acid, which can lead to bloating, gas, and discomfort. Supplementing with pepsin (usually alongside betaine HCl) could potentially improve protein digestion, leading to less gas production and more comfortable digestion. However, this is not universally recommended, as some IBS sufferers might find additional acid irritating.
3. IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease)
- Pepsin's Role in IBD: IBD, which includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, involves chronic inflammation in the digestive tract. Pepsin itself doesn’t directly treat IBD, but inflammation in the stomach and intestines is often a significant issue in these conditions.
How it Helps: Some theories suggest that the digestive process should be as efficient as possible in people with IBD to avoid inflammation in the stomach and intestines. Pepsin’s role in breaking down proteins in the stomach is a part of this process. If the stomach isn’t functioning optimally (e.g., low stomach acid), it could worsen digestive problems and trigger symptoms. In this case, ensuring proper stomach acid levels (with pepsin) might help prevent undigested food particles from entering the intestines, where they could aggravate inflammation.
HOW PEPSIN HELPS IN ACIDITY

Pepsin, the enzyme responsible for breaking down proteins in the stomach, plays a role in the overall digestive process, but it’s not directly related to reducing acidity. However, it can still have an impact on the body’s response to acidity, especially when it comes to managing low stomach acid.
- Pepsin and Acid Reflux/Acidity
- How Pepsin Works: Pepsin functions best in an acidic environment (low pH) in the stomach. It’s activated by stomach acid (hydrochloric acid or HCl) and helps break down proteins into smaller peptides.
- Low Stomach Acid (Hypochlorhydria): If someone has low stomach acid, the stomach may not be able to activate pepsin properly, which can lead to inefficient digestion of proteins. This could cause undigested food to pass into the intestines, potentially leading to bloating, gas, and discomfort.
- Acidity in GERD/Acid Reflux: In conditions like GERD or acid reflux, stomach acid (which includes pepsin) can flow back into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation. The presence of pepsin in the esophagus can worsen this issue by breaking down tissue and causing damage.
- Pepsin’s Role in Managing Low Acidity
- Supplementing Pepsin: For individuals with low stomach acid (hypochlorhydria), supplementing pepsin along with betaine HCl (hydrochloric acid) may help improve digestion. The HCl raises the acidity in the stomach, which activates pepsin and aids in protein digestion. In this case, pepsin supports efficient digestion by ensuring that proteins are properly broken down.
- Relieving Symptoms: If you have low stomach acid, supplementing with pepsin and HCl can help relieve symptoms like bloating, indigestion, or poor nutrient absorption that result from inadequate protein digestion.
- Pepsin and High Acidity
- High Acidity or GERD: If stomach acid levels are already too high (leading to conditions like GERD or heartburn), pepsin doesn’t directly reduce the acidity. In fact, excess stomach acid could cause more reflux, irritating the esophagus.
- Treatment for High Acidity: In cases of high stomach acid, doctors typically recommend antacids, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), or H2 blockers, which reduce stomach acid production to alleviate symptoms of acidity, rather than focusing on pepsin. Reducing the acidity prevents pepsin from reaching the esophagus, where it can cause damage.


